1 Name
advertisement

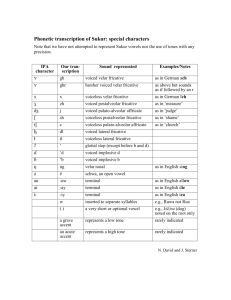
-1- Name……………………………………………………………………. Student Number……………………………………………… Week 3 Effective Pronunciation How to learn English Pronunciation 1. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 2. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 3. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. IPA refers to ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… The Sound of English (1): Consonants Three Phonetic Factors of Consonants 1. ………………………………………………………………. : ……………………….. 2. ………………………………………………………………. 3. ………………………………………………………………. All the consonants of English can be classified in terms of "………….." (…………………….………………-……………………). For instance, /f/ is a voiceless labiodental fricative, and /b/ is a voiced bilabial plosive (stop). Complete the Sounds Chart handout to describe the given sounds. Phonetic Factors IPA Voicing p t k b d Place of Articulation Manner of Articulation examples -2- Phonetic Factors IPA Voicing f v θ ð s z ʃ (š) ʒ (ž) tʃ (č) dʒ (ǰ) m n ŋ l w r j h Place of Articulation Manner of Articulation examples -3- Exercises 1. Give the appropriate three-term description for each of the following sounds. (e.g. [k]: voiceless velar stop): [f ] …………………………………………………………………………………………….. [b] …………………………………………………………………………………………….. [θ] …………………………………………………………………………………………….. [ʃ ] …………………………………………………………………………………………….. [t] …………………………………………………………………………………………….. [ j] …………………………………………………………………………………………….. 2. Give the appropriate phonetic symbol for each of the following sounds: (a) a voiced palato-alveolar fricative……………………………… (b) a voiced alveolar stop ……………………………… (c) a voiced velar stop ……………………………… (d) a voiced dental fricative ……………………………… (e) a voiced labio-dental fricative ……………………………… 3. What phonetic property distinguishes each of the following pairs of sounds (e.g. [p] and [b]: voicing; [s] and [S]: place of articulation; [t] and [s]: manner of articulation)? (a) [k] and [g] …………………………………………………………………….. (b) [b] and [d] …………………………………………………………………….. (c) [d] and [z] …………………………………………………………………….. (d) [z] and [ʒ] …………………………………………………………………….. (e) [ʃ ] and [ʒ] …………………………………………………………………….. (f ) [d] and [g] …………………………………………………………………….. 4. Which of the following English words begin with a fricative? ship psychology veer round plot philosophy think late xylophone -4- Which of the following English words end with a fricative? stack whale swim epitaph use path pleads cuts half halve hash haze phase Which of the following English words begin with a stop? philanderer plasterer parsimonious ptarmigan psyche charismatic cereal carping kinky ghoulish grueling guardian thick tickle bin dreary