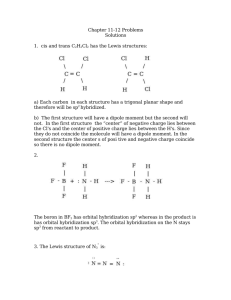
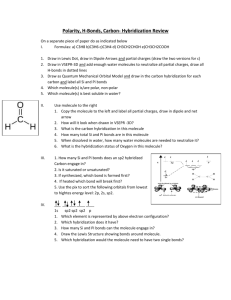
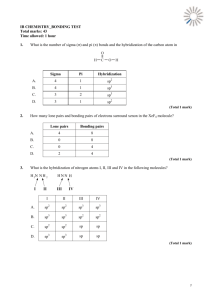
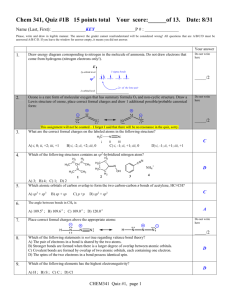
Hybridization & Intermolecular Forces Chemistry Worksheet

Name: ___________________________________ Date: ______________
1. Which of the following statements is (are) incorrect?
I.
The hybridization of boron in BF3 is sp2.
II.
The molecule XeF4 is nonpolar.
III.
The molecule HCN has two pi bonds and two sigma bonds.
A) All three statements are correct.
B) II is incorrect.
C) I and II are incorrect.
D) II and III are incorrect.
E) I, II, and III, are incorrect.
2. Atoms which are sp 2 hybridized can form a maximum of how many ____ pi bond(s).
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
3. The hybridization of the central atom in ClF
2+
is:
A) s p
B) s p 2
C) s p 3
4. What hybridization is predicted for the nitrogen atom in the NO
3–
ion?
A) s p 2
B) s p 3
C) none of these
Page 1
5. Consider the following Lewis structure
Which statement about the molecule is false?
A) There are 10 sigma and 2 pi bonds.
B) C–2 is sp 2 hybridized with bond angles of 120°.
C) Oxygen is sp 3 hybridized.
D) This molecule contains 28 valence electrons.
E) There are some H–C–H bond angles of about 109° in the molecule.
6. Which statement about N
2
is false?
A) It is a gas at room temperature.
B) The oxidation state is +3 on one N and –3 on the other.
C) It has one sigma and two pi bonds between the two atoms.
D) It can combine with H
2
to form NH
3
.
E) It has two pairs of nonbonding electrons.
Use the following to answer questions 7-10.
Consider the molecule and the following hybridization choices:
a) sp
b) sp 2 c) sp 3
7. What is the hybridization of the carbon atom that is double bonded to oxygen?
Page 2
8. What is the hybridization of the carbon atom that is bonded to chlorine?
9. What is the hybridization of the nitrogen atom?
10. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom?
11. Consider the molecule
Specify the hybridization of each carbon atom.
C-1 C-2 C-3 C-4 C-5
A) sp 2 sp 2 sp 2 sp 3 sp
B) sp 2 sp 2 sp 2 sp 3 sp 3
C) sp 2 sp 2 sp 3 sp 3 sp 2
D) sp 2 sp 2 sp 3 sp 3 sp 3
E) sp 2 sp sp sp 2 sp
C-1 C-2 C-3 C-4 C-5
Page 3
12. The hybridization of the central atom, Al, in AlBr
3
is
A) s p
B) s p 2
C) s p 3
13. Complete the Lewis structure for the following molecule:
This molecule has __________ sigma and __________ pi bonds.
A) 4, 5
B) 6, 3
C) 11, 5
D) 13, 2
E) 13, 3
14. Consider the structure of glycine, the simplest amino acid: a) Indicate the hybridizations at each N and C atom in the molecule.
b) What is the total number of bonds in the molecule?
c) What is the total number of π bonds in the molecule?
15. Which one of the following decreases as the strength of the attractive intermolecular forces increases?
A) The heat of vaporization.
B) The normal boiling temperature.
C) The extent of deviations from the ideal gas law.
D) The sublimation temperature of a solid.
E) The vapor pressure of a liquid.
Page 4
16. Order the intermolecular forces (dipole-dipole, London Dispersion, ionic, and hydrogenbonding) from weakest to strongest .
A) dipole-dipole, London Dispersion, ionic, and hydrogen-bonding
B) London Dispersion, dipole-dipole, hydrogen-bonding, ionic
C) hydrogen-bonding, dipole-dipole, London Dispersion, and ionic
D) dipole-dipole, ionic, London Dispersion, and hydrogen-bonding
E) London Dispersion, ionic, dipole-dipole, and hydrogen-bonding
17. Which of the following would you expect to have the highest boiling point?
A) F
2
B) Cl
2
C) Br
2
D) I
2
E) All of the above have the same boiling point.
18. Which of the following is most likely to be a solid at room temperature?
A) Na
2
S
B) HF
C) NH
3
D) N
2
E) H
2
O
19. On a relative basis, the weaker the intermolecular forces in a substance,
A) the greater its heat of vaporization.
B) the more it deviates from ideal gas behavior.
C) the greater its vapor pressure at a particular temperature.
D) the higher its melting point.
E) none of these
20. Which of the following is the correct order of boiling points for KNO
3
, CH
3
OH, C
2
H
6
, Ne from lowest to highest?
A) Ne < CH
3
OH < C
2
H
6
< KNO
3
B) KNO
3
< CH
3
OH < C
2
H
6
< Ne
C) Ne < C
2
H
6
< KNO
3
< CH
3
OH
D) Ne < C
2
H
6
< CH
3
OH < KNO
3
E) C
2
H
6
< Ne < CH
3
OH < KNO
3
Page 5
21. On the basis of your knowledge of bonding in liquids and solids, arrange the following substances in order of highest to lowest melting temperature: NaCl, Na, Cl
2
, SiO
2
A) Cl
2
, Na, NaCl, SiO
2
B) Na, NaCl, Cl
2
, SiO
2
C) SiO
2
, NaCl, Na, Cl
2
D) NaCl, SiO
2
, Na, Cl
2
E) SiO
2
, Na, NaCl, Cl
2
22. Generally the vapor pressure of a liquid is related to
I.
the amount of liquid
I
.
V
II.
atmospheric pressure
III.
temperature intermolecular forces
A) I, III
B) II, III, IV
C) I, III, IV
D) III, IV
E) all information is needed
23. Which of the following processes must exist in equilibrium with the evaporation process when a measurement of vapor pressure is made?
A) fusion
B) vaporization
C) sublimation
D) boiling
E) condensation
24. When a nonpolar liquid displays a convex meniscus, which of the following explains this behavior?
A) It has a low surface tension, and therefore clings to the glass.
B) The cohesive forces are stronger than the adhesive forces toward the glass.
C) The adhesive forces toward the glass are stronger than the cohesive forces.
D) The liquid's viscosity is low.
E) none of these
Page 6
25. You are given the following boiling point data: Which one of the below liquids would you expect to have the highest vapor pressure at room temperature?
A) water, H
2
O 100°C
B) methanol, CH
3
O H
C) ethanol, CH
3
CH
2
OH
64.96°C
78.5°C
D) diethyl ether, CH
3
CH
2
–O–CH
2
CH
3
E) ethylene glycol, HO–CH
2
–CH
2
–OH
34.5°C
198°C
26. Explain why water boils at a lower temperature up in the mountains versus at sea level.
Include at least one microscopic drawing in your explanation.
Page 7
Answer Key - Chapter9_Review_Problems_2013
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. A
5. C
6. B
7. b)
8. c)
9. a)
10. b)
11. A
12. B
13. E
14. a) N sp3
C2 sp3
C2 sp2 b) 10 bonds c) 1
π
bond
!!
15. E
16. B
17. D
18. A
19. C
20. D
21. C
22. D
23. E
24. B
25. D
26. The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is exactly the same as the pressure of the atmosphere around it. Water boils at a lower temperature up in the mountains because at high altitudes the atmospheric pressure is lower (see pictures A and B). Boiling occurs when the water is hot enough to have the same vapor pressure as the surrounding air, so that it can form bubbles. Since the air pressure is lower at high altitudes, the water does not have to get as hot for boiling to occur. It will take more heat for water at sea level to attain the same pressure as the surrounding air since the atmospheric pressure is higher (see picture B).
Picture A Picture B
Page 8
(high altitudes) (low altitudes)
Page 9