Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae – Review #2
advertisement

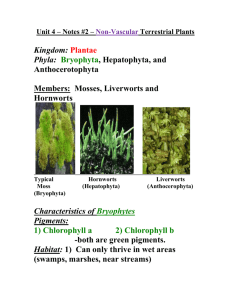
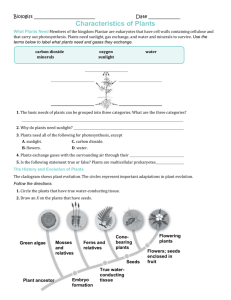
Name: _________________ Date: _____________ Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae – Review #2 Characteristics of Mosses and Ferns BRYOPHYTA: Mosses ____1. To which phylum do mosses belong to? ____2. Name three main groups of plants that belong to this phylum. ____3. Members belonging to phylum Bryophta, must still live in moist climates or at least seasonally moist climates. Give at least three reasons why they need guaranteed moisture. ____4. Why is it that Bryophytes are limited in height? ____5. Copy out a sketch of the diagram in Fig. 10.5 on p. 259, then label its parts. ____6. Just like algae, bryophytes use the same two pigments for photosynthesis, name them. ____7. Describe the difference between an organism whose cells are haploid and an organism whose cells are diploid. ____8. As humans, give a cell that is haploid, name one of our cells that is diploid. ____9. What is the name of the organism structure (generation) of a moss that is haploid? ____10. What is the name of the organism structure (generation) of a moss that is diploid? ____11. Name the part of the haploid moss structure that produces sperm cells. ____12. Name the part of the haploid moss structure that produces the eggs. ____13. In general what structure is produced when an egg and a sperm unite, and is this structure diploid or haploid? ____ 14. When this structure germinates upon the right conditions what new structure forms, and is this structure diploid or haploid? ____ 15. What type of cell division takes place inside the capsule of the structure named in #14? ____ 16.What are these new haploid cells called, and name the structure that they form when these haploid cells find a suitable environment? TRACHEOPHYTA: Ferns ____17. The most primitive vascular plants belong to which phylum? ____18. Define each root word : - Trachea and Phyta ____19. Why is this a good phylum name for these plants? ____20. Describe the function of XYLEM. ____21. Describe the function of PHLOEM ____22 Describe the structure and function of a Tracheid cell. ____23. Other than a vascular system for transport, name two other key characteristics that Tracheophytes have that make them more successful than the Bryophytes at living on land. ____24. Of the club mosses, the horsetails and the ferns, which members of the most primitive Tracheophytes have been the most successful at adapting to a modern dryer Earth climate? ____25. What name is given to the creeping underground stems that ferns possess? ____26. What are the leaves of a fern called? ____27. Is the main generation of a fern plant diploid or haploid? ____28. How are sporangia and sori related? (What do they have to do with each other?) ____29. When the spores of a fern find the appropriate environment they germinate to grow into a haploid gametophyte, what is this heart-shaped second generation structure called? ____30. Describe why ferns still need a moist environment for reproduction to take place. ____31. What does the archegonium produce? ____32. What does the antheridium produce? ____33. If you went to a fancy restaurant and you ate some fiddleheads, what would you be eating and would the cells of that food item be haploid or diploid? Alternation Of Generations ___ 1. In general, is the sporophyte diploid or haploid? ___2. The haploid gametophyte plants live up to their name, they produce gametes (sex cells). What is the proper name for the male gamete, also what is the name of the female gamete? ___ 3. What specific type of cell division must take place in the sporangium of the diploid sporophyte to give rise to the production of haploid spores? ___4. Which generation (gametophyte or spororphyte) is more dominant in algae and \ bryophytes?