Dissection 31
advertisement

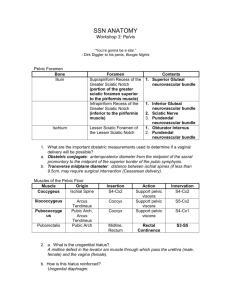
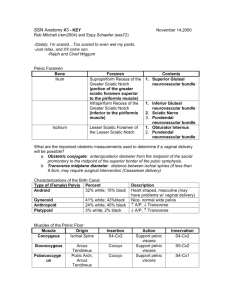
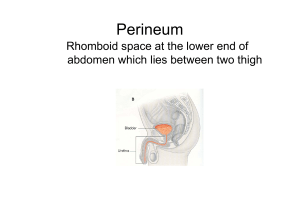
DISSECTION 31 The Perineum, Urogenital Triangle References: M1 402-409, 418-434; N 348, 360-368, 376; N361, 378-385, 395; R 327-347, 350-354 AT THE END OF THIS LABORATORY PERIOD YOU WILL BE RESPONSIBLE FOR THE IDENTIFICATION AND DEMONSTRATION OF THE STRUCTURES LISTED BELOW: 1. Muscles, fasciae, and fascial spaces: superficial perineal compartment, ischiocavernosus, bulbospongiosus, urogenital diaphragm, sphincter urethrae, deep transverse perineus, fascia penis, tunica albuginea, inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm (perineal membrane), deep perineal compartment. 2. Ligaments, etc.: symphysis pubis, pubic arcuate ligament, fundiform ligament of penis, suspensory ligament of penis or clitoris. 3. Nerves: dorsal nerve of penis or clitoris. 4. Arteries: internal pudendal artery, deep artery of penis or clitoris, dorsal artery of penis or clitoris. 5. Veins: superficial dorsal vein of penis, deep dorsal vein of penis. 6. Cavernous bodies: crura of penis and clitoris, bulb of urethra and vestibule, corpus cavernosum penis, corpus spongiosum. 7. Visceral structures: membranous urethra, spongy urethra. YOU SHOULD ALSO BE ABLE TO DO THE FOLLOWING THINGS: 1. Label on a diagram the fascias, muscles, nerves and vessels of the urogenital diaphragm. 2. Draw a diagram of the pudendal nerve and its branches. 3. Draw a diagram of the internal pudendal artery and its branches. 4. Demonstrate on the cadaver the boundaries and contents of the deep perineal space. 5. Identify on the cadaver the structures enclosed between the superficial perineal fascia (Colles' fascia) and the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm (perineal membrane). 6. Name the abdominal fascial layers that are continuous with the perineal fascias. 7. Demonstrate the course of lymphatic and venous drainage from the perineum. 8. Explain how urine can spread to the anterior abdominal wall and why it usually does not spread into the ischiorectal fossa or the thighs when the urethra is injured inferior to the urogenital diaphragm. Dissection 31, Perineum, Urogenital Triangle Examine the tela subcutanea of the urogenital triangle for superficial branches of pudendal arteries and nerves. The inner fibrous or deep layer of the tela of this region is called the superficial perineal [Colles'] fascia (N360, 363; N378, 380). Look for the superficial transverse perineus muscle along the posterior border (base) of the urogenital triangle. (It may be absent or unidentifiable.) Incise the superficial perineal fascia through the median line and across the base of the triangle, then reflect it laterally to open the SUPERFICIAL PERINEAL COMPARTMENT (A344, 346, 370-371; G3.44, 54; N361, 364, 376, 384, 385; N379, 381, 395, 404, 405). Identify and clean the following structures within this compartment (structures of the female in parentheses): [N364, 365 (361) N381, 382, (379)] Page 2 Cut the crura from their attachments to the ischiopubic rami, and the bulb from the INFERIOR FASCIA OF THE UROGENITAL (PERINEAL MEMBRANE). (In the female, transect the vagina just superior to the bulb of the vestibule.) Review the FUNDIFORM LIGAMENT of the penis and find the SUSPENSORY LIGAMENT, which attaches the fascia penis to the SYMPHYSIS PUBIS. Make a cross section through the body of the penis (G3.48, 51, 49; N364; N381; A348-350) and identify the following parts: DEEP FASCIA, called Buck's (FASCIA PENIS) fascia CORPUS CAVERNOSUM PENIS CORPUS SPONGIOSUM PENIS TUNICA ALBUGINEA of the corpora ISCHIOCAVERNOSUS MUSCLE DEEP ARTERY OF THE PENIS BULBOSPONGIOSUS MUSCLE SPONGY URETHRA CRURA OF THE PENIS CLITORIS) (CRURA OF THE BULB OF THE URETHRA (VESTIBULE) Expose the crura of the penis (or the clitoris) and the URETHRAL (vestibular) BULB by reflecting their investing musculature. In the male, reflect the skin from the dorsum of the penis. Trace the DORSAL ARTERIES (A347; G3.51B, 48A; N381, 389; N401, 409) and NERVES distally to the glans, then proximally to the site where they emerge from the UROGENITAL DIAPHRAGM (N385; N405). This diaphragm consists of deep fascia, SPHINCTER URETHRAE and the DEEP TRANSVERSE PERINEUS MUSCLE, which span the gap between the inferior rami of the pubic and ischial bones. Identify the SUPERFICIAL and DEEP DORSAL VEINS of the penis (A347; G3.51A, 48A; N364, 385; N381, 405), and trace the deep vein to its passage through the space between the PUBIC ARCUATE LIGAMENT and the anterior portion of the urogenital diaphragm. This fibrous part of the diaphragm is called the transverse perineal ligament (A366; G3.51B; N385; N405). DIAPHRAGM On one side, open the DEEP PERINEAL by careful removal of the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm and identify the main components within it, as follows (A366, 369; G3.51B; N385; N405): COMPARTMENT the DEEP TRANSVERSE PERINEUS MUSCLE the MEMBRANOUS SPHINCTER MUSCLE URETHRA and its the INTERNAL PUDENDAL ARTERY and its branches: the DEEP ARTERY (CLITORIS), OF THE PENIS the DORSAL ARTERY OF THE PENIS (CLITORIS) Remove muscle where necessary to trace the deep and dorsal arteries of the penis from their origin from the internal pudendal, through the deep compartment. Review the internal pudendal artery and its branches. Identify the superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm and review the transverse perineal ligament. Note that the ischiorectal (ischioanal) fossa, on each side of the midline, is prolonged as an anterior recess which lies between the urogenital and the pelvic diaphragms. Dissection 31, Perineum, Urogenital Triangle Page 3 STUDY QUESTIONS 1. With which abdominal fascia is the superficial perineal fascia (Colles' fascia) continuous? 1. The deep (membranous) (Scarpa's) layer of the tela subcutanea (superficial fascia). 2. Where does the superficial perineal fascia attach firmly to deep fascia? 2. Along the ischiopubic rami and to the posterior border of the urogenital diaphragm. 3. What is the superficial perineal space? 3. The space bounded superiorly by the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm and inferiorly by the Colles' fascia. It contains the root structures of the penis or clitoris and associated muscles. 4. What is the deep space or compartment of the urogenital diaphragm? 4. The area between the inferior and superior fascias of the urogenital diaphragm. 5. What name is given to the most anterior non-muscular part of the urogenital diaphragm? 5. Transverse perineal ligament. 6. What structures pass through the gap between the transverse perineal ligament and the arcuate ligament of the pubis? 6. Dorsal vein(s) of the penis to join prostatic plexus. 7. What is the crus of the penis? 7. The posterior attached portion of the corpus cavernosum penis. 8. What is the bulbospongiosus? 8. The striated muscle of the corpus spongiosum in the male and the vestibular bulb in the female. 9. What is the innervation of the bulbospongiosus? 9. Perineal branches of the pudendal nerve. 10. What is the central tendon of the perineum? 10. Often called the perineal body, it is a common attachment for the external anal sphincter, the bulbospongiosus and the superficial and deep transverse perineus muscles. Dissection 31, Perineum, Urogenital Triangle Page 4 11. What occupies the deep space of the urogenital diaphragm in the male? 11. The deep transverse perineus muscle and sphincter urethrae, membranous urethra, bulbourethral glands, dorsal nerve of penis, internal pudendal vessels, and origin of branches, deep and dorsal arteries of the penis and branches to bulb and urethra which pierce the inferior fascia of the UG diaphragm. 12. What other name is given to the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm? 12. Perineal membrane. 13. What is the lymphatic drainage of the penis or clitoris? 13. Lymph from the penis or clitoris drains to nodes directly in front of the pubic symphysis and bilaterally to inguinal nodes. 14. Where is the major vestibular gland? 14. The major vestibular gland is located in the superficial perineal space posterior to the bulb of the vestibule and deep to the bulbospongiosus muscle (A368, G3.54). 15. List the nerves that supply the vulva. 15. The vulva is supplied by the ilioinguinal nerve (anterior labial branches), the genitofemoral nerve (genital branch), perineal branch of posterior femoral cutaneous nerve, and the perineal nerve (posterior labial branches). 16. Name the structures that are incised in a 16. a) median episiotomy. a. skin, vaginal mucosa, central tendon of perineum b) mediolateral episiotomy. b. skin, vaginal mucosa, bulbospongiosus muscle, superficial transverse perineus muscle, inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm, deep transverse perineus muscle Dissection 31, Perineum, Urogenital Triangle 17. Draw a diagram showing the pudendal nerve and the internal pudendal artery and their major branches in the perineum. Page 5 17. LJ:bh revised 06/19/09