final review sheet
advertisement

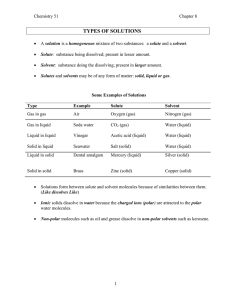
Chemistry Final Unit 1 Density= mass/volume Mixture o Homogeneous is uniform Solution Element o Heterogeneous isn’t uniform Suspensionparticles will settle out Colloidsmallest particle tyndal effect Ions o Differend groups on tables having different charges and knowing if they are (+) or (-) o Polyatomic ions (given on test) Acuracy how close you are to result Precision all the same but not necessarily close to actual result Significant figures o Add or subtract=least amount of decimal places o When multiplying or dividing you round to nearest significant figure Solubility o Solute what gets dissolved o Solvent what does dissolving o Saturated solution o Unsaturated o Supersaturated o Gases solubility decreases… Ways of measuring concentration o Volume % Volume solute/volume solution o Mass % Mass Solute/mass solution o PPM mass solute/mass solution x 10 (6) o PPB mass solute/mass solution x 10 (9) Acidity o Acids: less then 7 o Bases: over 7 Unit 2 Metals good conductors, malleable, ductile Non-metals (upper right hand corner) greater variation, mostly gases Metalloid properties of both: B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, At Periodic table o Mass#- protons + neutrons o Atomic #- protons o Electrons- negative, no real mass o Group 1: alkali o Group 2: alkaline earth o Group 7: halogens o Group 8: Noble gases Unit conversions o K, h, d, b, d, c, m Bohr model o Further you are away, more energy electron has o Energy levels: 1 (s) 2 (s,p) 3 (s, p,d)… o Electron levels: s 1 orbital p 3 d 5 f 7 o Each orbital holds 2 electrons Polyexclusion one up and one down in each orbital Huns up arrows go first Periodic trends o Atomic radius Decreases as goes across Increases as goes down o Electronegativity Increses as goes across Decreases as goes up o Ionic Decreases as goes across Increses as goes down *As you get to non-metals they become big again o Inonization energy Increses as goes across Decreases as goes up o Anions are bigger then ions and cations are smaller then their ions Redox o Oil Rig Balancing reactions Moles o 6.02 x 10 (23) o Molar mass and conversions Stoicheometry Percent composition o Mass element/mass of compound o Imperical (lowest numbers) and Molecular formula (Actual) Impericlal 25.9% N 74.1% O Assume 100 grams to divide each number by their molar mass Then write equation as N(x) O(y) with number of moles Then divide by smallest number Then if not whole numbers multiple until you get whole numbers Molecular Then, with imperical, whatever mass you are given to find molecular you multiply until you get molecular o Covalent- molecular Ionic- ionic Lewis structures o Add up valence electrons and make bonds and then fill out electrons and make double bonds if necessary Alkanes- saturated Carbons with hydrogens o C(n) H(2n+2) o All single bonds Alkenes- unsaturated o Double bonds o C(n) H(2n) Alkynes- unsaturated o C(n) H(2n-2) Benzene- C6H6 o Pheynl CH3 CH3-CH2- CH2-CH-CH2-CH-CH3 2-methryl-4-propylheptane CH2 CH2 CH3 Units o Meth, eth, prop, but, hex, hept, oct, non, dec Organic Chemistry o Halogens- R- halogen o Alchohol- R- OH o Carboxylic acid- R-C-OH o O (doubled to C) o Ester- R-C-O-R O (double to C) o Ether- R-O-R o Amine- R-NH2 o Amide- R-C-N-R OH o Aldehyde- N-C=O R o Ketone- R-C=O R Unit 3 Thermochemistry o Exothermic- releases hear positive enthalpy o Endothermic- absorbs heat positive enthalpy Q=mc (delta) T o When change in temperature and want to know how much energy released o Q=heat o M=mass o C=change of temperature o T=temperature Heats of combustion o CH4+ 2O2CO2+2H2O Delta H -X kj (exothermic) o How much heat releases if 32 grams of CH4? 32g/16g per mol=2 mol 50Kj=x o QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. 10 g solid at 10 degrees to 20 degrees o H of fusion=6.01 kj/mol o 1) -100 degrees: q=10(2.1)(10) Unit: J o 6.01 kj per mol x 10g/18 g per mol Unit: Kj o 0 20 degrees: q=10(4.184)(20) Unit: J Hess’ law o If flip reaction change from negative to positive or vice versa o If multiply then multiply enthalpy Unit 4 Ideal gases: gases act ideally at low temperature and high temp ALL OTHER LAWS! o Boyles o Charles o Avagago o Gay-Lussachs o Combined gas law Pv=nRTideal gas law At STP 1 mol of a gas occupies 22.4 L o STP=273 kelvin & 1 atm Acid & bases o Bronstead-Lowery theory o Acid+basesalt & H2O o OH and H concentrations Molarity=mol of solute/liter of solution Unit 5 Rates and equilibrium o Changing temp, adding catalysts, changing Lechatliers o When we add stress to a reaction the equation gets rid of it Could be pressure, temp etc. Equilibrium constants and problems o ICE PROBLEMS Electrochemistry o Voltaic cells: chemical electric energy o Electrolytic energy: electric energychemical energy Unit 6 Just did it!!!! Randoms: Balancing redox reactions Avagago #= 6.02 x 10(23) Limiting reaction problems o Theoretical yield o Actual yield Precipitation reactions o Solubility rulesfind precipitate (which is solid) o WRITE THE (S)!!! Complete ionic, net ionic