HumanBiologyCh.1Stud..
advertisement

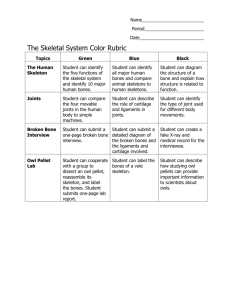
Human Biology Ch. 1 Study Guide Answer Key 1. List the 5 levels of organization in the body 1. Cells 2. Tissue- is made up of a group of cells 3. Organ- is made up of a group of tissues 4. Organ system is made up of a group of organs 5. Organism 2. What are the three types of muscles in a human muscular system? Identify where each type is found and state whether it is voluntary or involuntary. a. b. c. Skeletal – found attached to the skeleton - voluntary Smooth – found lining organs - involuntary Cardiac – found in the heart - involuntary 3. The outer surface of your body is covered with epithelial tissue. 4. The heart, lungs, and the brain are examples of organs in the human body. 5. Compare and contrast immovable and movable joints. They are both joints. Immovable joints provide no movement while movable joints allow movement in the body. 6. What is the main purpose of the human skeletal system? To support and protect the body. 7. Muscles work with pulling action. 8. What are the 3 main functions of the muscular system? How do the muscles perform each function? Movement- muscular system works with the skeletal system to allow movement b. Maintains body temperature – when muscles contract they release heat c. Maintains posture – most of the muscles in your body are always a little bit contracted to maintain posture a. 9. Nerve tissue can send signals to your brain. 10. Muscles are attached to your skeleton by tendons which are primarily made up of connective tissue. 11. Describe how the body tries to maintain homeostasis. The body maintains homeostasis by maintaining body temperature for example the body shivers on a cold day. 12. Why do muscles act in pairs? Muscles work in pairs because they can only pull in one direction. 13. What part of the skeletal system protects the spinal cord and supports the cranium? The vertebrae 14. Give at least two examples for each type of movable joint. a. Ball-and-socket shoulder b. Hinge elbow c. Pivot wrist and hip bone and knee and ankle d. Gliding back bone and any other joint 15. Which joint allows the most movement? Ball-and-socket joint 16. The skeletal system undergoes many changes during infancy and adolescence. Describe these changes. (At least 3 sentences) These should be in complete sentences but here are examples! Infancy - there are spaces in the skull to allow the brain to grow as a child develops these spaces lock together Childhood - children grow at their growth plates Adolescence – growth plates harden and growing stops occurring 17. What is a growth plate? The place where bone growth occurs 18. Where are growth plates located? At and femur. the ends of long bones such as the humerus 19. During which period in a human’s life does the humerus stop growing? adolescence 20. What stimulates muscle growth? Increased physical activity 21. A feeling of soreness several days after exercise indicates torn or damaged muscle fibers. 22. Make a Venn diagram comparing and contrasting the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. Be sure to include the parts of the skeletal system that make up each. (Hint – pages 16-17) Axial skeleton – provides support and protection, forms the axis Includes – skull, ribs, vertebrae Both – part of the skeletal system. Made up of bones. Provides body’s shape. Appendicular skeleton – allows movement Includes - shoulder, humerus, ulna, radius, wrist, hand, hip bone, femur, tibia, fibula (most important to know arms, legs, shoulder, and hipbone)