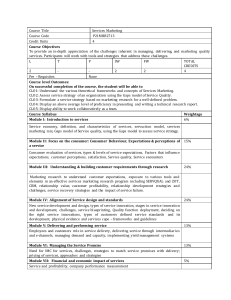
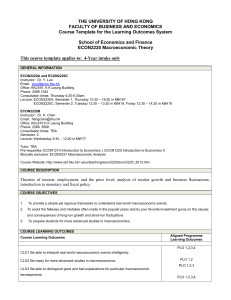
Macroeconomic Theory A - the School of Economics and Finance
advertisement

BE103/512 THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG FACULTY OF BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS School of Economics and Finance ECON2102 - Macroeconomic Theory GENERAL INFORMATION ECON2102A Instructor: Dr. Chung-Yi Tse Email: tsechung@econ.hku.hk Office: Room 1006 K K Leung Building Phone: 2859 1035 Lecture: Tuesday 12:30pm - 1:20pm in KB 419, Friday 12:30pm - 2:20pm in KB 419 Consultation times: Tutor: Mr. Yuen Cheuk Yi Kelvin ECON2102B Instructor: Dr. Heng Chen Email: hengchen@hku.hk Office: Room 915 K K Leung Building Phone: 2857 8506 Lecture: Friday 2:30pm - 5:20pm in MW T2 Consultation times: Tutor: to be confirmed Pre-requisites: ECON1001, ECON1002 Co-requisites: Mutually exclusive: ECON2114 Macroeconomic analysis Course Website: Other important details: COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is macroeconomics—the study of the entire economy as opposed to individual markets—at an intermediate level. Questions include but not are limited to: Why are some countries so poor while others so rich? Why do some countries grow and others stagnate? What drives booms and recessions? How do government policies affect aggregate output, unemployment, and inflation? A variety of models are developed in macroeconomics, each of which is more suited for certain questions than others. This course aims to introduce students to the basic workhorse models for each major macroeconomic question. COURSE OBJECTIVES 1. To provide a simple yet rigorous framework to understand real world macroeconomic events. 2. To avoid the fallacies and mistakes often made in the popular press and by your favorite investment gurus on the causes and consequences of long-run growth and short-run fluctuations 3. To prepare students for more advanced studies in macroeconomics. COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES Course Learning Outcomes CLO1 Be able to interpret real world macroeconomic events intelligently. CLO2 Be ready for more advanced studies in macroeconomics. CLO3 Be able to distinguish good and bad explanations for particular macroeconomic Aligned Programme Learning Outcomes PLO 1,2,3,4 PLO 1,2 PLO 1,2,3 developments. CLO4 Be able to understand and articulate the effects of important macroeconomic policy PLO 1,2,3,4 changes. COURSE TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES Course Teaching and Learning Activities Expected contact hour Study Load (% of study) 39 28.9 11 8.1 15 11.1 70 51.9 135 100% Weight Aligned Course Learning Outcomes 15% CLO 1,2,3,4 30% CLO 1,2,3,4 55% CLO 1,2,3,4 T&L1. Lecture T&L2. Tutorial T&L3. Homework T&L4. Readings and Revision … Total Assessment Methods Brief Description (Optional) A1. Homework A2. Midterm test A3. Final exam Total 100% STANDARDS FOR ASSESSMENT Course Grade Descriptors A+, A, A- Strong evidence of superb ability to fulfill the intended learning outcomes of the course at all levels of learning: describe, apply, evaluate, and synthesis. B+, B, B- Strong evidence of the ability to fulfill the intended learning outcomes of the course at all levels of learning: describe, apply, evaluate, and synthesis. Evidence of adequate ability to fulfill the intended learning outcomes of the course at low levels C+, C, C- of learning such as describe and apply but not at high levels of learning such as evaluate and synthesis D+, D F Evidence of basic familiarity with the subject. Little evidence of basic familiarity with the subject. Assessment Rubrics for Each Assessment (Please provide us the details in a separate file if the space here is not enough) COURSE CONTENT AND TENTATIVE TEACHING SCHEDULE 1. Introduction and national income accounting 2. Basic ingredients of macroeconomic theory: (a) Production function, labor market equilibrium and full-employment output (b) Consumption, saving, investment (c) Open economy 3. Long-run economic growth 1 week 2½ week 2 week 4. The asset market, money and prices 5. Business cycles (a) Business cycle facts (b) The IS-LM/AD-AS model (c) Classical business cycle theory (d) Keynesian business cycle theory 3½ week 6. Macroeconomic Policy (a) Inflation-unemployment tradeoff (b) Monetary policy (c) Fiscal policy 2 week 7. Exchange rates and international linkages 1 week 8. Advanced topic: The intertemporal approach 1 week MEANS/PROCESSES FOR STUDENT FEEDBACK ON COURSE o o o conducting mid-term survey in additional to SETL around the end of the semester Online response via Moodle site Others: ________________________ (please specify) COURSE POLICY (e.g. plagiarism, academic honesty, attendance, etc.) The University Regulations on academic dishonesty - behaviors in which a deliberately fraudulent misrepresentation is employed in an attempt to gain undeserved intellectual credit, either for oneself or for another will be strictly enforced. The Board of Examiners may impose a penalty in relation to the seriousness of the offence and may report the candidate to the Senate, where there is prima facie evidence of an intention to deceive and where sanctions beyond those imposed by the BoE might be invoked. Classroom etiquette 1. Please switch your cell phone to silent mode if you need to keep it on at all. 2. If you need to answer a call during class, quietly walk out of the classroom before you do so. When you finish, please leave and do not come back in again. 3. If you are late for more than 10 minutes, please do not bother to show up. Your entry in the middle of the class is a nuisance to everybody. 4. Unless for emergency, please do not leave the classroom before the class is over. Your doing so constitutes outright disrespect for the instructor. 5. Please do not come to the classroom to mainly surf the net during class. ADDITIONAL COURSE INFORMATION (e.g. e-learning platforms & materials, penalty for late assignments, etc.) Notes for using the course outline template: When preparing your course outlines, please feel free to amend the template format to suit your course. Some typical examples for some of the following items are extracted from the current practices for your reference. Course Description A short description of the course Example (BUSI0016): COURSE DESCRIPTION The purpose of this course is to develop a solid understanding of modern corporate finance and its application to corporations. The concepts and methods introduced here are heavily used in practice. These materials are very helpful not only to modern corporations but also to your personal investing. Course objectives Example (BUSI1002): COURSE OBJECTIVES 1. To provide students with basic knowledge regarding the key principles and concepts of financial accounting; 2. To develop students’ ability to use financial accounting information in different decision-making scenarios; 3. … Course Learning Outcomes and Alignment with Programme Learning Outcomes Course Learning Outcomes are statements which explicitly state the highest level of achievement with the subject matter that you would expect of the students by the end of this course. The recommendation is to aim for between four and six learning outcomes in a course. The learning outcomes are usually measurable and/or assessable and are not a statement of the process of learning but of what is to be achieved. Mapping Course Learning Outcomes with Programme Learning Outcomes indicates the relationship between the learning outcomes for the course and the learning outcomes for the program. Example (BUSI0006): COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES Course Learning Outcomes CLO1. Describe and explain the financial statement auditing process CLO2. Use relevant information for making decision of client acceptance, risk assessment and extent of audit work Aligned Programme Learning Outcomes PLO1, 2 PLO1, 2, 3,4,5,6,7,8 CLO3. Apply Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants to resolve ethical situations PLO3,4,5,6,7,8 CLO4. Demonstrate effective communication skills PLO3,4,5,9,10 Course Teaching and Learning Activities Having articulated the learning outcomes we can identify teaching and learning activities and expected contact hours that provide opportunities for students to develop and achieve the stated outcomes. The emphasis is on the learning and how the activities facilitate that learning and which outcomes are being targeted by specific activities. Example: COURSE TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES Course Teaching and Learning Activities Expected contact hour Study Load (% of study) T&L1. Lecture with interactive presentation 36 hours 30% T&L2. Tutorial and e-forum discussions 12 hours 10% T&L3. Case-based study and analysis T&L4. Self study Total 30 hours 25% 42 hours 120 hours (within 120150 hours) 35% 100% Assessment Methods and Alignment with Course Learning Outcomes Each learning outcome in a course should be assessed. A matrix can be a helpful way to check that the outcomes, teaching and learning activities and assessment tasks are aligned. Students can see the direct relevance of the activities and can see that they are being assessed on what is relevant and what they have been covering during the course. Students will be assessed by using the specific grading schedules or rubrics as shown in the course outline. Weightings of each assessment are to be specified in the following section. Example: Assessment Methods Brief Description (Optional) Weight Aligned Course Learning Outcomes A1. Written assignments Two short essays to explain the model and … 30% CLO1, CLO2 A2. Online assessment Participation in e-forum to discuss a specific topic for clarifying understanding of the concept 5% CLO1, CLO3 A3. Group project & presentation Case study to do analysis and synthesis of the chosen current issues of the study field 30% CLO4 A4. Final examination Open-book examination enabling student to demonstrate most of the stated CLOs 35% CLO1, CLO3, CLO4 Total 100% Course Grade Descriptors The criteria for assessment will indicate the degree to which a student has, or has not met the high standard set in the learning outcome. These standards let students know more explicitly what they have to do to achieve assessments at different levels. A general standard for the course is to be specified. Example: STANDARDS FOR ASSESSMENT Course Grade Descriptors A+, A, A- Candidate has consistently demonstrated a thorough grasp of the subject as evidenced by original or exceptionally astute analysis and synthesis… B+, B, B- Candidate frequently demonstrated a substantial grasp of the subject … C+, C, C- … some of the responses are well organized, clear but with insufficient elaboration… D+, D F … solutions to questions and problems containing unstructured but relevant observations, and marginally interesting and … … little evidence of basic familiarity with the subject… Assessment Rubrics for Each Assessment For specific standard for each assessment task (e.g., presentation and group project), assessment criteria or rubrics are to be developed and provided to students. In doing so, information of course learning outcomes and how individual assessment is to be assessed will give students a clear goal for their study, something against which they gauge their performance and make improvement accordingly. Means/Processes for Student Feedback on Course The SETL questionnaire is one of the ways HKU courses and teaching are evaluated. HKU places significant importance on student learning and on the continuous enhancement of teaching and learning outcomes. Students are asked to complete this evaluation of their learning experiences at the conclusion of each course in which they enrol. Questionnaire items relate to the overall evaluation of the course as well as an evaluation of teaching. In addition, individual teachers may seek other student feedback mechanism in the duration of their course such as through student forums or class discussion feedback. In this section, please indicate the means or processes for students to provide feedback on your course. Course Policy A student’s academic responsibility, such as issues of plagiarism is often highlighted in a course outline and other academic issues or procedures which may be pertinent to a specific program or course. Other policies including academic honesty, attendance etc. could also be included as appropriate. Course Content and Tentative Teaching Schedule This will include a schedule of topics, readings, continuous assessment and other activities for each week during the course.