Thermodynamics
advertisement

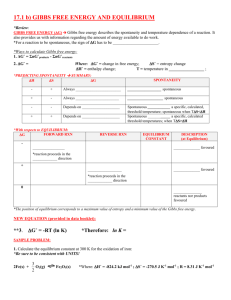
Thermodynamics Standard thermodynamic conditions 25 C°, and 1 barr = 100kPa ≈ 1 atm Heat Transferred Specific Heat (C) - Energy required to raise a gram of material by 1° C Constant based on material and state of matter Units in J/g° C C = 4.18 J/g° C (For Water) Heat Transferred (q) q= mC(ΔT) where C is specific heat, ΔT is the change in temperature (in ° C), and m is mass of matter in grams Units for q in J +q means heat transferred to system, -q means heat is transferred from system Bond Energies q = Σ Reactants Bond Energy – Σ Products Bond Energy (note: reactants – products) Endothermic reactions need heat/energy added to progress Breaking bonds requires heat/energy to progress Exothermic reactions give off heat/energy during the reaction Forming bonds gives off heat/energy Potential energy in an elemental state = 0 Enthalpy (ΔH) – Heat transferred into a system per mole or per gram ΔH = q/m= change in potential energy from products to reactants ΔHrxn = ΣHf products - ΣHf reactants -ΔH = exothermic +ΔH = endothermic Units (J/g or J/mol) Hess’s Law If a reaction = the sum of a series of reactions, then the overall ΔH = the sum of ΔH from each reaction Reverse reactions = reverse signs If you change the coefficients of a reaction by a certain factor, then change ΔH by the same factor Entropy ΔS = measure of randomness of molecules ΔS = the change in S from products to reactants Gases are the most random and have the highest entropy, solids the lowest Product favored reactions have higher entropy Units of J/K*mol Calorimetry Mmetal cΔT = mwater cΔT Mmetalc (Tf-Ti) = mwater c(Tf-Ti) q reaction = - (q water + q bomb) Changes of State q=mHf or q=mHv (Hf = Heat of fusion, Hv = Heat of vaporization) Heat of fusion = heat required to melt a substance into liquid Heat of vaporization = heat required to vaporize substance into gas Spontaneity Gibbs Free Energy ΔG = ΔH - TΔS (T is in K) When ΔG is negative reaction is spontaneous and vice versa Threshold Energy = when ΔG = 0, equation is at equilibrium Spontaneous reactions favor products Considering T= ΔH/ΔS when ΔS < 0 ΔS > 0 ΔH < 0 ΔH > 0 Spontaneous at Low Temps Always Spontaneous Never Spontaneous Spontaneous at Higher Temps ∆G = ∆G˚ + RT lnQ ∆G˚ = -RT lnK (at equilibrium) R=8.314 J/(mol*K) K = Thermodynamic Equilibrium Constant T = Temperature (K) Q= reaction quotient = K (at equilibrium) When ∆G˚ < 0 and K > 1 Reaction is product favored (spontaneous) When ∆G˚ = 0 and K = 1 Reaction is at equilibrium When ∆G˚ > 0 and K < 1 Reaction is reactant favored (non-spontaneous)