File
advertisement

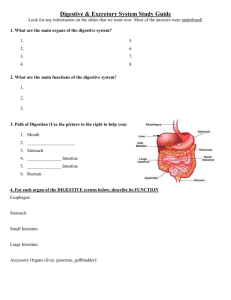
Biology 12 Human Biology – The Digestive System Chapter 21 Vocabulary absorption, anaerobic bacteria, anus, appendix, bile, capillary, cardiac sphincter, chemical digestion, digestive enzyme, digestive tract, duodenum, emulsification, epiglottis, esophagus, gall bladder, gastric juice, hydrochloric acid (HCl), insulin, intestinal juice, lacteals, large intestine (colon), lipase, liver, maltase, microvillus, nuclease, pancreas, pancreatic amylase, pancreatic juice, pepsin, pepsinogen, peptidase, peristalsis, pH, pharynx, physical digestion, protease, pyloric sphincter, rectum, salivary amylase, salivary gland, salivary juice/saliva, small intestine, sodium bicarbonate, stomach, swallowing, trypsin, villus It is expected that students will: C1 Analyse the functional inter-relationships of the structures of the digestive system C1.1 C1.2 C1.3 C1.4 C1.5 C1.6 identify and give a function for each of the following: – mouth – tongue – teeth – salivary glands – pharynx – epiglottis – esophagus – cardiac sphincter – stomach – pyloric sphincter – duodenum – liver – gall bladder – pancreas – small intestine – appendix – large intestine (colon) – rectum – anus describe swallowing and peristalsis identify the pancreas as the source gland for insulin, and describe the function of insulin in maintaining blood sugar levels list at least six major functions of the liver explain the role of bile in the emulsification of fats describe how the small intestine is specialized for chemical and physical digestion and absorption Biology 12: Digestive system Page 1 C1.7 C1.8 C1.9 C2 describe the structure of the villus, including microvilli, and explain the functions of the capillaries and lacteals within it describe the functions of anaerobic bacteria in the colon demonstrate the correct use of the dissection microscope to examine the various structures of the digestive system Describe the components, pH, and digestive actions of salivary, gastric, pancreatic, and intestinal juices C2.1 C2.2 C2.3 C2.4 C2.5 C2.6 relate the following digestive enzymes to their glandular sources and describe the digestive reactions they promote: – salivary amylase – pancreatic amylase – proteases (pepsinogen, pepsin, trypsin) – lipase – peptidase – maltase – nuclease describe the role of water as a component of digestive juices describe the role of sodium bicarbonate in pancreatic juice describe the role of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in gastric juice describe the role of mucus in gastric juice describe the importance of the pH level in various regions of the digestive tract Biology 12: Digestive system Page 2 This diagram illustrates the main stages of digestion: What is the difference between physical and chemical digestion? _________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ What are the two main sites of physical digestion in your body? _____________________________________________________________________________ What is the main site of chemical digestion in your body? ______________________________ Where does most absorption occur? ________________________________________________ Biology 12: Digestive system Page 3 During chemical digestion, polymers are hydrolyzed to monomers before they can be absorbed into the blood. Label the following diagram to show the hydrolysis of the four main groups of organic polymers: Biology 12: Digestive system Page 4 Label the parts of the human digestive system on the following diagram: mouth, salivary glands, pharynx, epiglottis, esophagus, cardiac sphincter, stomach, pyloric sphincter, duodenum, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, small intestine, appendix, large intestine (colon), rectum, anus. Biology 12: Digestive system Page 5 Here is a diagrammatic layout of the digestive system. Label the various parts. mouth, salivary glands, esophagus, cardiac sphincter, stomach, pyloric sphincter, duodenum, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, small intestine, appendix, large intestine (colon), rectum, anus. Biology 12: Digestive system Page 6 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b20VRR9C37Q overview of digestion Digestion in the mouth Mechanical digestion involves ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Chemical digestion in the mouth involves ___________________________ ________________. Saliva contains water together with two other important substances. What are they? __________________________________________________________________ What are the main functions of saliva? (3) __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ http://www.factmonster.com/dk/encyclopedia/mouth Biology 12: Digestive system Page 7 The following diagram illustrates the stages in the swallowing reflex. Label the following structures: tongue, nasal cavity, pharynx, glottis, epiglottis, trachea, esophagus, esophageal sphincter, bolus of food Indicate where on the diagram peristalsis is taking place. http://www.d.umn.edu/~mmizuko/video/whole.mov What normally keeps the esophagus closed when you are not swallowing? ______________________________________________________________________________ What prevents food from entering the trachea when you swallow? ______________________________________________________________________________ Biology 12: Digestive system Page 8 This diagram illustrates the passage of food from your throat to your stomach and through the intestines. Describe this process: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Label the diagram: Biology 12: Digestive system Page 9 What do we call the lump of food that travels down the esophagus and enters the stomach? ______________________________________________________ What is the function of the cardiac sphincter? __________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ What is the function of the pyloric sphincter? __________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Approximately how long does food stay in the stomach? _____________ hours Name one digestive enzyme produced by the stomach wall, and the type of food substance it helps to break up? __________________________________________________________________ The stomach also produces acid. What is this acid for? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ How is the stomach wall protected from the acid? __________________________________________________________________ How does the muscle in the wall of the stomach help digestion? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ What do we call the material that leaves the stomach and enters the duodenum? ________________________________ Biology 12: Digestive system Page 10 Biology 12: Digestive system Page 11 Label this diagram showing the organs associated with the first part of the small intestine: The digestive enzymes of the small intestine work best in alkaline conditions; how, therefore, is the acid from the stomach neutralised when it enters the duodenum? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Where is bile i) made? _______________________________________ ii) stored? ________________________ ______________ iii) mixed with food? ________________________ _____ What does bile do? _______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Biology 12: Digestive system Page 12 The pancreas produces a juice which contains four important enzymes; name the enzyme which hydrolyzes: i) starch ______________________________________________ ii) protein _____________________________________________ iii) fat ________________________________________________ iv) nucleic acids _______________________________________ This table summarizes the enzymes that hydrolyze polymers in the small intestine: Give two ways that the small intestine is adapted for digestion? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ As a result of digestion (hydrolysis) what are the following foods finally broken down into? i) starch ____________________________________________________ ii) protein __________________________________________________ iii) fat ______________________________________________________ iv) nucleic acids ______________________________________________ Biology 12: Digestive system Page 13 Absorption of nutrients takes place in the rest of the small intestine: Why must food be digested before it can be absorbed? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Give six ways in which the wall of the small intestine is adapted to absorb digested food. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Biology 12: Digestive system Page 14 What is the main function of the colon? ____________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Why is roughage (or dietary fibre - cellulose) important in the human diet? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ The large intestine (colon) contains a very large population of anaerobic bacteria. In fact 1/3 of your feces is bacteria. E. coli is a common bacterium in your colon. Your body actually has more bacterial cells in and on it than it has human cells! What are some benefits of these bacteria to your body? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Annotate this diagram: Biology 12: Digestive system Page 15 How does the liver act as the ‘gatekeeper of the blood’ with respect to: a) toxins such as alcohol picked up from the intestine? __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ b) nutrients such as amino acids and glucose picked up from the intestine? __________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ c) iron and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K, and B12)? ______________________________________________________________________________ d) plasma proteins? ______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________ Biology 12: Digestive system Page 16 Why is this system called ‘hepatic portal’ and what is its value to the successful functioning of the organism? Biology 12: Digestive system Page 17 Annotate this diagram that shows the relationship between the liver and the small/large intestines with the associated blood vessels: Biology 12: Digestive system Page 18 The liver can convert amino acids into glucose if glucose levels are low. What toxic nitrogenous waste molecule is produced from the deamination of the amino acids? __________________ The liver then converts the ammonia into another nitrogenous waste called urea. Which is more toxic, ammonia or urea? __________________________ by how much? _________________ How does the body rid itself of the urea produced by the liver and other body cells? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ The liver also produces bile, which it sends to the gall bladder for storage prior to secreting it into the duodenum. What are the two major components of the bile, and what is the main function of each? 1. ___________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. ___________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Biology 12: Digestive system Page 19 Complete the following table of digestive glands and their secretions: Name of enzyme Salivary Amylase Name of Secretion Saliva Name of Related Gland Salivary Glands Location of Gland 3 separate pairs of glands; beneath tongue, beneath lower jaw, side of face in angle of jaw Substrate Starch Product Maltose Notes -functions best at neutral pH -saliva also contains water and mucus for lubrication Pepsin (a protease) Trypsin (a protease) Lipase Pancreatic Amylase Nuclease Biology 12: Digestive system Page 20 Name of enzyme Name of Secretion Name of Related Gland Location of Gland Substrate Product Notes Peptidases Maltase From the two lists below, match each structure with its correct function. _____ Salivary glands a. produces enzymes which pass into the duodenum _____ esophagus b. controls the passing of feces _____ stomach c. produce saliva _____ pyloric sphincter d. is where most water is absorbed _____ duodenum e. carries food from the mouth to the stomach _____ small intestine f. stores bile _____ bile duct g. receives juices from the gall bladder and pancreas _____ pancreas h. controls the amount of food leaving the stomach _____ gall bladder i. stores waste feces for several hours _____ colon j. produces hydrochloric acid _____ rectum k. is where most digested food is absorbed _____ anus l. takes bile from the gall bladder to the duodenum Biology 12: Digestive system Page 21 Glucose Homeostasis What do we mean when we say that the pancreas is an exocrine gland? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ What do we mean when we say that the pancreas is an endocrine gland? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ What is the source gland for insulin? (ie. Which endocrine gland produces insulin?) ______________________________________________________________________________ Biology 12: Digestive system Page 22 The set point for blood glucose is about 100 mg/100 mL of blood. This is the concentration that the body tries to maintain. It does this by a process of NEGATIVE FEEDBACK. Study the following negative feedback diagram to see how insulin affects glucose homeostasis: Biology 12: Digestive system Page 23 What is the STIMULUS for the release of the insulin? _________________________________ Where are the RECEPTOR cells? _________________________________________________ What is the CONTROL CENTRE? _______________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ What are the EFFECTORS and what do they do? ____________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Biology 12: Digestive system Page 24 What is the RESPONSE? __________________________________________________ Why do we refer to this process as NEGATIVE FEEDBACK? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ If the blood glucose level drops too low (for example, after you have not eaten for a while), how does your body bring the level back up to the SET POINT again? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ If the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin, the person has _____________________. This condition is treated with _______________________________________________. If the body secretes enough insulin, but the body cells do not respond to the insulin, the person has ____________________________________. This condition is treated with __________________________________________________________. In both types of diabetes, the person’s urine contains large quantities of __________________________. Draw a graph to show the combined effects of insulin and glucagon on the level of glucose in your blood over time: Biology 12: Digestive system Page 25 Biology 12: Digestive system Page 26