Types of Cellular Respiration
advertisement

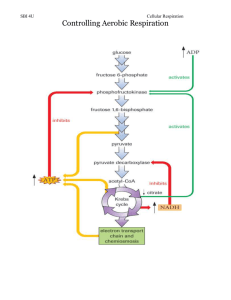
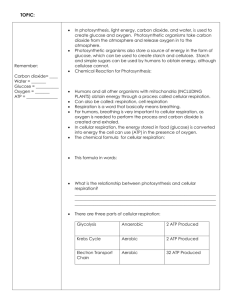
Name:_____________________________ Period:______ Date:_________ Points:_____pts=_________% Types of Cellular Respiration An Introduction Reading Cellular Respiration- Cells get energy for active transport, building materials, and other processes through cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process by which glucose is broken down to make energy available for cellular activity. Two types of cellular respiration- There are two main types of cellular respiration, aerobic and anaerobic (also known as fermentation). During aerobic cellular respiration, oxygen combines with glucose. In a series of steps which begin in the cytoplasm and end in the mitochondria, glucose is broken down. Water and carbon dioxide are released as waste products. Energy is released as the bonds of glucose are broken. This energy is used to form 36 molecules of ATP for the cell. C6H12O6 + 6CO2 6CO2+6H20 +36ATP Sometimes oxygen is not available to a cell or an organism does not contain the enzymes necessary for aerobic cellular respiration. In such cases, since the cell still requires energy, the organism must carry out anaerobic cellular respiration (fermentation). Fermentation is the process in which glucose is broken down without oxygen. There are two types of fermentation, which both occur in the cytoplasm. In one type of fermentation, muscle cells, lacking in oxygen due to strenuous exercise, break glucose down into a compound called lactic acid. Only 2 molecules of ATP are formed from the energy released from glucose in this reaction, called lactic acid fermentation. Lactic acid causes muscles to burn and does not meet the cell’s demand for energy. The human body works hard to obtain more oxygen (by heavier breathing) so cells can quickly return to aerobic respiration. Some bacteria also carry out lactic acid fermentation. The food industry makes use of lactic acid fermentation in bacteria for the production of yogurt, sour cream, and buttermilk. These foods get their sour taste from the lactic acid formed by bacteria using the sugars in milk for anaerobic respiration. C6H12O6 Lactic Acid + 2 ATP If you have ever observed bread rise, you have observed a second type of anaerobic respiration called alcoholic fermentation. Yeast cells in dough break down sugars forming carbon dioxide bubbles causing the dough to expand. A second end product of alcoholic fermentation is ethyl alcohol. The beverage industry takes advantage of the process of alcoholic fermentation to make beer and wine. Yeast cells use sugars in grapes or grains and form carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol used for making wine or beer, as well as 2 ATP molecules (for their own use). C6H12O6 Ethyl Alcohol + CO2 + 2ATP Types of Cellular Respiration- Review Questions Aerobic Cellular Respiration Does it require oxygen? Reactants Products Where in the cell does it occur? Amount of ATP made in the cell Lactic Acid Fermentation Alcoholic Fermentation