OHS2011 S1 HWB Booklet Bones and Joints
advertisement

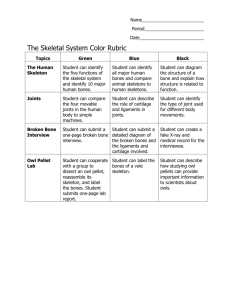
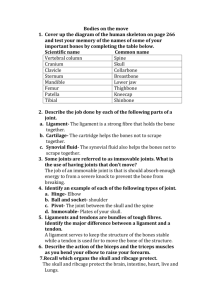
OBAN HIGH SCHOOL PHYSICAL EDUCATION DEPARTMENT S1 P.E. ACE Workbook Health and Well Being Unit 1 BONES AND JOINTS Name Class Teacher What will you learn about during this block ? Why do we have a skeleton ? The names of the major bones that make up the skeleton. The different types of bones. The main types of joints in the body ? The structure of Joints The movement that different joints create. WHY DO WE HAVE A SKELETON ? Functions of the Skeleton. There are 4 main reasons why we have a skeleton. • Protection Parts of the body are delicate and could be easily damaged. The skeleton protects them. The most delicate part is the brain which is protected by the cranium. The spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae. Your ribs and sternum protect the heart and lungs. • Blood formation Inside the larger bones of the body bone marrow produces red blood cells. Areas where this take place include the humerus, ribs and femur • Movement Some of the bones in the body are held together by freely moveable joints. This means that you can bend and move your body about. • Support • The skeleton gives the body shape otherwise it would be flabby and shapeless. It also holds your vital organs in place by providing a framework. THE MAJOR BONES OF THE SKELETON The skeleton gives the body its shape it is made up of 206 bones in total which come in four types • Long bones • Short bones • Flat bones • Irregular bones These are held together by joints THE JOINTS OF THE BODY A joint is the place where two or more bones meet, There are many types of joint in the body, including joints that we do not move and joints that only move slightly. The movement of joints are important factors affecting participation and performance. JOINT STRUCTURE Muscles Muscles make the joints stable. You can not make the joints move without a muscle. Muscles are attached to bones by tendons. Muscles always work in pairs as one muscle contracts (gets shorter) the other lengthens. Tendons Tendons attach muscles to bones. When a muscle contracts to move a joint, the muscle pulls on the tendon which is joined to the bone and the bone moves. Cartilage Cartilage is fibrous elastic tissue found in the body. In the knee and it acts as a pad/shock absorber between the bones of the upper and lower leg Cartilage is a soft cushioning substance which covers the ends of the bones and helps reduce stress by making the surface smooth and reduces the rubbing of the bone surfaces. Ligaments Hold joints in place/restrict the movement of joints. Ligaments hold the bones together and prevents over-twisting and over-stretching. Muscles/Muscle groups and Joints in the body Shoulder elbow JOINTS The type of joints that are particularly important for physical activity and sport are: Ball and socket joints The hip and the shoulder are ball and socket joints. Range of movement of a ball and socket joint Full range of movement/all the way around/360 degrees. Hinge joints The knee and elbow are hinge joints. movement in one plane: flexion and extension. JOINT MOVEMENT Range of movement of a hinge joint Back and forward in one plane of movement. Type of joint Hinge Ball and socket Where joint is found in the body Knee and elbow Hip and shoulder Range of movement Back and forward in one plane only Full range of movement/all the way around/360 degrees Movement of a Hinge Joint To straighten the arm the triceps shortens/contracts while the biceps lengthens/extends. This is because muscles work in pairs. Muscles are attached to bones by tendons. As the triceps shortens, it pulls on the tendon which pulls on the bone causing movement. To bend the arm, the biceps shortens/contracts and the triceps lengthens extends. For movement of the leg, substitute: Hamstring for Biceps Quadriceps for Triceps DIFFERENT TYPES OF MOVEMENT: FLEXION - flexion is the bending of a joint. For example, flexion occurs at the knee as the foot is drawn back to kick a ball. EXTENSION - extension is the straightening of a limb at the joint. For example, when putting the shot the elbow is straightened during release. ROTATION - rotation is the ‘swivelling of a joint. for example, moving the head from side to side. Abduction involves moving a limb(s) away from the the central axis of your body. Adduction is the opposite from abduction, moving a limb(s) back towards the central axis of your body. The central axis is a straight line travelling from the top of your head straight down to the ground. USEFUL LINKS CALCIUM http://www.kelloggs.co.uk/health/lifestages/children/calcium.aspx YOUR DIET NEEDS HEALTHY BONES http://health.marksandspencer.com/your-diet-needs/healthy-bones THE VIRTUAL BODY NARRATED http://www.medtropolis.com/VBody.asp BUILD A SKELETON http://www.medtropolis.com/VBody.asp Homework 1 Complete the table below by filling in the type of joint and the range of movement which it has. An example has been given. Name of Joint Type of Joint Movement wrist hinge one direction shoulder ball and socket elbow knee one direction hinge hip 2 all directions Name a skill which involves a jumping action and list 2 joints which you used in the jump. Skill Joint 1 Joint 2 3 What attaches the muscle to the bone. 4. Use arrows to join up the correct words and phrases Attach muscles to bones cartilage Always work in pairs ligaments Reduces the rubbing of the bone sufaces muscles Holds bones together preventing Over twisting and stretching tendons Structure and Function Name 2 activities and the main joint used in the performance of a skill or technique. An example has been given for you ACTIVITY: Swimming SKILL/TECHNIQUE: Backstroke MAIN JOINT: Shoulder joint (Ball and Socket) ACTIVITY: SKILL/TECHNIQUE: MAIN JOINT: ACTIVITY: SKILL/TECHNIQUE: MAIN JOINT: BONES WORDSEARCH S I A S D X B G E H H N W S X P C V H M N X L M N B V F L M T I B I A C V F F J N J S H D A F G V K T D P K J G V S U K A D J M D V C D R D J M P O S T U R E L W C S P I N E D M L R F M K F F X D G R M K X R W E N M R P O F T C L B R I B S S P O N G Y B O N E X L C T D L J K T X H G F F A G T Y A C A O F G B M O X X D S P D G S L M L E D U E G V K T E H R F L J D T G K N S C M D Z F P L A T E B O N E R G D H B N N V S K V E R T E B R A C P G S K N A S R V D H F B F N R G J G F N L S Z L M H L R F H H D L H S X A F R N G H G J A R S B G I M M E T A T A R S A L J F J S K E L E T O N F K L T T N B D N C X P R D M O W L K K R M G L N N D N N M J M C C E H R I K V M A R R O W C A V I T Y F P H J A J J K N K O F R J F A H M A V O C N H X N L R K E D F J M N K M L K J L O N G G P E N N H W V H I P G I R D L E D M K D I E T M L U M U B T H F H D N T F U D P E N E N L Z R K L S L K M V F M K M G D Y D J I L I U M F W S J G J O S S I F I C A T I O N L X H E S X K B D H G E G R L M U W W S C X D X N N V X B N P D N F I B U L A F H R R T P K L D M D A S F Z M H G C V H S C J J S X Z E N G J U C M E T A C A R P A L S K J B C O C C Y X K V D X V J V N S V F P C R M R F U G F N L M N R L T L X P M F F C J M B M M C R I F H K R S L R T J P K J A P R A D A L G G V S K A K N E G P V T H O R A C I C C D K N D E V C S N H T D K L C D J R H H G N L W P J A L A D G S I F G I V L K N J F X S K G K V C Y B U J L L U R K R A D I U S F C F D L J M S T D B F L I D S H L K F L A T J P S N R M M H L G K P M K J P R O T E C T I O N H T U F I H A W H D N F J E B F H K L S U C N D X A N S G A D H J E L V L D J H J E K N M J J L P J J D E C S L H J H M F M D G A G S A C R U M L M K V K S H M K F L V D B J M J K G S S H G T B V H N M U P K L N L W N K N V M F C G M P E R I O S T E U M H E X E R C I S E Below is a list of words related to BONES. Try to find them in the wordsearch. The words can only be found in rows or columns; no words are hidden along diagonal lines. BACKBONE CARPALS CLAVICLE DIAPHYSIS EXERCISE FLAT ILIUM LUMBAR METACARPALS PATELLA PLATE BONE RADIUS SACRUM SKELETON STERNUM TIBIA VERTEBRA BONE MARROW CARTILAGE COCCYX DIET FEMUR HIPGIRDLE IRREGULAR MANDIBLE METATARSAL PERIOSTEUM POSTURE RED MARROW SCAPULA SPINE TARSALS TWO HUNDRED AND SIX VERTEBRAE YELLOW MARROW CERVICAL CRANIUM EPIPHYSIS FIBULA HUMERUS LONG MARROW CAVITY OSSIFICATION PHALANGES PROTECTION RIBS SHORT SPONGY BONE THORACIC ULNA VERTEBRAL COLUMN BONE CLASSIFICATION On the skeleton below, classify the bones of the body using a color-coding system. Complete the color key by assigning a color to represent the long bones, another color to represent the short bones, one for the flat bones and one for the irregular bones and one for the sesamoid bones. Use the key to color the skeleton. Bone Classification Colour Key Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones