Exchange Reactions: What are the Products
advertisement

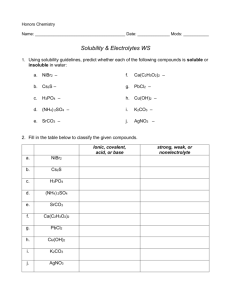
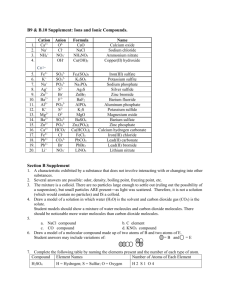
Exchange Reactions: What are the Products? / Will it Occur? An exchange reaction (also called a double displacement reaction or a metathesis reaction) is a reaction in aqueous solution between two compounds which are acids, bases, or salts. The cation from the first compound joins with the anion from the second compound, to form one of the products. The second product is from the anion of the first compound and the cation of the second. If the product turns out to be carbonic acid, then really carbon dioxide and water will form and should be written on the product side of the equation. Similarly, if a product is sulfurous acid, then really sulfur dioxide and water will form and should be written on the product side of the equation. An exchange reaction will occur if one of the products is an insoluble solid (precipitate), a gas, a nonelectrolyte, or a weak electrolyte. These are the driving forces. Refer to other review pages for help determining which physical state the compounds are and whether they are strong or weak or nonelectrolytes. EXAMPLES: Write a balanced molecular equation for each of the following aqueous reactions. Indicate whether or not the reaction will occur, and briefly explain why. (1) Ammonium Phosphate + Calcium Acetate Cation Anion Compound State Reactant 1 Reactant 2 Product 1 Product 2 NH4+ Ca2+ NH4+ Ca2+ PO43- C2H3O2- C2H3O2- PO43- (NH4)3PO4 Ca(C2H3O2)2 NH4C2H3O2 Ca3(PO4)2 (aq) (aq) (aq) (s) ---> Answer: 2 (NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3 Ca(C2H3O2)2(aq) ---> 6 NH4C2H3O2(aq) + Ca3(PO4)2(s) An insoluble solid is formed, so this reaction DOES occur. (2) Potassium carbonate + perchloric acid Cation Anion Compound State Reactant 1 Reactant 2 Product 1 Product 2 K+ H+ K+ H+ CO32- ClO4- ClO4- CO32- K2CO3 HClO4 KClO4 H2CO3 (aq) (aq) (aq) (aq) ---> Answer: K2CO3(aq) + 2 HClO4(aq) ---> 2 KClO4(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) A gas and a nonelectrolyte (water) are formed, so this reaction DOES occur. PRACTICE EXERCISES: Write a balanced molecular equation for each of the following aqueous reactions. Indicate whether or not the reaction will occur, and briefly explain why. QUESTIONS: 1. barium chloride + copper(II) sulfate 2. gold(III) nitrate + strontium hydroxide 3. aluminum iodide + lead(II) acetate 4. sodium sulfite + nitric acid 5. acetic acid + calcium hydroxide 6. hydrobromic acid + barium sulfide 7. lithium cyanide + hydrochloric acid 8. iron(III) acetate + calcium sulfate 9. mercury(I) nitrate + sodium bromide 10. rubidium phosphate + chromium(III) chloride 1:00-2:00 ANSWERS (If you do not understand any of these, the see me) : 1. BaCl2(aq) + CuSO4(aq) --> BaSO4(s) + CuCl2(aq) YES this reaction occurs, because an insoluble solid is formed. 2. 2 Au(NO3)3(aq) + 3 Sr(OH)2(aq) --> 2 Au(OH)3(s) + 3 Sr(NO3)2(aq) YES this reaction occurs, because an insoluble solid is formed. 3. 2 AlI3(aq) + 3 Pb(C2H3O2)2(aq) --> 2 Al(C2H3O2)3(aq) + 3 PbI2(s) YES this reaction occurs, because an insoluble solid is formed. 4. Na2SO3(aq) + 2 HNO3(aq) --> 2 NaNO3(aq) + H2O(l) + SO2(g) YES this reaction occurs, because a gas and a nonelectrolyte are formed. 5. 2 HC2H3O2(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) --> 2 H2O(l) + Ca(C2H3O2)2(aq) YES this reaction occurs, because a nonelectrolyte is formed. 6. 2 HBr(aq) + BaS(aq) --> H2S(g) + BaBr2(aq) YES this reaction occurs, because a gas is formed. 7. LiCN(aq) + HCl(aq) --> LiCl(aq) + HCN(aq) YES this reaction occurs, because a weak electrolyte (HCN) is formed. 8. 2 Fe(C2H3O2)3(aq) + 3 CaSO4(aq) --> Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + 3 Ca(C2H3O2)2(aq) NO this reaction does not occur, because none of the driving forces is present - all of the products are soluble strong electrolytes. 9. Hg2(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NaBr(aq) --> Hg2Br2(s) + 2 NaNO3(aq) YES this reaction occurs, because an insoluble solid is formed. 10. Rb3PO4(aq) + CrCl3(aq) --> 3 RbCl(aq) + CrPO4(s) YES this reaction occurs, because an insoluble solid is formed. \