Glandular Epithelia Glandular epithelia are formed by cells
advertisement

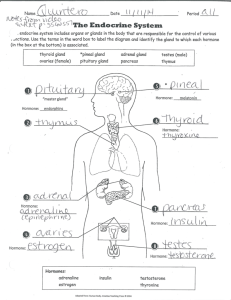
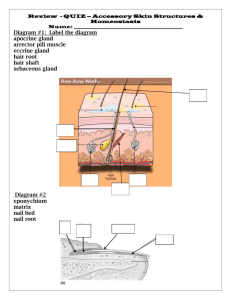
Glandular Epithelia Glandular epithelia are formed by cells specialized to produce secretion the molecules to be secreted are generally stored in the cells in small membrane-bound vesicles called secretory vesicles Called secretor granules Glands divided into: unicellular gland Exocrine glands multi cellular gland Endocrine gland two types of endocrine glands can be recognized based on the arrangement of their cells a. The endocrine cells may form anastomosing cords interspersed between dilated blood capillaries e.g. Adrenal gland, parathyroid b. The endocrine cells arrange as vesicles, follicles filled with noncellular material. E.g.: thyroid gland Exocrine gland classified into: Simple gland: have only one unbranched duct compound gland have duct that branch repeatedly Exocrine gland has a. secretory portion b. ducts According to the number of cell, exocrine gland Classified into: 1. Unicellular gland (goblet cell) : found in the living epithelium of small intestine and respiratory tract. The cytoplasm of the goblet cell filled with mucigen granules secreting: mucin (proteinpolysaccharide) Structure of exocrine gland most glands are enclosed in a fibrous capsule, the capsule often gives off extensions called septa or trabecular that divide the gland into compartment called lobes, B.V, N. and the gland own ducts travel through those septa C.T of the gland called its stroma support and organizes the tissue . The cells that perform the tasks of synthesis and secretion called parenchyma these branches communicate with the secretory acini According to the type of secretion 1. Mucous: secret a glycoprotein called mucin that mixes with water after it is secreted and forms the sticky product mucus .e.g. goblet cell 2. Serous cells: the acinar cells of the pancreas and parotid salivary glands are examples of serous cells between the nucleus and the free surface found a welldeveloped Golgi complex, several immature secretory granules derived from the Golgi complex, nature secretory granules formed after water is removed from the immature granules. The mature secretory granules accumulate in the apical cytoplasm. In cells that produce digestive enzymes (e.g. Pancreatic acinar cells), these granules are called