acid base review key chem40S11b
advertisement

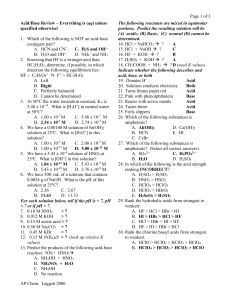
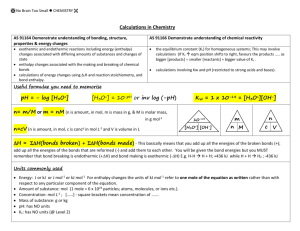
CH40S Acid-Base Equilibria Review Key 1. HZ 2.a) Strong acids/bases completely dissociate, whereas weak acids/bases only partially dissociate. b) Concentrated means that there is a high molarity (e.g. dissolved in a small amount of water), whereas dilute means that there is a low molarity (e.g. dissolved in a large amount of water). 3. Yes, the acid could be dissolved in a small amount of water but still only partially dissociate. 4. NaHCO3 + HCl NaCl + H2CO3 Since HCl is a stronger acid than H2CO3, the reaction will be product favoured since HCl is more likely to donate H+. 5. NH4+ + HS– H2S is a stronger acid than NH4+, therefore it donates more H+, so rxn is product favoured. 6. a) Equilibrium will shift to the right (shift to the product side) because the OH– of the NaOH will combine with the H3O+ to form water, this rxn between the hydroxide and hydronium ion reduces the concentration of the hydronium ion. b) Equilibrium will shift to the left (shift to the reactant side) because the H+ (actually H3O+ because it’s in an aqueous solution) of the HCl will cause the concentration of H3O+, in the reaction listed, to increase. 7. [H+] and [HS–] = 2.24x10–4 mol/L [H2S] = 0.49998 or 0.5 mol/L pH = 3.65 % diss. = 0.045% **** need to use Ka value from Ka table 8. Ka = 1.33x10–7 9.(HClO4 is a strong acid, so ….) [H+] 4.and [ClO4–] = 4x10–3 mol/L, pH=2.40 10. 4.2x10–4 mol/L 11. 0.0267 L 12. 0.0125 L 13. 200g 14. [H3O+] = 2.51x10–5 mol/L, [OH–]=3.98x10–10 mol/L 15.(****Ka is not required for answer… tricky!) [H3O+] =9x10–5 and pH= 4.05 16.% diss = 0.0325% 17. Ka=9.09x10–10 18. [H+]=8.66x10–5 mol/L, pH=4.06, pOH=9.94 19. C2O42– + H2CO3 b) Equilibrium favours the products since HC2O4– is a stronger acid than H2CO3 20. Ka = 1.33x10–7 21. (*** must Ka from Ka table) a) [H3O+] = 0.016 mol/L b) pH=1.80 c)% diss. = 3.19% 22. omit (compound formula was typed incorrectly) 23. 0.044L 24. 0.8g NaOH 25. a) Acids: An acid is a substance that releases H+ ions in water. Eg) HCl(aq) H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Bases : A base is a substance that releases OH- ions in water. Eg) NaOH(aq) Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) b) An acid is a proton (H+) donor, and a base is a proton acceptor acid e.g. HCl + H2O H3O+ + Cl– base e.g. NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OH– c) An acid accepts an electron pair during a reaction, a base donates an electron pair during a reaction. Acid e.g AlCl3 Base e.g. NH3