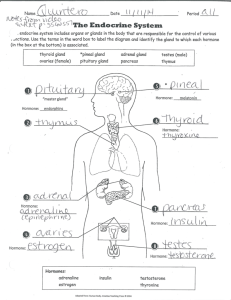
Understand how hormones and glands control the homeostasis of
advertisement

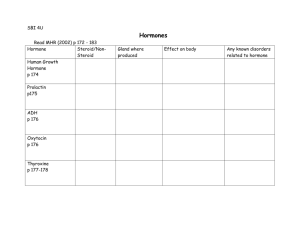
Understand how hormones and glands control the homeostasis of the body! The endocrine system is composed of a group of glands that secrete chemical substances, called hormones that control many body activities. This assignment will help you review the main facts about the system. Read the information on the endocrine system, located on pages 172 through 177. As you read about the endocrine system, complete the following worksheet Steroid hormone 1. What are hormones? What are the two main kinds of hormones and how are they different How are hormones transported through the body? 2. List five (5) functions of hormones. 3. Name the endocrine glands located in each of the following areas of the body Description Above each kidney On each side of the uterus in the female Master gland located just under the brain (sella turnica) In front of the upper part of the trachaea Behind and attached to the thyroid Glandular organ behind the stomach Endocrine Gland Endocrine System Worksheet 1. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine gland. 2. Make a drawing of the human body. Map out/label all the endocrine glands in the body. 3. Which type of hormone functions by entering the cell? Which type of hormone functions by binding to receptors on the cell membrane? 4. Make a data table with the following info.... Gland Hormone(s) released by gland Target cell/organ of hormone Function of hormone on target cell/organ Pituitary Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pancreas Ovaries Testes Gland Hormone(s) released by gland Target cell/organ of hormone Function of hormone on target cell/organ Pituitary Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pancreas Ovaries Testes Endocrine System Worksheet 1. Label page 116 of study guide 2. What is the difference between an endocrine gland and an exocrine gland? 3. What is the difference between a prostaglandin and a hormone? 4. What is the difference between steroid and protein hormone action? 5. Describe how both negative and positive feedback mechanisms control hormone production. 6. Complete endocrine gland/hormone chart attached. GLANDS AND HORMONES OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Thyroid Gland 1. T3 (______________________________) and T4 (_________________________________) o target = ________________________________ o stimulates ______________________________ o increases body _________________ and ______________________ consumption o works in association with ___________ (ie. GH) 2. Calcitonin o target = __________________________ o decreases ________________________ in blood (excess is absorbed by bones) o works antagonistically to _______________________________ Parathyroid Glands 1. Parathormone (____________) released from 4 small glands on back of thyroid gland o target = _________________ and __________________ o increases ______________________ in blood by stimulating release from ______________ Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) 1. Insulin o o o o o o produced by ___________ cells target = ___________________ and ___________________ ____________________ blood sugar levels (reduces hyper_________________) increases __________________ storage in liver and muscle promotes synthesis of proteins and fats antagonistic to _________________________ 2. Glucagon o produced by ___________ cells o target = ___________________ and ___________________ o ____________________ blood sugar levels (reduces hypo_________________) o stimulates ___________________ breakdown (to release glucose) o antagonistic to _________________________ 3. Somatostatin o produced by ___________ cells o target = __________________________________ (moderates them) o stimulates _______________________ metabolism (helps control digestion) Pineal Gland 1. Melatonin o target = _________________ o controls ____________________ cycles and involved in biorhythms o this gland is ____________sensitive and as a result, melatonin is secreted in the _________________ of light promoting ___________________ Thymus Gland 1. Thymosin o target = _________________ o stimulates the _________________ system Adrenal Glands 2 major regions of the adrenal release hormones. The adrenal cortex (outer portion) and adrenal medulla (inner portion) 1. Glucocorticoids (eg. Cortisol) o produced by adrenal ________________ o target = ________________ cells o increases blood ________________ levels o decreases _______________________ response 2. Mineralocorticoids (eg. Aldosterone) o produced by adrenal ________________ o target = ________________ o promotes _________ reabsorption (so not excreted in urine) o if Na+ or B.P. decreases, aldosterone is released to make blood more __________tonic 3. Adrenalin o also called ____________________________ o produced by adrenal _____________________ o release is stimulated by _____________________ nervous system (autonomic division) o target = ___________________, ___________________ and ______________________ o ____________________ blood sugar levels o increases _________________ rate 4. Noradrenalin o also called ____________________________ o produced by adrenal ____________________________ o release is stimulated by _____________________ nervous system (autonomic division) o target = muscles of __________________________ o controls ______________________ and ____________________ of blood vessels Ovaries 1. Estrogen o produced by developing ________________ o causes development of secondary ____________ characteristics (ie. pubic hair, breast enlargement, etc.) and development of _____________ in follicle o also causes thickening of ________________ lining 2. Progesterone o produced by _______________ ____________________ (ruptured follicle after ovulation) o causes development of __________________ lining and breast enlargement Testes 1. Androgens (ie. testosterone) o produced by ______________ cells outside of __________________________ tubules o stimulates ___________________________ (sperm development) and male secondary __________ characteristics (pubic and facial hair, muscle mass) Heart 1. Atrial Natriuretic Hormone (ANH) o produced by ____________ of heart o target = ____________________ o increases ___________________ excretion in urine (therefore antagonistic to ____________________) o lowers __________ Liver 1. Somatomedin o target = _____________ cells o together with STH, stimulates overall growth and development (therefore _______________ to STH, ie. same function) Kidneys 1. Renin o acts on proteins in blood to produce __________________________ (which helps control ____________) 2. Erythropoietin o target = __________________________ o increases __________________________ (RBC) production (more O2 can be carried therefore more cell resp. and energy to body) o released at high ____________________ or greater need for RBC's Gastrointestinal Tract 1. Gastrin and Secretin o target = stomach and pancreas o stimulates release of digestive enzymes and activity of digestive organs Fill in the gaps in the sentences below using the words in the list. target; blood system; ducts; hormones a. Endocrine glands release their secretions directly into the blood. In other words they have no ducts. b. Endocrine glands secrete chemicals called hormones. c. Hormones are transported from the endocrine glands to all parts of the body by the blood system. d. Although hormones are carried throughout the body they only affect specific target organs and tissues 2. The position of endocrine organs have been indicated in red on the diagram of a composite male and female dog shown below. Add the labels in the list to the diagram. Ovary; Pancreas; Thyroid gland; Pituitary gland; Testis; Adrenal gland; Pineal gland; Parathyroid gland 3. On the diagram of the brain below indicate the position of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland. 4. In the table below list 3 hormones produced by the pituitary gland and state the function of each. Hormone Function 1.Growth hormone. Stimulates growth of the body by increase in length of the long bones 2.Oxytocin Stimulates milk "let down" 3.Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) Stimulates the development of the ovarian follicle. Plus: Luteinising hormone(LH) Stimulates development of the corpus luteum of the ovary Plus: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Stimulates the production of concentrated urine Plus some others 5. Fill in the following table with the endocrine organ the hormones are produced by. Hormone Produced by: Insulin Pancreas Progesterone Corpus luteum Oestrogen Ovarian follicle Growth hormone (Anterior) pituitary gland Adrenaline Adrenal medulla Antidiuretic hormone (Posterior) pituitary gland Testosterone Testis Aldosterone Adrenal cortex Melatonin Pineal gland Oxytocin (Posterior) pituitary gland Thyroxine Thyroid gland 6. Match the hormones in the list below with their functions. Oxytocin; Insulin; Oestrogen; Growth hormone; Antidiuretic hormone; Testosterone; Adrenaline; Cortisone; Melatonin; Progesterone; Thyroxine; Luteinising hormone; Follicle stimulating hormone Hormone Function Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) 1. Stimulates development of the ovarian follicle. Oxytocin 2. Stimulates milk “let down”. Insulin 3. Controls blood glucose levels. Thyroxine 4. Influences the rate of growth and development of young animals. Growth hormone 5. Stimulates the growth of long bones. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) 6. Stimulates absorption of water from the kidney tubule. Melatonin 7. Influences the development of sexual maturity. Luteinising hormone (LH) 8. Stimulates the development of the corpus luteum. Oestrogen 9. Stimulates the development of female sexual characteristics. Testosterone 10. Stimulates the development of the male sexual characteristics. Cortisone 11. Affect glucose, protein and fat metabolism. Progesterone 12. Prepares the lining of the uterus for pregnancy. Adrenaline 13. Prepares the body for emergency situations. 7. Circle the odd one out. 1. melatonin; oxytocin; growth hormone; antidiuretic hormone; follicle stimulating hormone. Melatonin is the only hormone in the list not produced by the pituitary gland. 2. progesterone; oestrogen; luteinising hormone; cortisone; follicle stimulating. Cortisone is the only hormone in the list not involved in any major way with reproduction. 3. adrenaline; cortisone; aldosterone, oestrogen, insulin. Insulin is the only hormone in the list not produced by the adrenal gland.