Acid-Base Equilibria
advertisement

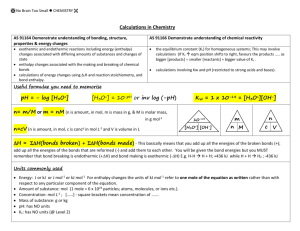
www.thisisrevision.com for tests, flashcards and revision courses www.thisisrevision.com for tests, flashcards and revision courses Acid – base equilibria, definitions. Calculating the pH of strong acids and bases. An acid is a proton donor, a base is a proton acceptor. As strong acids and bases fully dissociate, calculating their pH values is straightforward. Conjugate acid – base pairs are species that differ from each other by H+ For example, calculate the pH of 0.1 mol dm-3 HCl solution. + NH4 acid 1 + ↔ H2O base 2 + - Kw = [H3O ][OH ], Kw = 1.00 x 10 -14 NH 3 + conjugate base 1 H 3O conjugate acid 2 → H2O HCl + 0.1 mol dm- 3 + H3 O+ + 0.1 mol dm-3 Cl- Ideally, we ought to add the 1 x 10-7 mol dm -3 of H + from the auto ionisation of water, but it is very small compared to 0.1 mol dm- 3 from the HCl, so we don’t need to bother. 2 mol dm-6 at 298K pH = - log [0.1] = 1. + 2 pH = -log[H ] -3 -14 -6 For example, calculate the pH of 0.1 mol dm NaOH solution, if Kw is 1 x 10 mol dm Strong acids and bases dissociate completely, e.g. HCl, NaOH. NaOH + 0.1 mol dm- 3 Weak acids and bases do not fully dissociate completely, even at high dilution, e.g. CH3CO2H, HF, NH3, C6H5NH2. + ↔ Kw = [H3O+ ][OH-] From the equation, for each OH- an H3O + ion is formed, so they have the same + concentration. As we want to find pH, we get rid of [OH ] by substituting [H3O ] for it. + or [H3O ] = √ Kw Kw = [H3O ] , + -14 At 298K, [H3O ] = √ 1 x 10 + At 373K, [H3O ] = √ 1.1 x 10 -7 -7 = 1.00 x 10 , therefore pH = - log 1.00 x 10 = 7.00 -14 OH-(aq) ↔ - [H3 O+] = 1 x 10-14 / 0.1 = 1 x 10-13 pH = - log 1 x 10-13 = 13. CH3CO2H - H 3O + OH Kw at 298K is 1.00 x 10-14 mol2dm-6 , whereas at 373K it is 1.1 x 10-14 mol2dm-6. + 2 Na +(aq) + 0.1 mol dm-3 Calculating the pH of weak acids. Calculating the pH of pure water at different temperatures H2O + H2O → (aq) -7 -7 Ka = H 2O + + CH3CO2 + H3O + - [H3O ][CH3CO2 ] [CH3CO2H] What is the pH of a 0.1 mol dm-3 solution of ethanoic acid, if Ka is taken as 1 x 10- 5 mol -3 dm As ethanoic acid is a weak acid, the [CH 3CO2H] at equilibrium can be taken to be equal to 0.1 mol dm- 3. It would actually be less than this as some of the molecules are dissociated, but not many, precisely because ethanoic acid is a weak acid. Also, as for every H3O+ obtained a CH3 CO2 - is also obtained, they have the same concentration, so [CH3 CO2 -] can be replaced by [H3 O+], and the equation becomes… = 1.048 x 10 , therefore pH = - log 1.048 x 10 = 6.98 Ka = Is the heat change of the dissociation of water endothermic or exothermic? The reaction has shifted to the right hand side when heated (as Kw has increased, or pH has decreased) and heat favours the end othermic pathway, according to Le Chatelier’s principle, therefore the forward reaction is endothermic. www.thisisrevision.com for tests, flashcards and revision courses [H3O+]2 [CH3 CO2 H] or [H3O+] = √ (Ka x [CH3 CO2 H]) = √(1 x 10-5 x 0.1) = 1 x 10-3 pH = - log 1 x 10-3 = 3. Again, the 1 x 10-7 mol dm- 3 of H + from water itself has been ignored. www.thisisrevision.com for tests, flashcards and revision courses