GLOSSARY TYPE OF INTERNET SERVICE CONNECTION Dial up
advertisement
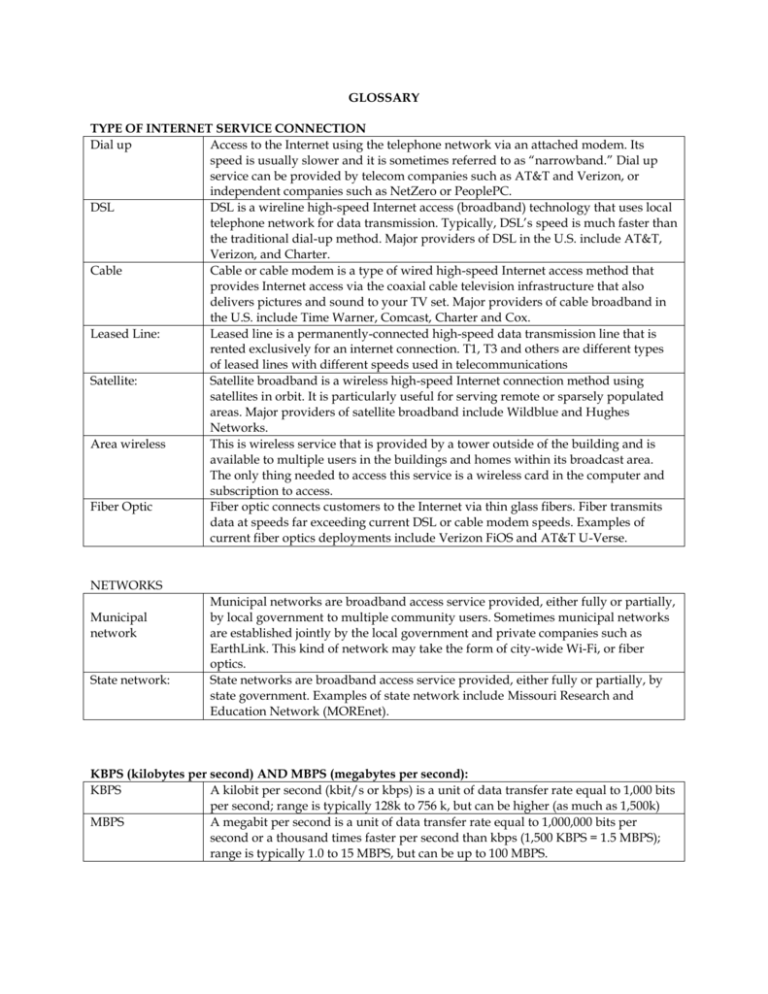
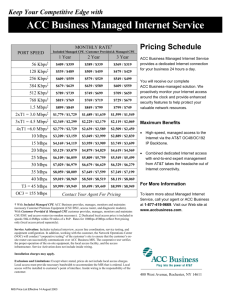
GLOSSARY TYPE OF INTERNET SERVICE CONNECTION Dial up Access to the Internet using the telephone network via an attached modem. Its speed is usually slower and it is sometimes referred to as “narrowband.” Dial up service can be provided by telecom companies such as AT&T and Verizon, or independent companies such as NetZero or PeoplePC. DSL DSL is a wireline high-speed Internet access (broadband) technology that uses local telephone network for data transmission. Typically, DSL’s speed is much faster than the traditional dial-up method. Major providers of DSL in the U.S. include AT&T, Verizon, and Charter. Cable Cable or cable modem is a type of wired high-speed Internet access method that provides Internet access via the coaxial cable television infrastructure that also delivers pictures and sound to your TV set. Major providers of cable broadband in the U.S. include Time Warner, Comcast, Charter and Cox. Leased Line: Leased line is a permanently-connected high-speed data transmission line that is rented exclusively for an internet connection. T1, T3 and others are different types of leased lines with different speeds used in telecommunications Satellite: Satellite broadband is a wireless high-speed Internet connection method using satellites in orbit. It is particularly useful for serving remote or sparsely populated areas. Major providers of satellite broadband include Wildblue and Hughes Networks. Area wireless This is wireless service that is provided by a tower outside of the building and is available to multiple users in the buildings and homes within its broadcast area. The only thing needed to access this service is a wireless card in the computer and subscription to access. Fiber Optic Fiber optic connects customers to the Internet via thin glass fibers. Fiber transmits data at speeds far exceeding current DSL or cable modem speeds. Examples of current fiber optics deployments include Verizon FiOS and AT&T U-Verse. NETWORKS Municipal network State network: Municipal networks are broadband access service provided, either fully or partially, by local government to multiple community users. Sometimes municipal networks are established jointly by the local government and private companies such as EarthLink. This kind of network may take the form of city-wide Wi-Fi, or fiber optics. State networks are broadband access service provided, either fully or partially, by state government. Examples of state network include Missouri Research and Education Network (MOREnet). KBPS (kilobytes per second) AND MBPS (megabytes per second): KBPS A kilobit per second (kbit/s or kbps) is a unit of data transfer rate equal to 1,000 bits per second; range is typically 128k to 756 k, but can be higher (as much as 1,500k) MBPS A megabit per second is a unit of data transfer rate equal to 1,000,000 bits per second or a thousand times faster per second than kbps (1,500 KBPS = 1.5 MBPS); range is typically 1.0 to 15 MBPS, but can be up to 100 MBPS. INTERNET SERVICE CONNECTION – SPEED RANGES Please note that for Q.8, the speed of the internet connection refers to the download speed or committed speed on the bill (not the boost rate or upload speeds). It is the internet connection speed the internet service provider (ISP) states the library will get, not the speed that it will necessarily get every time. Dial up DSL Cable Leased Line (partial T1, T1, T3) Satellite Area wireless Fiber Optic Up to 128 KBPS Typical is 256 KBPS to 1.5 MBPS, but may be as high as 24 MBPS Typical speed is 5 MBPS, but can range from 1.5 MBPS to 50 MBPS Speed by line type is: T1 = 1.544 MBPS T2 = 6 MBPS T3 = 45 MBPS T4 = 275 MBPS Typical speed is 56 KBPS to 1.5 MBPS, but can be as fast as 500 MBPS Typical speed is 12 MBPS to 40 MBPS depending on the equipment used. Typical speed is 10MBPS to 50MBPS