Wind Patterns Flip Book: Air Movement Vocabulary
advertisement

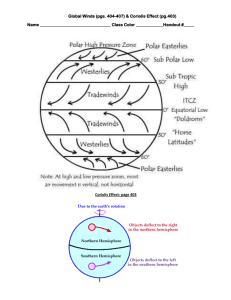
Wind Flip Book “Air Movement” Wind Patterns Using textbook 14-3 & 15-3 Students will identify, describe and draw wind patterns. 1) Label vocabulary words 1. Surface current 2. Trade winds Tropical wind the blows almost continually towards the equator from either the northeast or the southeast. 3. Mountain breeze Valley Breeze 4. Prevailing Westerlies Between 30 degrees and 60 degrees latitude north or south of the equator, winds blow in the opposite direction of the trade winds. Prevailing easterlies Between 30 degrees and 60 degrees latitude north or south of the equator, winds blow in the same direction as the trade winds. 5. Polar Westerlies The winds blow from northwest to the southeast near the North Pole and from the southwest to the northeast near the South Pole Polar easterlies Winds blow from the northeast to the southwest near the north pole and from the south east to the north west near the south pole. 6. Sea breeze Daily movements of air created when cooler, denser air moving inland from the ocean forces warm air over the land to rise Land breeze Nightly movements of air created when cold air over the land forces up the warmer air above the sea. 7. Coriolis Effect Global Winds 8. Jet stream Air Mass 9. Climate Weather 10. Cold Front Warm Front 11. Layers of the Atmosphere 3) Define terms 4) Draw an illustration representing vocabulary terms.