Study Guide in preparation for Exam II
advertisement

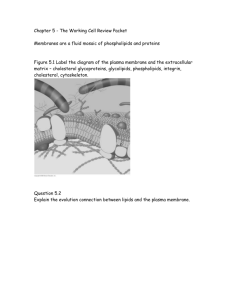
Study Guide in preparation for Exam II A Tour of the Cell i) Why is it more beneficial for cells to be smaller rather than larger? ii) Know what organelles are used in the four different processes of the cell: Manufacturing, Breakdown, Energy processing, Structural support iii) Be able to identify organelles based upon their structure or function. iv) Understand the endomembrane system. Be able to draw out the path of a hydrolytic enzyme from the starting point, to its ending point in the lysosome. v) What is the difference between smooth and rough ER both structurally and functionally? vi) What is the purpose of vacuoles? vii) Know the functions and parts of the cytoskeleton. How does it help the other systems of the cell to perform their respective functions? viii) What is the purpose of the ECM and what types of proteins interact with it? Know how to identify these proteins in a diagram. ix) Be able to distinguish the different types of cell--‐ cell junctions. Membrane Structure and Function i) Know about membrane fluidity. What contributes to it? ii) What kinds of proteins are integrated into the membrane and what are the different functions of the proteins? Know how to identify each. iii) The selective permeability of the membrane allows what kind of molecules to move through? What kind cannot move through? iv) How do polar molecules move through the membrane? v) What is diffusion? What is osmosis? vi) What is the difference between active and passive transport? vii) Know the effects that solutions of varying tonicities will have on red blood cells or plant cells. viii) There will be at least one U--‐ bend question on the exam. ix) Know what kinds of proteins are involved in active or passive transport. Know how this relates to facilitated diffusion. x) Know all terms associated with membrane potential. xi) What is co--‐ transport? xii) What is the difference between exo and endocytosis? xiii) Be able to identify the three different forms of endocytosis. Metabolism Understand the difference between anabolic and catabolic. What are the different forms of energy? Know the definitions for each. Know what the first two laws of thermodynamics state. Know the formula for free energy: G = H --‐ TS Know what the different values of G tell you in regards to the spontaneity of a reaction as well as whether or not that reaction is anabolic/catabolic, or exergonic/endergonic If given pictures/graphs, know how to identify a reaction based upon the parameters listed in the previous point. Know how coupled reactions (exergonic feeding endergonic) work and know if the net coupled reaction would be classified as exergonic or endergonic (subtracting the G values for each reaction from each other) Know that one molecule of ATP has a G = - ‐ 7.3 kcal/mol What is an enzyme and how does it work? What does it bind to? What factors affect enzymatic activity? Can you identify optimal conditions on a graph? Are all cofactors also coenzymes? Are all coenzymes also cofactors? What is the difference between a cofactor and an inhibitor? What are some similarities that exist? What are the different types of inhibitors, and how do they work? What is allosteric regulation and how can it help/hinder enzymatic activity? Understand how feedback inhibition works.