Drug-Induced Liver Disease - Cleveland Clinic Center for
advertisement

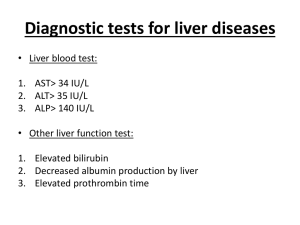
Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Drug-Induced Liver Disease: 2012 Paul J. Pockros,MD Director of Clinical Research, Scripps Translational Science Institute Director of Liver Disease Center and Senior Consultant, Division of Gastro/Hepatology Scripps Clinic With thanks to Willis Maddrey,MD for many of these slides Drug-Induced Liver Injury • Occurs in small fraction of individuals • Difficult to predict • Major clinical problem; often life-threatening • Leading cause of acute liver failure • Reason drugs removed from development and widespread use O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 1 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Importance of DILI in US Drug Market DILI is the most common cause of death from acute liver failure and accounts for approximately 13% of cases of ALF in US. DILI is the most frequent adverse drug event leading to abandonment of otherwise promising new drug candidates during preclinical or clinical development DILI is most common reason for withdrawal or restriction of prescription drug use after initial approval. Navarro VJ, Senior JR. Drug-related hepatotoxicity. N Engl J Med. 2006;35:731–739 Examples of Drugs Withdrawn Due to Liver Disease Iproniazid Ibufenac (in Europe only) Ticrynafen Benoxaprofen Perhexiline (in France) Dilevalol (in Portugal, Ireland) Bromfenac Troglitazone Serzone O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 1956 1975 1979 1982 1985 1990 1998 2000 2004 2 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Putative Mechanisms • Mechanism often involves drug metabolites – Affect critical biochemical functions – Specific immune responses • Only a few drugs demonstrate these underlying causes • Tissue susceptibility: imbalance between protoxicants and protectants – Environmental factors – Genetic polymorphism Cellular mechanisms of drug hepatotoxicity. Kaplowitz N Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:S44-S48 © 2004 by the Infectious Diseases Society of America O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 3 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Hepatotoxicants Potentiated by Exposure to Small Doses of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Xenobiotics Source CCl4 Galactosamine Ethanol T2-toxin Cadmium Halothane Lead Allyl Alcohol Aflatoxin B1 Chlorpromazine Ranitidine Formal et al., 1960 Galanos et al., 1979 Nolan et al., 1980 Tai and Petska, 1988 Cook et al.., 1974 Lind et al., 1984 Honchel et al., 1991 Sneed et al., 1997 Barton et al., 2000 Buchweitz et al., 2002 Luyendyk et al., 2003 Cellular Level Events of LPS LPS TLR4 Macrophages Neutrophils Endothelial Cells Epithelial Cells Cytokines Coagulation Factors Platelet Activating Factor Complement Activation Leukotrienes Arachidonic Acid Metabolites Prostaglandins Reactive Oxygen Species Nitric Oxide O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 4 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Drug Liver Reactive Protein Metabolites Protective Adducts Factors Response Cellular Homeostasis Toxicity IL-6, IL-10, COX-2 Protection Stress Proteins Altered Extensive (Inhibition) Liver Injury And Death Does a loss in hepatoprotective factors result in drug-induced liver disease? Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Disease • Complex “multihit” process • Liver protoxicants and protectants have a role in the overall pathogenesis – Environmental Factors – Genetic polymorphisms • Underproduction of hepatoprotective and overproduction of hepatoprotoxicant factors (i.e., imbalance) influences susceptibility to this liver disease O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 5 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Determination of Susceptibility Factors • Identification of liver protoxicant and protectant factors results in better understanding of mechanism and in facilitating prediction of drug-induced liver disease – Inflammatory mediators – COX-2 products – Heat shock proteins • Application of new technologies – Toxicogenomics – Proteomics – Metabonomics Is Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury Dose Related? Idiosyncratic Reactions • Unpredictable • Poorly Understood • Likely Multifactorial Drugs given at a dose of < 10 mg/d rarely associated with injury 598 Cases of DILI Patients Taking: 77% >50 mg/d 14% 11 - 49 mg/d 9% O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric <10 mg/d 6 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Drug-Induced Liver Injury Consider the Possibility Often a Diagnosis of Exclusion The Weight of Evidence Approach Recognize That Underlying Liver Injury Can Divert Attention From the Role of a Drug Importance of Deceleration After Withdrawal Response Question #1 Which of the following are true statements about drug-induced liver disease in the US: 1. DILI is caused by a single prescription medication in most of the cases 2. DILI is caused by dietary supplements in most of the cases 3. Antimicrobials account for > half of cases 4. CNS agents account for > half of cases 5. 1 and 2 O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 7 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Causes of DILI in a Large Cohort NIH Trial DILI was caused by a single prescription medication in 73% of the cases dietary supplements in 9% multiple agents in 18% antimicrobials (45.5%) central nervous system agents (15%) Causality was considered to be definite in 32%, highly likely in 41%, probable in 14%. Chalasani N,et al. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1924-34. Risk factors for susceptibility to drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Kaplowitz N Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:S44-S48 © 2004 by the Infectious Diseases Society of America O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 8 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Inadequate Disposition Intermediates Overproduction Intermediates Contributions of the Innate Immune System Mechanisms Intracellular Accumulation Site/Extent Mitochondrial Damage P450 levels Genetics Immune Response Failure to Adapt Disruption of Oxidative Phosphorylation Aminotransferase Elevations in Healthy Adults Receiving 4 Grams of Acetaminophen Daily Watkins, 2006 O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 9 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Response Question #2 Which prescription drug is the most common cause of DILI in the US? 1. Acetaminophen 2. Amoxicillin/clavulanate 3. Nitrofurantoin 4. Isoniazid 5. Valproate Most Common Drugs causing DILI (out of 217 single Rx cases) Amoxicillin/clavulanate (n = 23) Nitrofurantoin (n = 13) Isoniazid (n = 13) TMP/SMX (n = 9) Duloxetine (n = 6) Valproate (n = 6) Interferon beta (n = 6) Ciprofloxacin (n = 5) Lamotrigine (n = 5) Methyldopa (n = 5) Telithromycin (5) Phenytoin (n = 5) Diclofenac (n = 4) Chalasani N,et al. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1924-34. O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 10 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Most Common Drugs causing DILI (out of 217 single Rx cases) Amoxicillin/clavulanate (n = 23) Nitrofurantoin (n = 13) Isoniazid (n = 13) TMP/SMX (n = 9) Duloxetine (n = 6) Valproate (n = 6) Interferon beta (n = 6) Ciprofloxacin (n = 5) Lamotrigine (n = 5) Methyldopa (n = 5) Telithromycin (5) Phenytoin (n = 5) Diclofenac (n = 4) Chalasani N,et al. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1924-34. Metabolism of Isoniazid in the Liver Isoniazid acetylation Acetylisoniazid N-acetyltransferase (NAT2) hydrolysis Acetylhydrazine oxidation CYP 2EI N-acetyltransferase (NAT2) Hepatotoxins acetylation Diacetylhydrazine O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 11 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM NAT2 Slow Acetylator Genotype and Susceptibility NAT2 slow acetylator (lacking wild type NAT2*4 allele) 26% vs. 11.1% Cytochrome P450 2E1 Genotype And Susceptibility to Isoniazid-Induced Hepatitis Genotype Risk of Hepatotoxicity CYP 2E1 c1/c1 20% Odds Ratio 2.52 CYP 2E1 c1/c2 9% Or c2/c2 O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 12 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Most Common Drugs causing DILI (out of 217 single Rx cases) Amoxicillin/clavulanate (n = 23) Nitrofurantoin (n = 13) Isoniazid (n = 13) TMP/SMX (n = 9) Duloxetine (n = 6) Valproate (n = 6) Interferon beta (n = 6) Ciprofloxacin (n = 5) Lamotrigine (n = 5) Methyldopa (n = 5) Telithromycin (5) Phenytoin (n = 5) Diclofenac (n = 4) Chalasani N,et al. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1924-34. Diclofenac Serious Hepatotoxicity Presentation Within 6 Months 6.3/100,000 85% Elevated Aminotransferases 15% ALT > 3X Presentation After 1 Year 3% If Jaundice Develops, 8-20% Fatalities 5% O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 13 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Diclofenac: Metabolic Pathways Biliary excretion UGT2B7 Diclofenac acylglucuronide 4'-OH-diclofenac acylglucuronide ? Diclofenac ?UGT2B7 4'-OH-diclofenac Covalent adducts 5'-OH-diclofenac Diclofenac-2,5quinoneimine ? Diclofenac: Metabolic Pathways Biliary excretion MRP2 (ABCC2) UGT2B7 Diclofenac acylglucuronide 4'-OH-diclofenac acylglucuronide ? Diclofenac ?UGT2B7 4'-OH-diclofenac Covalent adducts O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 5'-OH-diclofenac Diclofenac-2,5quinoneimine ? 14 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Diclofenac: Genetic Polymorphisms of Interest Specific Allele Promotes: UGT2B7*2 MRP2 (ABCC2) Reactive Metabolites Extracellular Transport Most Common Drugs causing DILI (out of 217 single Rx cases) Amoxicillin/clavulanate (n = 23) Nitrofurantoin (n = 13) Isoniazid (n = 13) TMP/SMX (n = 9) Duloxetine (n = 6) Valproate (n = 6) Interferon beta (n = 6) Ciprofloxacin (n = 5) Lamotrigine (n = 5) Methyldopa (n = 5) Telithromycin (5) Phenytoin (n = 5) Diclofenac (n = 4) Chalasani N,et al. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1924-34. O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 15 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid Clavulanic Acid Hepatotoxicity Cholestatic Injury 1:100,000 Onset 1- 6 weeks: Mean 18 days Onset up to 6 weeks after therapy Recovery 1- 4 months Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Flucloxacillin Cholestatic Hepatic Reactions Risk Factors Female Elderly Prolonged Therapy Occurs in 8.5 / 100,000 New Users 1-45 day onset Considerable Differences Based on Ancestry Higher: Northern Europeans Lower: Asians and Africans Daly, 2009 O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 16 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Minocycline Semisynthetic Derivative of Tetracycline Widely Used Treatment For Acne Mimicks or Unmasks Autoimmune Hepatitis + ANA + Anti-Smooth Muscle Antibody Iminoquinone Metabolite Causes A Lupus-like Syndrome Activates T-cells Immunomodulatory Anti-Inflammatory Response Question #3 The following statements regarding HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (statins) are true: 1. Risk of drug-induced hepatotoxicity is extremely high 2. Patients should be monitored regularly 3. Patients with liver disease should avoid them 4. All of the Above 5. None of the Above O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 17 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors All cause ALT ALT may be related to lipid dose Risk of drug-induced hepatotoxicity extremely low Increases often transient adaptation No evidence monitoring of value Common Herbals and Dietary Supplements Associated with DILI Right approach Herbalife Formula Green tea (mega tea, Arizona green tea) Herbalife Cell Activator, Herbalife shake, Herbalife Total Control, Herbalife Xtra Lavender oil, Frankincense oil Nixia redMelatonexDHEA VPX Redline Fat Burner M one T (17 α methyl 1testesterone) Testron-Sx Hydroxycut Slim QuickLipozene Niacin Airborne Cimicifuga racemosa G3 (Gac fruit juice with other Chinese fruit juices Airborne O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric MT-80 (methyl testosterone) 18 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Drug-Induced Liver Disease Patterns of Histologic Injury Acute Chronic Hepatocellular Hepatocellular Cholestatic Cholestatic Mixed Granulomas Vascular Fibrosis/cirrhosis Vascular Neoplasms Drug-Induced Liver Disease Patterns of Injury - Examples Tetracycline Microvesicular fat Chronic cholestasis (rare) Chronic hepatitis (minocycline) Amoxicillin-Clavulanate Cholestasis cholangitis, hepatocellular injury, granulomas Nitrofurantoin - incidence approx. 1/3000 Acute hepatitis - 30% Chronic hepatitis - 50% Cholestasis - 10% O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 19 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Drug-Induced Liver Disease Suspect Always Atypical Patterns Cholestatic hepatitis Granulomatous hepatitis Hepatitis + eosinophils Zonal necrosis Severe acute hepatitis CLINICAL AND PATHOLOGICAL SYMPTOMS OF DRUG-INDUCED LIVER DISEASES. Kaplowitz N Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:S44-S48 © 2004 by the Infectious Diseases Society of America O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 20 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Model Compound • Many of the protective factors discovered through acetaminophen (APAP) toxicity research on • Acetaminophen – Clinically relevant; analgesic, antipyretic – Over 50,000 ER visits per year – 450 death per year • Suicide • Accidental ingestion • “Therapeutic misadventures” – Unlike with drug idiosyncrasy, it is well characterized and reproducible in animals • Bioactivation to N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) APAP-Induced Liver Injury O HN Sulfation CH 3 Glucuronidation Detox Detox P450 2E1 P450 1A2 P450 3A4 OH ACETAMINOPHEN O N Cysteinyl Conjugate CH 3 GSH Detox Depleted O NAPQI O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric Protein Adducts Mitochondria Dysfunction Reactive Oxygen Species LIVER INJURY 21 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Acetaminophen cases as % of all ALF per year Percent of ALF Cases Total ALF cases: 60% 85 94 50% 123 133 128 47% 44% 38% 40% 30% 99 51% 38% 28% 20% 10% 0% 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 YEAR O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 22 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Suicidal vs. Accidental APAP cases Suicidal (n=101) Female (%) 75 ACM dose(g) 28 Dose per day 28 Coma (%>3) 39 ALT (IU/L) 6118 Spont surv (%) 67 Antidepress’t 35 Narcotic cpd (%) 19 Unintentional (n=109) p-value 76 34 10 55 3975 66 36 62 NS NS 0.001 0.026 0.001 NS NS 0.001 ACM/Narcotic compounds (n=98; 43%) Brands most commonly reported Vicodin 72 Percocet 8 Lortab 8 Tylenol #3 7 Darvocet 5 Lorcet, Norco: 3 each Compound users were more likely to receive NAC, had higher coma grades but similar survival to others O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 23 Drug Induced Liver Disease:2010 7/24/2012 10:17 AM Prognosis in Acute Liver Failure Etiology an important outcome determinant Bad prognosis: Good prognosis: Drugs Acetaminophen Indeterminate Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Shock Wilson Disease SUMMARY • Occurs in small fraction of individuals • Difficult to predict • Major clinical problem; often life-threatening • Leading cause of acute liver failure • Reason drugs removed from development and widespread use O:/VPCLINICAL/Speaking/2010/DILD2010_G eneric 24