Name of Course Physics V Course Code PPHY1104 PPHY = the
advertisement

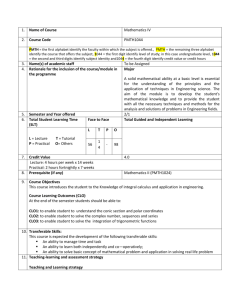
1. Name of Course Physics V 2. Course Code PPHY1104 PPHY = the first alphabet identify the faculty within which the subject is offered., PPHY = the remaining three alphabet identify the course that offers the subject, 1104 = the first digit identify level of study; in this case undergraduate level, 1104 = the second and third digits identify subject identity and1104 = the fourth digit identify credit value or credit hours 3. 4. 5. 6. Name(s) of academic staff Rationale for the inclusion of the course/module in the programme Semester and Year offered Total Student Learning Time (SLT) L = Lecture P = Practical 7. 8. 9. T = Tutorial O= Others A solid Physical ability at a basic level is essential for the understanding of the principles and the application of techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to develop the student's Physical knowledge and to provide the student with all the necessary techniques and methods for the analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering fields 3/1 Total Guided and Independent Learning Face to Face L T 56 14 - Credit Value Lecture: 4 hours per week x 14 weeks Practical: 2 hours fortnightly x 7 weeks Prerequisite (if any) P To be Assigned Major O 168 98 4.0 Physics I (PPHY1064) Course Objective This course introduces students to the knowledge of heat and application in civil engineering Course Learning Outcomes (CLO) At the end of the semester students should be able to: CLO1: Understand The fundamental of heat and its application in engineering CLO2 Understand The fundamental of thermodynamic and its application in engineering CLO3 Understand The fundamental of ideal gases and its application in Engineering 10. Transferable Skills: This course is expected the development of the following transferable skills: An ability to manage time and task An ability to learn both independently and co—operatively; 11. Teaching-learning and assessment strategy Teaching and Learning strategy Formal Lectures will provide theoretical understanding for CLO1, CLO2 and CLO3. Assessment Schedule and strategy 1. Assessment Schedule: Quizzes will be conducted on 4th week to demonstrate the CLO1. Midterm Exam will be conducted on 7th week to demonstrate CLO1 and CLO2 Assignment to will be given on the 9th week to demonstrate CLO3 A three Hours Examination will be conducted 16th week to assess CLO1, CLO2 and CLO3 2. Assessment strategy: Quizzes (Q) 10% Midterm Exam (ME) 20% Assignment (ME) 10% Final Exam (FE) 60% Total 100% 12. Synopsis: This course provides an introduction to the principles of heat, thermodynamics and gas Behaviour 13. Mode of Delivery: Lectures Tutorials 14. Assessment Methods and Types: Performance Criteria : CLO-PLO Assessmen t Tool 1 2 3 4 5 0-39 40-49 50-59 60-74 75-100 (F) (D,D+) (C-,C,C+) (B-,B,B+) (A-,A,A+) Q, ME , FE Fail To: - learn both independently and cooperatively Poor To: - learn both independently and cooperatively Satisfactory To: - learn both independently and cooperatively Good To: - learn both independentl y and cooperatively ME, FE Fail To: - manage time and task - learn both independently and cooperatively Poor To: - manage time and task - learn both independently and cooperatively Satisfactory To: - manage time and task - learn both independently and cooperatively Good To: - manage time and task - learn both independentl y and cooperatively Outstanding To: - learn both independentl y and cooperativel y Outstanding To: - manage time and task - learn both independentl y and cooperativel y Fail To: - learn both independently and cooperatively Poor To: - learn both independently and cooperatively Satisfactory To: - learn both independently and cooperatively Good To: - learn both independentl y and cooperatively Marks Grade CLO1: Understand The fundamental of heat and its application in civil engineering CLO2: Understand The fundamental of thermodynamic and its application in engineering CLO3: Understand A, ME, FE The fundamental of ideal gases and its application in Engineering 15. Mapping of the Programme Objectives to the Programme Learning Outcomes Outstanding To: - learn both independentl y and cooperativel y Fundamental knowledge PLO8: - Understanding of the need to undertake life-long learning, and an ability to do so by taking up the opportunities available in the different fields PLO7: Ability to use the skills, techniques, and contemporary tools necessary for engineering course study. PLO6: Understanding of professional and ethical responsibilities and commitment to them. PLO5: Ability to communicate effectively to successfully enrol into engineering degree course PLO4: - Ability to undertake problem identification, formulation and solution; PLO3: Understanding of the rapid development of engineering industry Programme Objectives (PO) PO1: PLO2: Ability to apply knowledge of Physics and science PLO1: - Knowledge of the Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry Programme Learning Outcomes (PLO) of mathematics and basic science to enable them to gain entry into the bachelor of 3 3 1 3 3 1 1 3 1 1 1 1 3 3 1 1 engineering degree course. PO2: Proficiency in communication, understanding of professional ethics, and the ability to demonstrate success and leadership, as well as the ability to engage in continuing professional development. 1= Related to PLO without formal assessment; 2= Partial fulfilment of the PLO with formal assessment; 3= Total fulfilment of PLO with formal assessment. 16. Mapping of the course Learning Outcome to the Programme Outcome PLO4 PLO5 PLO6 PLO7 PLO8 3 heat and its application in civil engineering CLO2: Understand The fundamental of 3 PLO3 CLO1: Understand The fundamental of PLO2 Course Learning Outcome (CLO) PLO1 Programme Learning Outcomes (PLO) 3 1 3 1 1 3 1 3 1 3 1 1 3 1 thermodynamic and its application in engineering CLO3: Understand The fundamental of 3 3 1 ideal gases and its application in Engineering 1= Related to PLO without formal assessment; 2= Partial fulfilment of the PLO with formal assessment; 3= Total fulfilment of PLO with formal assessment. 17. Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic Details 3 1 1 3 1 SLT L T P O Tota l Topic 3 Topic 2 Topic 1 Introduction to heat Temperature scale Thermal expansion heat and internal energy mode of heat transfer Thermodynamics thermodynamics system and their surrounding laws of thermodynamics thermal processes heat engines Carnot’s principles and Carnot engine refrigerators, air conditioners and heat pumps entropy Ideal gases Molecular mass, the mole and Avogadro’s numbers The ideal gas law Kinetic theory of gases Diffusion Total SLT Hour 20 5 - 35 60 20 5 - 35 60 16 4 - 28 48 56 14 - 18. Main references supporting the course 1. Physics - Hardcover (Jan. 1, 2009) by John D. Cutnell and Kenneth W. Johnson 2. Advanced Physics Demystified by Stan Gibilisco (Jun 1, 2007) 3. Stev Adams, Jonathan Alldeny’ advanced . physics, Oxford university press 2000. 19. Additional references supporting the course 1. S.R. Paranjothi, 2000,” Electric Circuit Analysis”, Pearson 2. Boylested and Nashelsky, 2001,”Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory”, Prentice-Hall. 3. Cheong F. C., Pre U/STPM/Matriculation, Pearson and Longman, 2004, Malaysia 4. Hutchings, R., Physics, published by Nelson, 20. Other additional information All materials will be available to the students in the library. 98 168