Ch 21 Politics: Local, State, and National Why was the time period
advertisement

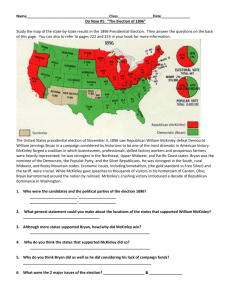
Ch 21 Politics: Local, State, and National 1. Why was the time period so turbulent? 2. Did farmers have a chance to be a serous player? 3. The populists were right. Do you agree? 4. 1870 – 1910 Time to dodge the BIG issues City machines – loose knit neighborhood organizations 1. Ward bosses performed services for their “constituents” – new immigrants, future voters Found jobs Distributed food “fixed” minor legal problems Provided for the homeless Birthday parties and Christmas for children Summer activities, games, picnics, boat rides Helped assimilate new immigrants Bosses WERE NOT reformers Primarily interested in maintaining and expanding their influence and power Directed their “constituents” for whom to vote in return Bosses receive payment or kickbacks on building projects Boss Tweed – thrive because needy were largely ignored and left behind o Bosses filled the need of the lower SES Republicans v. Democrats Presidential politics o South – Democratic/New England - Republican o Primarily battle ground states: NY, N.J., Oh, In., and Ill. o Elections and campaigns were big shows – bands, food, banners, speeches o Corruption was rampant – dead people voted Hayes (D) 1877 – 1881 o Very moderate o Remain on gold standard, veto paper currency bills o Opposed contributions form federal officeholders o Took little action on increasing erosion of southern blacks rights Garfield (R) 1881 – 1885 o Rs split between stalwarts – want to continue spoils system and Half breeds – less vocal but also wanted to continue system o Assassinated July 1881 – angry political office seeker Chester Arthur (R) o Pendelton Act – 1883 Civil Service system Government jobs based on ability not who you know No forced political contributions o Regulation of RR Grover Cleveland (D) 1885 – 1889 o Mugwumps – Rs who campaigned for Cleveland Benjamin Harrison (R) 1889 – 1893 o Favored protective tariffs o Sherman Anti-Trust Act o Silver Purchase Act – government coins silver money o Force bill to protect black voting rights by Federal control of elections Cleveland Part II 1893 – 1897 Agriculture demise By 1890s farm prices in major decline o Wheat from $1.50 in 1870 to .60 in 1890s o Cotton from .30 in 1866 to .06 in 1890s Economic depression of 1893 o Over speculation of RR, land, and tight credit supplies leads to major economic collapse In response – Populism o Farmers organize Co-ops Buy seed in bulk Set prices for crops Attempted to negotiate transportation costs o By 1892 farmers begin to win elections in many agricultural states o R and D continue to ignore o New party – Populists Farmers and industrial workers align Election of 1892 Platform: o graduated income tax o national ownership of RR, telegraph, telephones o farm loan subsidies to farmers o unlimited coinage of silver o Initiative and referendums o Direct election of senators o 8 hour workday Not great success Failure to unite black and white farmers; agricultural and industrial workers o Silver and gold o Fed buys large amounts of silver to inflate its value 1878 Bland Allison Act – Government buys $2 – $4 million/monthly 1890 Sherman Silver Purchase Act Government buys 4.5 million ounces/monthly amount of silver/dollar continues to rise Depression of 1893 - over speculation of land, RR, and fear of uncontrolled money supply Coxey’s Army – unemployed workers march on DC demanding massive government spending onpublic works projects Coxey arrested in DC, marchers dispersed Workers have little confidence in government heling average citizen Pullman Strike put down with Federal troops EC Knight – Sherman Anti Trust not allowed to break sugar trust SC allows Eugene Debs to remain in jail for organizing RR strikes. 1894 Gold supply falls as citizens turn in greenbacks (paper) currency for Hard currency – gold o 1895 JP Morgan “guarantees” US government money supply Fear that corporations and business now run government o Populist continue to gain strength demanding silver as the currency Rs go for gold standard nominate McKinley Ds for silver – William Jennings Bryan Gold East v. Silver West Gold industrialists v. Agriculture West o Cross of Gold speech Ds nominate Bryan o Populist dilemma Support Bryan and lose their individual power Run a 3rd party populist candidate – split D vote McKinley (R) wins o Election of 1896 McKinley wins Bryan framed as a social revolutionary o Populist could adequately unit N and S farmers or agricultural west and Industrial workers in east Industrial workers pressured to vote for McKinley McKinley’s world view carries the day v. Bryan’s more internal view Progressivism – regulate and reform o Take on big business, corruption, improve working and living conditions - return government to the people not special interests or big business o Take on slum conditions and child labor o o o o o o o o 1.7 million child laborers under the age of 16 Muckrakers – journalists who dug up dirt on politicians and conditions Ida Tarbell, Lincoln Steffens Very diffuse group with many different people/groups demanding various and numerous reforms Had difficulty defining what reforms were necessary Radical Progressives Eugene Debs socialist election of 1900, 100, 000 Election of 1904 400,00 votes AF of L allows skilled and unskilled workers IWW – “Big” Bill Haywood Laborers and employers have nothing in common Political reforms in cities Ward bosses lose power as appointed city managers take control Political reform in states Robert La Follette – Wisconsin Idea took on state level political bosses/machines Grass roots organizing Direct primary Brought best and brightest into government Used commissions and agencies to regulate RR, road construction, and tax assessment Initiative – allow citizens to put legislation on ballot Referendum – allow citizens to vote on legislation Social reforms in states – States begin to take on big business Sweatshop regulation – conditions and hours Child labor issues – age and hour laws Mine regulation – safety Tenement regulation - safety 14th amendment used to both enact and defeat social reforms Women workers still fighting for voting rights Jacob Riis How the other half lives and Upton Sinclair The Jungle Women’s Suffrage NWSA Elizabeth Cady Stanton Susan B Anthony Carrie Chapman Catt Movement handicapped by infighting and continue leading struggles for other reforms 19th Amendment 1919 Income taxes and Direct election 1913 16th Amendment Income tax 1917 17th Amendment Direct Election of Senators Both Populist ideas from 1896 election 1918 18th Amendment Prohibition