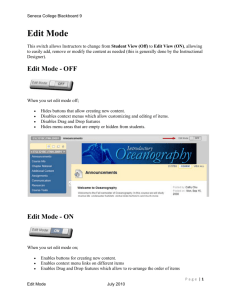
Using Practice Partner to Document Patients on Longitudinal
advertisement

Longitudinal Experience in Doctoring 3 Using an Electronic Medical Record System to Manage Chronic Disease SOAPware Expectation of Students As a part of the longitudinal experience of Doctoring 3, build a complete medical record in SOAPware on 6 patients in your longitudinal panel. Students will work with their faculty to develop a panel of 8-12 patients who have chronic diseases and select from panel of patients 6 patients that have the same chronic diseases, preferably from the following list: • diabetes, asthma, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, CHF, osteoarthritis, depression, obesity, ADHD If the longitudinal faculty member is not in a specialty that treats these specific diseases, the specialists can choose 6 patients with chronic illness typical of their specialty. For pediatrics, well child care of a newborn to 3 years will qualify. For OB, prenatal care for an entire pregnancy will qualify. Keep a paper list of these six patients in a secure location in the clinic and indicate on the list the fictional name you assign each patient. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. When you have an encounter with a patients that seem to be likely candidates for a member of your panel, create a chart in SOAPware using the demographics and document the encounter in SOAPware. After their second visit, confirm the patient as one of your 6, then populate the Summary page. The Summary page should be living document that gets updated with every subsequent visit as medications, problems, etc. change. Pick one chronic condition per patient to track in the EMR. List this disease first in the Problems List, indicated with a *. Mine chronic patient’s chart for information pertinent to their chosen chronic illness. We will attempt to determine if this patient was one used by a student last year, and import their chart into your records so you can use the data they collected. Utilizes the health maintenance reminder systems, disease flow sheet, vital signs, etc. to manage the patient’s chronic condition. a. Identify the elements that will need to be in each patient’s reminder system (both disease specific and health maintenance) and set up the patient’s reminder system. Consult with your preceptor and guidelines to determine the frequency with which these should be done, then check for the dates last performed in the patient’s record. b. Select a pertinent Flow Sheet to use with this patient’s problem. Modify if needed. If a Flow Sheet does not exist for the problem you have selected to follow, let us know what you need on it and we will help create one. Find historic data from the patient’s chart (labs, vitals, meds, notes) to complete one column dated prior to your first visit for comparison purposes. Document each encounter with these patients by creating a new Encounter Note, updating pertinent parts of the EMR throughout the year. Remember that we will be monitoring your entries so you can not use patient identifiable data (name, birth date, address, SS number) All other chronic disease panel patients seen during longitudinal clinic will need their encounters entered into CDCS at the beginning. Do not document patients with acute problems who are not a part of your panel in CDCS. Once a patient 1 8. has been identified as one you will document in the EMR, you can stop doing CDCS entries on that patient. Once per month, during the first week of each month starting in September, export your medical records for patients that you are sure will be in your pane of 6 from SOAPware (see directions) and upload the file to the SOAPware intranet site for your regional campus. Each Visits with Patients on Panel: 1. Create a new column on the Flow Sheet for the chosen disease and complete with findings, labs, etc for visit. 2. Create progress notes for each visit. We will use these progress notes as evidence of continuity with the patients in your panel. 3. Update appropriate health maintenance reminder system, medication, problems lists and so forth based on new information that has come in since last visit. 4. Deal with specific delinquent health maintenance items with your faculty member’s supervision and approval. Bring your computer with you to your longitudinal and use it while seeing the patient to help guide your care. You can also load M-Business desktop on your computer and use it to document in the CDCS system. 2 Starting and Stopping SOAPware Close all other running programs prior to starting SOAPware as it needs all the resources on your laptop to run. Run StartSOAP icon on your desktop. If it asks: your UserID is your FSU CoM account UserID; ie, nbc05a The password is also your FSUCoM account UserID—not your normal network password; ie, nbc05a Click Login Once you exit SOAPware, click the StopSOAP icon on your desktop to stop the MSDE SQL database from running to save memory. Create a New Patient Chart To Create a new patient, 1. File Menu 2. Chart Rack 3. Create Chart HIPAA compliance measures: Due to the lack of encryption of SOAPware patient data to be stored on the student laptops, we will have to make sure that there are no patient identifiers in the medical records. When a New chart is created, the Demographics screen comes up. Complete the form in the following manner: Chart Rack 1. Last Name: Use the last name of the student. 2. First Name: Use one letter or name starting with A for the first patient, B for the student’s second patient, C and so on. 3. SSN: Either leave blank or put in a fake one. 4. Chart#: There is space for 11 characters. Use this to help you identify your patient. Start with the initials of the student followed by the age of the patient, a letter that stands for race, and a letter for gender, and the number of the month and day of your first visit. Example: NBC30WF0914 This would translate to the student being NBC, the patient being a 30 year old white female whose first visit with the student was September 14th. We need to try to avoid Demographics 3 having the same patient number assigned to two patients. That would mess up the system when the patients are synced back to the server. 5. Date of Birth: Use January 1 of the year that the patient was actually born in. This helps the program assign the correct age to the patient for health maintenance purposes. If this is a child, it may be necessary to pick either Jan 1 or July 1, so that the age is close for the health maintenance immunizations tracking and growth charts to function correctly. 6. Gender: pick the correct gender of the patient 7. Primary Physician: Make sure student’s name is there. 8. Marital Status: Select the patient’s correct marital status. Remaining fields can be left blank or filled with made up information. Do not put the patient’s real information in these areas. Click OK when finished. You can come back later and add information to the patient’s demographics. The new Chart will open automatically. HIPAA mandate: In the chart, no text entries should/will contain the patient’s name, real date of birth, city, or the name of the clinical faculty in whose clinic the patient is seen. Students will be cautioned to only refer to the patient as “this patient” or “This 30 yr old white female…” Tabs Summary side SOAPnote side 4 SUMMARY SIDE Second Visit with Patient on Panel The student should obtain from the patient (and confirm with paper/clinic record) a complete history and complete the following sections in the medical record Summary: Active Problems List List chosen condition to track first and indicate with a *. Identify STABLE PROBLEMS: and UNSTABLE PROBLEMS. (note: select diagnoses from the Assessment Codes list with ICD-9 #s. See Assessment Quick Keys below.) Pertinent Inactive Problems Surgeries (include dates) Medications List (confirm with paper/clinic record) Identify RX:, OTC: and Suppliments/herbals. Can be picked from View > Codes List > Medications. Make sure that there is an appropriate problem in the problems list for each medication listed in the medications list. (medicine reconciliation) Also identify any potential drug/drug interactions. Family History Use Family History Template: quick keys FHx followed by a space for adults, GeriFHx for geriatrics, and type in who, relationship, at what age, etc. Tobacco indicate smoking status Alcohol there is a quick key for CAGE Interventions These are items like immunizations, diagnostic tests, health maintenance reminders. See example in sample at right. Indicate here if an advanced directive is on file. Documents can like a living will can be scanned and added to the record under the Reports tab, Misc. Reports. Social History Use quick key sochx for adults, GeriSHx for geriatric patients. Common Assesment Quick Keys (type words on left and press space bar to unlock) Quick Key Description artost ast bacpai cad chf copd cysfib dep dm2 gerd hamig herlos htn hypl obe Arthritis, osteoarthritis #715.90 Asthma, unspecified #493.90 Back Pain #724.2 Coronary Artery Disease #414.9 Congestive Heart Failure #428.0 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease #496 Cystic Fibrosis, staging not determined #277.00 Depression #311 Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 #250.00 GERD – Esophagitis, reflux #530.10 Headache, migraine #346.90 Hearing Loss NOS #389.9 Hypertension, #401.9 Hyperlipidemia #272.4 Obesity #278.00 5 obemor ost ra Obesity, Morbid #278.04 Osteoporosis #733.00 Rheumatoid Arthritis #714.0 See all Assessment Codes under View Menu, Code Lists. ROS: Use for a complete past medical history. As review of systems changes often, not required to be a ROS. (quick key rosextend). For pediatric patients, this is a good spot for things like birth history. Physical: Document a complete baseline physical in this section once you have had the chance to perform one. Several quick keys bring up templates for a complete physical exam: px is an extended physical exam template, GeriPE is a geriatric physical exam. Using (+) (-) and __ The underscores are designed for easy completion of templates. You can use F12 to jump from underscore to underscore to type in findings. Also, by clicking on an underscore, it changes it to a (+) or (-). The (+) will print as either “reported” in the Subjective field or “noted” in the Objective field. The (-) will print as “denied” in the Subjective field and “ABN not detected” in the Objective field. One should replace the under lines with either text (typing) or change to a (+) or (–) if addressed in the visit. Delete All Underlines When the documentation is complete, to delete unused sections of the expanded quick keys, under the Edit Menu is a “Remove All Underlines” command which will delete all text between periods where an underline appears unchanged. Entering Vital Signs 1. Click the Vital Signs tab, 2. New Column, 3. Enter Vital Signs for that day in the format specified. 4. BMI is calculated from the Height and Weight of the patient, so always enter the height of the patient. 5. Click OK. Vital Signs Window 6 Create a New Encounter SOAP note File Menu New Encounter. When the new note opens you will see a blank encounter note Complete the note. There are a lot of quick keys that will make completing the note faster. Save typing meds and problems list Under Edit menu are the commands SOAP to Summary and Summary to SOAP. This sends the contents of the Meds List, Problems list and physical exam to the note. Cut (CTRL-X), Copy (CTRL-C) and Paste (CTRL-V) SOAPnote work in SOAPware just like Word or PowerPoint. Right click in any area to get the Codes List of quick keys for that section. Do not use the comlete SOAPware templates for encounter notes. If you want to create a template, however, it is allowed for you to use your original template. Print Printing the note shows you how the note looks with the (+) and (-) replaced by the words either denied, reported, observed, etc. You can choose to Print Preview the note and not send it to the printer, but store it instead. Signing the Note – Recommended to Not Sign Notes Electronic Signatures: Once the note is complete, you have received feedback from your informatics curriculum director and made modifications to it, you can electronically sign then print the encounter. Signing the note finalizes the note and changes cannot be made to the note after you sign it. This is under the File Menu. You can leave a note open and sign it days later if you wish, even close and reopen the chart. The note will be there waiting for you in your To Do list (under File Menu) with all other documents needing signatures. So do not sign until you are through with the note. It will sit in the record unsigned. 7 Chart Browser All Messages, Reports, Encounters and Flow Sheets tabs on the Summary side of the screen open the Chart Browser shown here, which organize these entries and saves them by date/time. Chart Browser Flow Sheets: Flow sheets allow you to follow all the aspects of a chronic disease in one place. Here is where the patient’s disease progression can be viewed and graphed. They can pull data from different areas of the record like vital signs and health maintenance items. We will use Flow Sheets instead of the Lab Reports used last year to record patient pertinent labs. To insert a Flow Sheet, in the 1. Chart Browser tab 2. Flow Sheets 3. New 4. Pick from list of available Flow Sheets. a. Pick the Chronic Disease of your patient you are choosing to follow: ADHD, Asthma, cystic fibrosis, CHF, HTN, hyperlipidemia COPD, depression, diabetes, obesity, osteoarthritis b. lab panels: lipids, LFT, CBC, basic metabolic panel c. growth charts, etc. 5. Be patient, these are slow to come up. 6. In the chronic disease flow sheets, if you have 8 entered vital signs, a column will be created for you. Complete the column with findings for current visit. 7. If no column is there, click Add Col, putting in the date of the visit, and complete with findings for current visit. Use this same flow sheet to follow the patient’s progress, adding columns with each visit. Hyperlipidemia Flow Sheet You can select from one of the Flow Sheets for each of the diseases. There are some pediatric growth flow sheets, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and several other chronic diseases. Customizing Flow Sheets, 1. View Menu > Customization Wizards > Edit Flow Sheets. 2. To Add or modify items on an existing flow sheet, a. Click on the Flow Sheet you wish to edit, then click Edit b. Pick an item on the left that you want to remove and click on it. Click the -> button. c. Pick an item on the right that you want to add and click on it. Click the <- button. d. If the item you want to add is not on the list at the right, click Manage Items. i. Click New ii. Complete the form at right. This can be a number, a pick list in which case you will need to add items to pick from 9 at bottom, Start/Stop which gives you only those options, or just a text box to write in. iii. Click OK e. Then add the new item to the existing Flow Sheet. 3. To create a new Flow Sheet, on the Edit Flow Sheets screen a. Click Add b. Type in the name and description of the new Flow Sheet, and click c. Select items on the right and click the <- to add them to the new Flow Sheet d. Items that start with Lab are pulled from the Lab Reports section. This would require you to complete a Lab Report on each lab finding. Use lab tests that don’t start with the word Lab. Those labeled VS are pulled from the Vital Signs flow sheet. e. If you need items not there, follow the instructions above to add new items. Sample Flow Sheet Items Diabetes Vitals Wt BMI BP Pulse RR Labs/tests HbA1c Lipids Fasting Glucose Microalbumin Meds/doses Comments Mental Health Diet Foot Exam Exercise Hypoglycemic episodes? Compliance Asthma Obesity Vitals BMI BP Pulse RR Vitals Wt BMI BP Pulse RR Labs/tests Lipids Fasting Glucose Labs/tests Peak Flow PFT-FEV1 PFT-FVC Spirometry Meds/doses Comments Compliance Exacerbations Inhaler Use Nebulizer Use Mental Health Meds/doses Comments Diet Exercise Lifestyle Mental Health Body Image Compliance Sleep Apnea 10 Reminder System (Health Maintenance): SOAPware will remind you every time you open the patient’s chart if they are overdue for any procedure, lab, counseling, or screening. You will need to set up the patient’s Reminder System (Health Maintenance) schedule. First decide what items you need to put in this patient’s reminder system. To set up a patient’s health maintenance schedule, with the patient’s chart open, 1. View Menu, 2. Select Health Maintenance. The first time you will see the blank Health Maintenance box (right). 3. Click Add Blank Health Maintenance Form 4. Where it says View by, change from Protocols to Rules. 5. Click on an item to add to the patient’s reminders, then click OK, 6. Set the Frequency this item a. Beside the Frequency box click Add b. Complete the Interval Definition box. Click OK c. Then enter the Date Performed and click the Perform button. d. It should automatically tell you when the next one is due. If overdue, a Red Check will appear next to the Active Item on the left. If within the Variance of the due date, the check will be Yellow. Adjust the variance accordingly. List of HM Rules 11 7. Continue adding rules until your Reminder System is complete. a. If your preceptor handles this patient’s health maintenance issues, add these items based on USPSTF recommendations for a patient this age and gender, like colon CA screenings, flu shots, pneumovax, etc. b. Add items for the major disease you have chosen to follow for this patient: i.e. if diabetes add A1c, retinal exam, microalbinurea, etc. Do not repeat items on the flow sheet as the flow sheets will remind you of these items. If you address an item during a visit, click on the item in question, like Cholesterol, Under Date Performed, select today’s date, then click Perform, which will tell the system that this was performed today. To Customize Health Maintenance Rules and Protocols 1. View menu, 2. Customizations Wizards, 3. Edit Health Maintenance Protocols 4. To create a protocol that contains many rules like the immunizations protocol, a. Click on Unfiled then click New Protocol b. Now you must expand Unfiled, click on the new protocol and click Edit Protocol. c. Give it a name and description, then click OK d. Click on one rule at a time at right and click the Add button to add it to the protocol. 5. To Add or edit existing Rules a. under Unfiled, pick All Rules, b. Click Edit Protocol c. To add a new Rule, Click on New Rule, fill out form with name, description, frequency and variance and click OK d. To Edit a Rule, Click on a Rule under Available Rules and click Edit Rule. Change the name, description, frequency etc and click OK 12 How to export your patient charts to a ZIP file and place on the Sharepoint SOAPware site so that they can be evaluated by faculty. 1. IN SOAPware: The patients must be in the PULLED charts rack already. They will probably be there already. You are only dealing with 6 patients total. Select the FILE menu and EXPORT … 2. Backspace over the SW_Exported_Charts default filename and use YOUR NAME as the file name in this format: firstname_lastname (Use the underscore character, not a space) 3. CLICK on SAVE…. 4. The next screen brings up the list of patients in the pulled charts rack. Select the patients in your final panel of 6. If you do not select the patient names, no files will export. 5. You now have a file with your firstname_lastname.zip on your desktop or in My Documents or wherever you saved it. 6. Next, you need to upload this file to the sharepoint SOAPware site. 7. Go to FSU Med School Website 8. Click on Intranet 9. Click on SOAPware Information https://mcintranet.med.fsu.edu/sites/academicaffair s/ome/Informatics/SOAPware You can click on this link to take you to the same place. PLEASE NOTE: If you are NOT on campus, and you go to the Sharepoint Portal, you may be prompted for userid and password … MAKE SURE YOU PRECEED YOUR LOGIN NAME WITH “med\userid” You must include the domain name preceding your login name. 10. At the SOAPware Sharepoint site, on the left you will see document libraries for each Regional Campus … click on the correct RC, and then UPLOAD the zip file containing your patient charts. 11. As the year goes by, to save your Informatics Curriculum Director time, each month send an email with a list of patient charts that have changed so he/she won’t waste time reviewing data you have not changed since the last month. 13