Cell Membrane & Energy Review Packet
advertisement
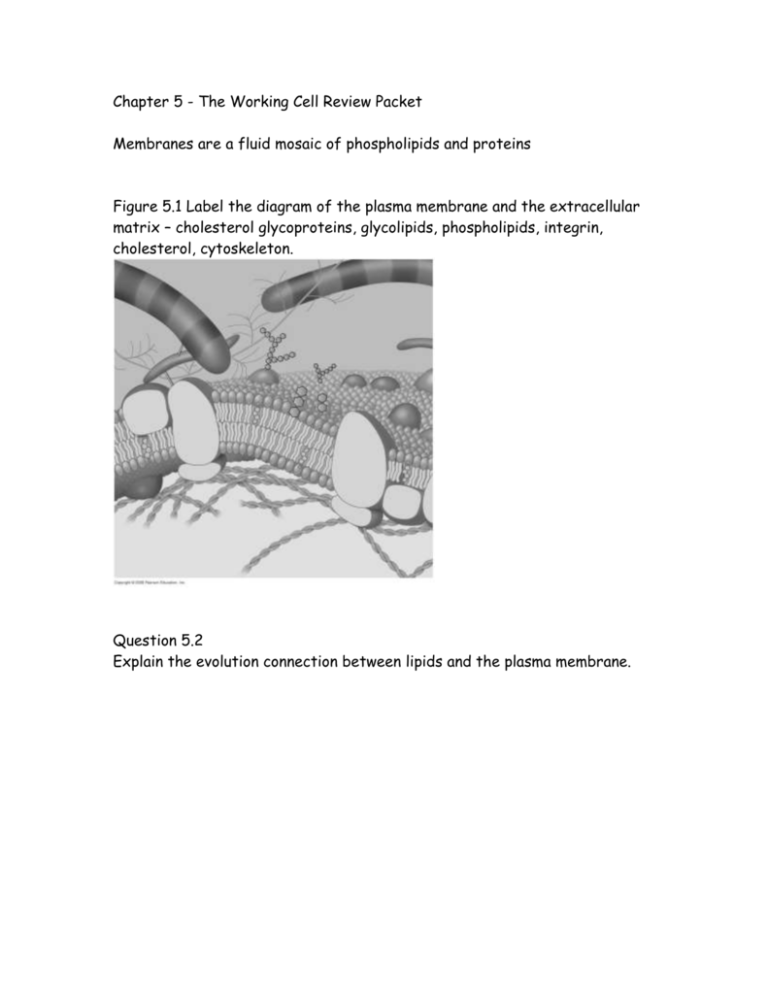
Chapter 5 - The Working Cell Review Packet Membranes are a fluid mosaic of phospholipids and proteins Figure 5.1 Label the diagram of the plasma membrane and the extracellular matrix – cholesterol glycoproteins, glycolipids, phospholipids, integrin, cholesterol, cytoskeleton. Question 5.2 Explain the evolution connection between lipids and the plasma membrane. Question 5.3 Describe the process in this diagram. Specifically, what is going on, what is the process called, and what do we call this when molecules move back and forth at an equal rate, with no net change? Question 5.4 Indicate the direction of movement and the material that moves for the following problem. Two solutions are separated by a semipermeable membrane (water can diffuse, glucose can’t). On the left side there is a .7% glucose solution and on the right side as a .4% concentration of glucose. What moves, in what direction, and why? What is the movement called? Question 5.5 Label the diagram below; identify plant and animal cell, label the isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions. Compare “normal” cell water balance in an animal cell with the ”normal” cell water balance in a plant cell. Questions 5.6 What is facilitated diffusion? What properties of the cell membrane make this possible? Give an example. How is water transported? Section 5.8 In active transport, a cell must expend ____________________ to move a solute _________________ its concentration gradient. Section 5.8/5.9 Exo/endocytosis Fill in the table below: Description Exocytosis Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Receptor mediated endocytosis Sodium potassium pump Energy and the cell 5.10 Cells transform energy to do work Define the term energy- What is it? Fill in the table below. For the definition use no more than 4 words. Type of energy Definition (by association) Kinetic Heat Potential Chemical Question 5.11 How does the second law of thermodynamics help explain the diffusion of a solute across a cell membrane? 5.12 Chemical reactions Make a concept map that summarize the two pathways chemical reactions take using – exergonic, endergonic, cell respiration, photosynthesis, metabolism, and energy coupling. Figure 5.12 – label using the words exergonic, endergonic, energy released, energy required, reactants, and products Questions 5.13 What types of cellular work is performed by ATP? How do exergonic processes power endergonic reactions? Figure 5.14 Label this diagram Mr. Gorbachev! Question 5.15 Explain how sucrose is enzymatically broken down into glucose and fructose. What effect does temperature and pH have on enzyme activity? 5.16 Inhibitors and feedback Distinguish between competitive and non competitive inhibition by drawing 1 example of each. Your book introduces feedback inhibition in a rather abbreviated way. Why is it important for a cell to regulate metabolism?