Related Pathways starvation
advertisement

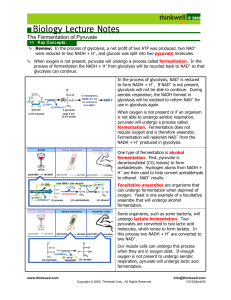
Related Pathways Organisms are able to metabolize nutrients other than carbohydrates during times of starvation Once broken down, these monomers are able to feed into various parts of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle (Fig.1, p.117) Protein Catabolism Through a process called deamination, proteins remove amino groups from the amino acids converting the group to ammonia, NH3 (urea is expelled from the body in urine) Lipid Catabolism Glycerol can be converted to glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis Fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation where 2-C acetyl groups are removed Fats can produce 20% more ATP than carbohydrates Anaerobic Pathways (does not require oxygen) Mainly used by bacteria and protistans that live in oxygen-free settings, although lactate fermentation can occur in multicellular organisms 1. Ethanol Fermentation (through glycolysis) 2 ADP 2 ATP (Fig.2, p.119) Glucose (6-C) 2 NAD+ 2 NADH (x2) Pyruvate (3-C) CO2 (x2) acetaldehyde (2-C) 2 NADH 2 NAD+ (x2) ethanol (2-C) Ex/when yeast consumes sugar and releases CO2, it causes bread to rise) 2. Lactate Fermentation (through glycolysis) 2 ADP 2 ATP Glucose (6-C) 2 NAD+ 2 NADH (x2) Pyruvate (3-C) 2 NADH 2 NAD+ (x2) Lactate (3-C) Ex 1/ Lactic acid builds up in muscle cells Ex 2/ Producing yogurt from milk (Fig.4, p.120)