parts of speech - Lake County Schools
advertisement

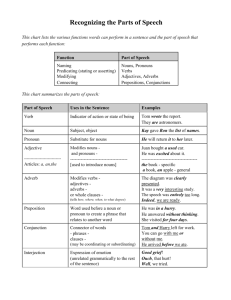
PARTS OF SPEECH
There are several different kinds of words, or parts of speech that you use every day:
Nouns
Pronouns
Verbs
Adjectives
Adverbs
Prepositions
NOUNS
- A noun is a word that names a person, a place, a thing, or an idea.
- A noun can name something that occupies space :
Example:
baby, balloon, plane,
- A noun can name something that does not occupy space:
Example:
Wednesday, health, happiness
Activity
Underline the 20 nouns that appear in the following passage.
The British queen, Victoria, the very symbol of the empire for over sixty years,
died in the first year of this century. Gradually, the British colonies gained independence
and formed a federation of nations united under the merely symbolic powers of the
monarchy. The national wealth and international influence that had been a British way of
life were quickly becoming memories of the past. This decline was hastened by the two
great wars.
PROPER AND COMMON NOUNS
Proper noun - this is the name of a particular person, place, thing , or idea.
Example : Aunt Shirley, Atlantic Ocean, Thanksgiving Day,
Common noun -
this is the general -- not particular -- name
of a person, place, thing, or idea.
Example: Car, Bank, Dancer, Newspaper
Activity- Label the following words either C for common noun or
P for proper noun.
1.
2.
3.
5.
6.
7.
Houston
National Geographic
Magazine
Singer
City
Africa
8. Empire State Building
9. State
10. Mrs. Fisher
11. Car
12. Happiness
13. Kleenex
Collective Noun - A collective noun names a group.
Example: army, team, school (of fish), Boy Scouts, choir, public
Activity
Underline the 5 collective nouns in the following paragraph.
After the crew of the merchant ship had finished their chores, they loved to watch
the sea. Once at night a swarm of plankton made the ocean glow softly. A young sailor
watched in amazement as a pod of feeding whales suddenly broke the calm surface. At
another time, along the coast of California, the sailor spotted a herd of sea lions frolicking
in the waves. The varied population of the sea never ceased to delight the young sailor.
Compound Noun - a noun that is made up of more than one word.
Example: housekeeper, ice cream, bookmark, high school, necklace, dining room
Concrete Nouns name an object that occupies
space or that can be recognized by
any of the senses.
Example: thorn, gas, stars, milk,
Florida
Abstract Nouns names an idea,
a quality, or a characteristic.
Example:
softness,
harmony, excitement, innocence
Activity
For each concrete noun below, write an abstract noun that names an idea with which the
concrete noun can be associated.
1. Quarterback ______________
2. Scream
______________
3. Perfume
______________
4. Test ________________
5. Puppy
________________
6. Chocolate ________________
VERBS
A verb is a word that expresses action or a state of being and that is
necessary to make a statement. There are many types of verbs:
ACTION VERB - tells what someone or something does
Activity 1 - Circle the action verb that appears in each sentence.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Frisbee disks soar through the air as gracefully as birds.
Their path and speed depend on the player’s grip, the force of the throw, and the wind.
The lighter disks fly farther and faster than the heavier ones.
Players still prefer the heavier ones for team sports.
Ordinarily players set their own rules.
TRANSITIVE VERB - action verb that is followed by a word or words that answer the
question what? who? or whom? (The what, who, and whoms are called direct objects)
Ex -
Fleas bite people.
(D.O.)
Hawks see their prey from far away.
(D.O.)
INTRANSITIVE VERB - an action verb that does not have a direct object.
Ex -
Fleas bite.
Hawks see well in most weather conditions.
Activity 2 - Circle the action verb in each sentence and indicate if it is transitive or
intransitive.
1. Anteaters prefer the warmer regions of the world.
2. Anteaters posses no teeth whatsoever.
3. On the whole, anteaters live rather peacefully.
4. Like other toothless animals, anteaters often hide from their enemies for protection.
5. When fearful, though, anteaters react fiercely.
6. In general, they attack only insects.
LINKING VERB - links the subject of a sentence with a word or expression that
identifies or describes that subject.
The most common linking verbs - is, are, am, was, were, will be, has been, was being
Other possible linking verbs - look, grow, feel, remain, appear, seem, sound, become,
taste, stay, smell
HINT - If you are unsure whether a word is a linking verb,
substitute the word SEEM in the sentence. If the sentence still
makes sense, the word is probably a linking verb.
Ex - Small airplanes grow (seem) more popular every year.
Activity 4 - Circle the verb in each sentence. Indicate whether it is an action or linking
verb.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
People outdoors often grow sick of insects.
Insect colonies grow quite quickly.
The noises of insects sound an alarm to other insects.
To Chinese people, crickets sound cheerful.
Many insects feel through their antennae.
Insects appear in all corners of the world.
ADJECTIVES & ADVERBS
ADJECTIVE - a word that modifies (changes) the meaning
of a noun or pronoun by making it more specific. Adjectives may do 4 things:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Describe: a rainy afternoon, a smooth surface
Classify: female spiders, Alaskan winters
Identify: this book, those horses, our party, his car
Quantify: an apple, three cents, no water
CLEAN BABY!
Activity: Complete the following sentences by
replacing each blank with the kind of adjective
named in the parentheses.
1. There are _____basic kinds of stereo systems: the component and the compact.
(quantifying)
2. In the component system each part can be bought separately, and the sound is very
_________. (describing)
3. Some people prefer the component system because they can buy the best parts from
_______________ manufacturers or American manufacturers. (classifying)
Activity: Underline the adjectives in the following paragraph.
Hawaii consists of a chain of 132 islands. These
islands extend northwest for 1,523 miles. Main
islands of Hawaii include Maui, Lanai, Nihau, and
Hawaii, an island that is quite large and famous for
active volcanoes. Although there are a number of
islands, Hawaiian people live only on major ones.
Kahoolawe, for example, had no inhabitants and is
used only for naval purposes. Minor islands, only as
big as great rocks, are too small and infertile to
support human life.
ADVERB - A word that modifies (changes) a verb, an
adjective, or another adverb by making it more
specific.
Example : Extremely few eagles now nest very successfully in the area.
ADVERBS also answer the questions of time (when?), place (where?), manner (how?),
and degree of intensity (to what degree?)
When: The baby cried now .
Where: The baby cried there.
How: The baby cried loudly.
To what degree: She was completely cried out.
Activity: Underline the adverbs in the following
sentences. There may be more than one in each sentence.
1. Very intense heat and pressure crystallize carbon into diamonds underground.
2. Diamonds vary rather widely in value.
3. Experts usually determine diamond value quite simply by evaluating the cut.
4. A high weight in carats definitely raises a diamond’s value.
5. The carat weight of a rough diamond may be greatly reduced when the diamond is cut
6. If a diamond is polished and shaped expertly, it is more valuable than a diamond of the
same weight that is not polished.
7. Fifty-eight facets sparkle brilliantly from the most popular diamond cut.
8. Well-cut diamonds are breathtakingly beautiful.
9. Diamonds that are heavily flawed almost always cost less than flawless stones.
10. Colorless diamonds are the most highly valued for use in precious jewelry.
CHOOSING ADVERBS AND ADJECTIVES
When choosing a modifier, you must often decide if you need an adjective or an adverb.
There are two pairs of words which often cause confusion:
Good vs. Well & Bad vs. Badly
GOOD vs WELL:
Always use good as an adjective.
The child is a good speaker. The soup was good and hot.
Well may be used as an adverb of manner telling how ably
something was done or as an adjective meaning “in good health.”
The child speaks well.
BAD vs BADLY:
The child is not well right now.
Always use bad as an adjective.
The machine made a bad copy.
The potato was bad.
Use badly as an adverb (it usually follows action verbs)
Activity:
Chose the correct modifier by filling the blank with either good, well,
bad, or badly.
1.
A person who can speak ________ can make a
lasting impression on the audience.
2.
_____________ organization is important in a speech.
3.
A speech that is __________ written will usually
confuse the audience.
4.
A ___________ delivery is just as important as the content of the speech.
5.
Even a speaker who is not feeling _______
should speak forcefully.
6.
If a speech begins _________, an audience may
immediately lose interest.
7.
A speaker can promote a _______ relationship with
an audience by making eye contact.
8.
A speaker must know the content of a speech very
___________ in order to be effective.
NOUN OR ADJECTIVE?
Many words commonly listed as nouns in a dictionary may act as adjectives by modifying
other nouns.
NOUNS
The couple pledged their love to each other.
The wall was made of concrete.
ADJECTIVES
They read a love poem.
The built a concrete wall.
ACTIVITY
Use each noun below as an adjective by having it modify another noun.
EX: Noun = Shirt Adjective = shirt button
1. Kitchen = _______________
3. Flower = ________________
2. Beach = ____________________
4. Telephone = _________________
Prepositions & Prepositional Phrases
A PREPOSITION is a word that shows the relationship of a noun or pronoun to another
word. It usually tells where or when.
EXAMPLE: The squirrel ran (to, up, on, down, over, toward, under,) the tree.
A prepositional phrase includes a
preposition the object of the preposition
and any modifiers of that object.
EXAMPLES:
Arlene climbed up the ladder.
[The preposition is up and the object of the preposition is ladder.]
The picture on the cover is mine. [The preposition is on and the object of the
preposition is cover.]
EXERCISE A Underline the prepositional phrase in each of the following sentences.
1 She found her jacket in the closet.
2. An enormous picture was painted on one wall.
3. The picture reached above the second story.
4. It showed an eighteenth-century man in a white shirt.
5. The picture was painted by a local artist.
EXERCISE B
In each of the following sentences underline the preposition
once and the object of the preposition twice.
6. Spike Lee was born in Georgia.
7. He studied at a New York university.
8. The video store near my house carries his films.
9. Lee appears in some films.
10. His father wrote the music for this movie.
11. She lived just one mile down the road.
12. The director wore a hat with a large X.
13. During a recent newscast I heard Lee speak.
14. He talked about a film he had just finished.
15. In fifteen minutes, I’ll need to go to class.
Common Prepositions
about
beside
across
between
after
beyond
along
by
around
down
before
from
inside
like
near
off
onto
over
Common Compound Prepositions
according to
because of
ahead of
by means of
along with
in addition to
through
to
toward
underneath
up
with
instead of
in front of
in spite of
next to
on account of
on top of
PRONOUNS
Pronouns -
These are words that take the place of nouns, groups of nouns, or other
pronouns. Pronouns allow you to avoid unnecessary repetitions when you
speak or write.
Examples:
When Sylvia Plath was a young girl, she decided to become a writer.
George Orwell wrote Animal Farm. It remains very popular today.
Antecedent- the word or group of words to which a pronoun refers
Examples:
The apple, because of its texture, is used for filling in pies.
Personal Pronoun - This refers to a specific person or thing by indicating the person
speaking, the person being addressed, or any other person being discussed.
Examples:
I, me, we, us, you, he, him, they, them, she, her, it
“My Doll”
Possessive Pronoun - a personal pronoun that indicates
ownership or possession.
Examples :
My, mine, our, ours, your, yours, his, hers, theirs, its
ACTIVITY:
Replace the underlined words or groups of words with personal or
possessive pronouns.
In the late twentieth century eight riders and the riders’ horses
retraced the Santa Fe Trail, once a major route for pioneers going west. The trip’s leader,
Allan Maybee, made sure that the riders planned carefully. Maybee asked Maybee’s
friend, Ms. Evelyn Vinogradov, to drive Vinogradov’s truck ahead of the riders. The
truck carried groceries, and Vinogradov had filled the truck with jugs of water as well.
Vinogradov also arranged for places where the group could stay overnight. Would the
reader of this passage be interested in planning the reader’s own trip along the Santa Fe
Trail?
Reflexive Pronouns - refers to a noun or another pronoun and indicates that the same
person or thing is involved. These always end with -self or -selves.
Ex:
Today, for the first time in months, she is herself.
As cooks they have no faith in themselves.
Intensive Pronoun - Adds emphasis to another noun or
pronoun. These also end with -self or -selves.
Ex:
You yourself told me to stop.
I myself cooked the soup.
ACTIVITY
Supply the appropriate reflexive or intensive pronoun for each blank.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Many of us have transformed _______________ from joggers to serious runners.
Running _______________ is not a difficult sport.
If you are new to running, be sure to pace _______________ carefully.
Some runners use a stopwatch to time _________________.
I ________________ enjoy a morning run most of all.
?????
Interrogative Pronoun - is used to form questions.
Examples: Who? Whom? Whose? What? Which?
Who is here?
Which shall I take?
What will I find?
Indefinite Pronoun - refers to persons, places, or things in general
terms.
Examples:
All, another, any, anybody, anyone, both, each,
everyone, few, many, most, neither, none, no one, others, several,
somebody, something
ACTIVITY
Underline the eight indefinite pronouns in the following paragraph.
Everyone cheered as the rocket rose from the launching pad. During the first orbit
everything went well. Then someone realized that the spacecraft was swinging to the
right. Obviously, something was wrong. The astronaut quickly reviewed the problem.
Taking several of the controls off automatic, he flew the craft manually though the final
two orbits. Nobody had ever done anything like this before. Nor had any of the earlier
American astronauts orbited the earth.
PRONOUNS AS SUBJECTS AND OBJECTS
In a sentence, a pronoun changes form according to its function.
Nominative Case - When the pronoun is the subject of the sentence (doing the action)
Ex - He gave John the radio.
Objective Case - When the pronoun is the object of the sentence (receiving the action)
Ex - Ted gave him the radio
The following chart shows you which pronouns go with each case:
Nominative Case (subject)
Objective Case (object)
Singular:
I, You, He, She, It
Me, You, Him, Her, It
Plural:
We, You, They
Us, You, Them
Note: Don’t forget your objects found within prepositional phrases!
Which is correct?
The dog sat between him and me.
or
The dog sat between he and I.
The correct pronouns would be him and me because they are objects within the phrase of
the preposition, between.
Activity: Underline the appropriate pronoun in each sentence.
1. The traffic officer gave Don and (I, me) a stern lecture.
2. Did you know that Jon and (we, us) were arranging the picnic?
3. Between you and (I, me), video games are my hobby.
4. (He, Him) and (I, me) are the friendliest people around town.
5. There has always been a friendship between Mary and (I, me).
6. Mary and (he, him) are the luckiest people on earth.
7. Please give (she, her) that piece of paper.
8. (We, Us) cannot belieive that winter is almost here.
9. John bumped into (she, her) as he walked out the door.
10. Why don’t you tell (they, them) how you really feel?
Pronoun Complements when the pronoun may be switched with the subject
without changing the meaning of the sentence.
Ex - She is the first contestant in the pageant / The first contestant in the pageant is she.
He was the loser. / The loser was he.
Because it has the same meaning as the subject,
the pronoun used is usually in the nominative case.
Activity: Underline the appropriate pronoun.
1. It must have been (they, them) who were sitting behind us.
2. There are (she, her) and Amy, standing by the road.
3. If I were (she, her), I wouldn’t leave(he, him) alone.
4. The last to arrive were Greta and (I, me).
5. Fortunately, (she, her) and not her sister was behind the wheel last night.
6. It is (we, us) not (they, them) who must finish the job.
7. The only people remaining were Joyce and (I, me).
PRONOUNS IN COMPARISONS
The words than and as are used frequently to make comparisons.
Ex - No one is as funny as she is funny.
Ernie was more surprised than we were surprised.
Sometimes, however, the comparisons are not completely stated.
Ex - Did Jon get paid more than they? {got paid}
In order to help you choose the correct pronoun you must mentally complete the sentence,
even if it is not completed for you.
Ex: My younger brother never had to work as hard as I. {had to work}
Activity: Choose the correct pronouns in each sentence.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Even a young child would use money more wisely than (he, him).
Mr. Smith admitted that he was stricter with Stan than with (he, him).
Do you have as much freedom as (she, her)?
No one was happier than (I, me) at the news of your rescue.
Were you as bothered as much as (I, me) by the traffic jam?
Luke is better at baking than (she, her).
Though we look the same age, Ed is actually two years older than (I, me).
Lyle was more concerned about capsizing than (he, him).
PRONOUN OR ADJECTIVE?
Many pronouns may be used just like adjectives. All types of pronouns (demonstrative,
possessive, interrogative, indefinite) can be used as adjectives when they modify a noun.
Possessive Pronoun
Possessive Adjective
The book is his.
His book is lost.
Demonstrative Pronoun
Demonstrative Adjective
This is the one I want.
This book is my choice.
Interrogative Pronoun
Interrogative Adjective
Whose are you playing?
Whose symphony are you playing?
Indefinite Pronoun
Indefinite Adjective
Some grew tired.
Some swimmers grew tired.
ACTIVITY
Determine whether each italicized word is used as a pronoun or an adjective.
“Affinities” is a game that challenges players to make a list of words commonly
joined by “and.” The player whose list is longest wins. There are many words which
would qualify as affinities. In another game, called “Hidden Words,” the leader gives
several words of ten or more letters. A little creativity is needed for the game, “Alphabet
Tale.” For this game players write a story 26 words in length; each of the words must
begin with a successive letter of the alphabet. This is an excellent way to learn new
words. These brain teasers are sure to challenge your powers of thinking. All can be
played without much difficulty, and several are as educational as they are entertaining.
PREPOSITION OR ADVERB?
Many words that appear to be prepositions may often be adverbs. If the word stands
alone and answers a question such as where? or when? and if it does not connect a noun
or pronoun to the rest of the sentence, consider the word an adverb. Otherwise it is a
preposition.
ADVERB
The players assembled inside (where?)
PREPOSITION
The players assembled inside the auditorium.(connects the noun
auditorium to the rest of the sentence)
ACTIVITY
Decide whether the italicized word in each sentence is a preposition or an adverb.
1. An upholstered chair has springs and padding inside.
2. Springs and padding inside a chair make it comfortable.
3. Furniture makers upholster a chair by stretching strips of heavy cloth across the
bottom of the frame.
4. These strips are placed across to give good support.
5. Upholsterers then put coil and zigzag springs throughout the chair.
6. Lighter springs may also be used throughout.
7. Next, furniture makers put padding over the springs.
8. Upholsterers use padding to give comfort all over.
THE COMMA
The comma should be used in the following situations:
1. To divide two complete thoughts separated by a coordinating conjunction ( and, but,
or, nor, yet, or for).
Example - a. I told Sue what he said, and she advised me to forget it.
b. I carefully picked up the vase, yet it crashed to the floor.
Helpful Hint -
If you can place a period after each thought, you will need to
use a comma along with a coordinating conjunction.
2. Commas are used to set off introductory phrases.
Example - a. With a powerful thud, the book fell to the ground.
b. Without a sound, the baby sat quietly.
3. Commas must be used to set off interjections (such as yes, no, and well) and transitions
such as after all, however, moreover, etc
Examples - Yes, I hope to build my own home one day.
After all, I did my best.
Philadelphia, on the other hand, is three centuries old.
4. Commas must be used to separate three or more words, phrases, or clauses in a series.
Example - The movie was long, dull, and humorless.
He can throw, catch, and hit as well as anyone else.
ACTIVITY
Add commas where they are needed.
1. Actors actresses and filmmakers greatly influence the lives of many people.
2. Bette Davis a famous and talented actress was the first woman to receive
the Life Achievement Award.
3. In the movie Mr. Skeffington Davis played a selfish unloving character.
4. Mel Gibson is known for his great acting ability and he is labeled as one of the finest in his craft.
5. Several actors even though successful in college leave school to act.
6. The screenwriter Joan Tewkesberry wrote several screenplays for many actors.
7. Throughout history only a few actors can be said to have changed the course of filmmaking.
8. Because many actors influence each other they are all considered significant.
THE COLON
Colons should be used in the following situations:
1. When making lists
USE A COLON TO INTRODUCE A LIST, ESPECIALLY
AFTER A STATEMENT THAT USES SUCH WORDS AS
THESE, THE FOLLOWING, OR AS FOLLOWS.
Example: To make a good sandwich, you need the following
ingredients: peanut butter, jelly, and bread.
Note that your introductory statement is a complete sentence!
2. To introduce material that explains or restates the
preceding material
Example: You can see how cold the winters are in Alaska: On a windy
morning your breath freezes into ice crystals in front of your face.
3. To introduce a long or formal quotation
Example: Lincoln began the Gettysburg Address with these famous words: “Four score and seven years
ago....”
Activity- Add colons where they are needed.
1. There are three animals which make good pets cats, dogs, and fish.
2. Among the natural rights of the colonists are these a right to life, a right to liberty, and
a right to property.
3. There are three faithful friends a good spouse, an old dog, and ready money.
4. Poet Karl Shapiro and composer Aaron Copland have something in common. Each
won a Pulitzer Prize.
5. Dorothy Parker asked to have this engraved on her tombstone “Excuse my dust.”
THE SEMICOLON
1. USE A SEMICOLON TO SEPARATE MAIN CLAUSES THAT ARE NOT JOINED BY
COORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS.
Incorrect is
The acting ability of Orson Welles is considered phenomenal; and his film Citizen Kane
still appreciated.
Correct -
The acting ability of Orson Welles is considered phenomenal; his film Citizen Kane is
still appreciated.
2. USE A SEMICOLON TO SEPARATE COMPLETE THOUGHTS
SEPARATED BY TRANSITIONS: HOWEVER, THEREFORE,
FURTHERMORE, FOR EXAMPLE, ETC.
Example - The dessert was terrific; therefore, we all had a second helping.
3. USE A SEMICOLON TO SEPARATE THE ITEMS IN A SERIES
WHEN THESE ITEMS CONTAIN COMMAS.
Example -There are several great writers such as Ralph Waldo Emerson, who wrote Nature; Henry David
Thoreau, who wrote Walden; and Maragret Fuller, who wrote Women in the Nineteenth Century.
4. USE A SEMICOLON TO SEPARATE 2 COMPLETE THOUGHTS JOINED BY A
COORDINATING CONJUNCTION WHEN THERE ARE INTERNAL COMMAS.
Example -
Leonardo da Vinci pursued a wide range of subjects including mathematics, music,
astronomy, and engineering; but he always returned to his primary interest, which was, of
course, art.
ACTIVITY-- Add semicolons where they are needed.
1. Mary was strongly discouraged to practice gymnastics however, she won several awards for her abilities.
2. People who eat candy may become overweight people who eat vegetables may perhaps remain thin.
3. All the trees were conifers therefore, they were cone-bearing evergreens.
4. Mark Twain attached the preceding notice to Huckleberry Finn he felt that too much analysis of art
made it less enjoyable.
5. Many artists live and work in Dallas, Texas Orlando, Florida and Hollywood, California .
6. We must remember that art is not a form of advertising it is a form of truth.
7. Many people enjoy Italian food including spaghetti, ziti, and ravioli but they may also enjoy American
food like hamburgers, potato chips, and apple pie.
Plural Nouns
RULES:
Form the plural of nouns ....
- by adding -S or -ES
Ex: towns, parks / boxes, churches
- ending in a vowel + Y by adding an -S
Ex: days, keys, boys
- ending in a consonant + Y by changing the Y to I and adding -ES
Ex: country = countries
- ending in a vowel + O by adding an -S
Ex: patio = patios / rodeo = rodeos
- ending in a consonant + O by adding -ES (there are exceptions to this rule)
Ex: potato = potatoes / hero = heroes
- changing the spelling
Ex: mouse = mice / man = men
- not changing the spelling
Ex: one deer = three deer / one dozen = five dozen
ACTIVITY
Write the plural form of each word on the line provided
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
journey ____________________
gentleman __________________
tax ________________________
bonus ______________________
moose ______________________
6. cameo ______________________
7. potato ______________________
8. dent ________________________
9. woman ______________________
10. enemy ______________________
Possessive Nouns
Possessive Nouns show ownership or possession
RULES: Add an apostrophe ‘ ....
- + an S to make a singular noun possessive
Ex: John’s paper / the cat’s toy
- after the S to show ownership of plural nouns
Ex: Plural noun - The Ladies (more than one lady)
Possessive Plural noun - The Ladies’ hats (hats belonging to many ladies)
- + an S to make a plural without an S at the end
Ex: Plural noun - The men (more than one man)
Possessive Plural noun - The men’s cigars (cigars belonging to several men)
Singular noun
Boy
Chair
Woman
Singular Possessive
Boy’s dog
Chair’s seat
Woman’s
Plural noun
Boys
Chairs
Women
Plural Possessive
Boys’ dogs
Chairs’ seats
Women’s
Underline the proper word in each sentence.
1. Each year the Smith family goes to the (rodeos, rodeo’s) in northern Georgia.
2. We were invited to the (Gomezes, Gomezes’ ) housewarming party.
3. On our hike we saw three (deer, deer’s) grazing in the pasture.
4. My (parents, parents’) gift to me was a new car.
5. Some Eskimos still use (igloos, igloo’s) when out fishing.
6. All my (cousins, cousins’) birthdays fall in the month of July.
7. Uncle Robert had dozens of (stories, story’s) to tell us.
8. Those bowling (alleys, alleys’) lanes are in poor shape.
9. The (Kellys, Kelly’s) are planning a trip.
10. The (childrens’, children’s) clothing is on the third floor.
Mark A if the underlined word is used correctly, or mark B if it is used incorrectly.
66. The teacher’s have the day off today.
67. My nephew’s birthday is today. He turns nine years old.
68. All of the childrens’ toys were scattered under the Christmas tree.
69. Three deers crossed the road.
70. The male deer’s antler was cracked when he ran into the tree.
71. The little girl loved to listen to bedtime stories.
72. My parents cooked the Thanksgiving turkey together.
73. The mans’ cigar was left on the table. He should have taken it with him.
74. All of the lady’s purses were stolen from the mall yesterday.
75. Those were Chris’ keys on the table.