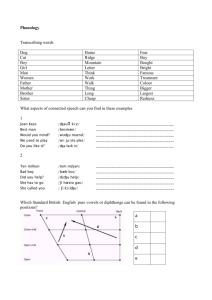
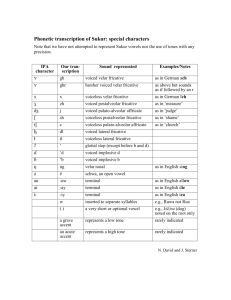
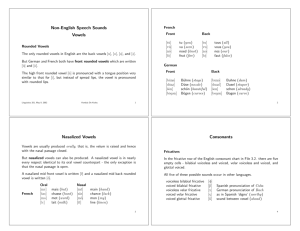
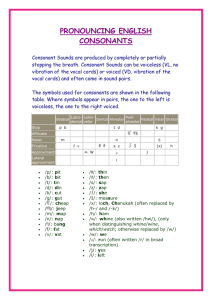
Phonetic symbols
advertisement

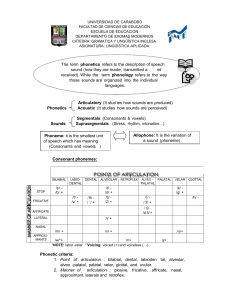
Phonetic symbols Consonants The consonant-symbols b d f h k l m n p r s t v w z have their usual English values. Note that s is always voiceless, not voiced as in “days”. g ŋ θ ð y ɣ ʍ girl č sing ŝ thin, thigh (voiceless) ǰ then, thy (voiced) ž yes, ye, yacht ç OE bugan (voiced velar fricative) x whine contrasted with wine (voiceless /w/) Vowels i peat, see, green ɪ pit, sit, lyric e pate e: ME swete (sweet) (close e) ɛ pet ɛ: ME breeth (breath) (open e) æ æ: a ʊ̈ ü: u ʊ o o: church, chug ship judge, jug measure, vision German ich, Scots licht German ach, Scots loch (voiceless velar fricative) French lune, OE fyllan (fill) German Küche, OE mȳs (mice) pooh, fool, moon put, full1 Poe same as Poe but lengthened, OE fōda (food), ME rood (cross) (close o) paw, law2 ME rood (rode) (open o) pot (Am.), watch pot (British) ɔ ɔ: ɑ ɒ father (Br), pasta, ask (E New England) ə about, putt, pert, father, sofa, motor, ago [shwa: half open central] ə: bird, fur ʌ but (British) pat, cat, pastor OE dǣl (deal) Diphthongs (vowel glides; “a sequence of two vowels in the same syllable,” Algeo 27) eɪ day ɪə here əʊ go ɛə there aɪ fly ɔə more aʊ now uə gourd ɔɪ boy 1 Note that Algeo represents this sound as /ʊ/ in the textbook (see, e.g. p. 25), but as /U/ in the Workbook. The /U/ represents a handwritten form of the /ʊ/. Note also that in some varieties of American and British English full is more like /fəl/ or even /fɨl/. 2 Note that “an increasingly large number of Americans do not distinguish between /ɔ/ and /ɑ/. For them, caught and cot are homophones.” (Algeo, p. 26) Thus in exercise 2.3 in the Workbook, wrought is not distinguished from rot. But even if the /ɔ/ sound is not used in your dialect, it’s as well to be aware of it as a distinctive sound in other dialects.