Large Intestine - Honors Class Help
advertisement

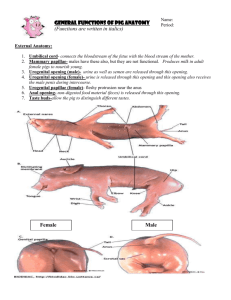
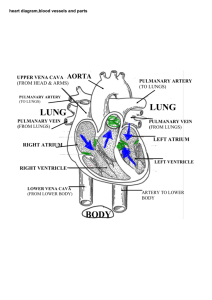
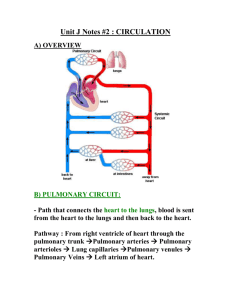
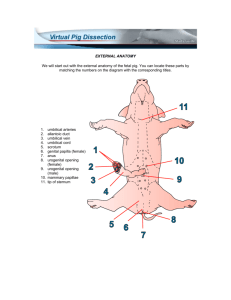
Structure Function Digestive System Esophagus - Muscular tube that carries food and liquids from mouth to stomach Stomach - Storage and digestion of food Liver - Creates bile, aids in digestion, creates some blood proteins Gall Bladder – Stores and secretes bile which helps digest fats in the small intestine Small Intestine - Digestion of food and absorption of nutrients Large Intestine - Reabsorbs water Rectum - Lowest portion of the large intestine that connects to the anus. Collects waste for expulsion from body Anus - Expulsion of solid waste from the body Pancreas - Secretes digestive fluid into sm. intestine and insulin into bloodstream *Cardiac Sphincter - Muscular ring between esophagus and stomach *Pyloric Sphincter - Muscular ring between stomach and sm. Intestine Spleen - Destroys old blood cells, stores blood, produces white blood cells Epiglottis - Fold of skin to close the trachea while swallowing Appendix - Accessory part of a bodily organ, attached to large intestine Mesentery – Thin layer of skin holding intestines together Papillae – Taste buds, located on the end and base of the tongue Salivary glands - glands located in the mouth that produce saliva. Saliva contains enzymes that break down carbohydrates (starch) into smaller molecules. Duodenum - The beginning portion of the small intestine; it is C-shaped and runs from the stomach to the jejunum. Peritoneum - The serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal cavity and folds inward to enclose the viscera. common bile duct -duct in the liver through which bile leaves Circulatory Vena Cava - Oxygen poor blood returns to (heart) right atrium Aorta - Carries O2 rich blood away from the heart and distributes it throughout the body Coronary Artery - Supplies O2 rich blood to the heart itself Right Atrium - Receives O2 poor blood from body. Sends blood to right ventricle Left Atrium - Receives O2 rich blood from the lungs Right Ventricle - Receives O2 poor blood from right atrium and sends it to lungs Left Ventricle - Receives O2 rich blood from left atrium and sends it to the body Pericardium - Protective membrane that encloses the heart Tricuspid Valve - Controls the flow of blood from the right atrium to the right ventricle Bicuspid Valve - Controls the flow of blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle Pulmonary Artery - Transports O2 poor blood to the lungs Thymus Gland – Aids the immune system Thyroid Gland - Gland found in all vertebrates which regulates the rate at which your body carries on its necessary functions Spleen - Destroys old blood cells, stores blood, produces white blood cells aorta -major systemic artery that originates from the left ventricle of the heart pulmonary vein -major vein carrying oxygen rich blood from the lungs to the heart renal artery -major artery supplying blood to the kidney renal vein -major vein taking blood from the kidney into the postcaval vein ductus arteriosus -connection between the pulmonary artery and aorta that prevents much of the blood from reaching the lungs during fetal development Respiratory Glottis - Vocal apparatus of the Larynx Nares - Passageways for air to enter the trachea; nostrils Larynx - Walls of muscle and cartilage that contains the vocal cords Trachea - Transports air from mouth/nose to lungs and lungs to mouth/nose Lungs - Site of Gas (CO2 and O2) exchange Diaphragm - Muscular membrane separating abdominal and thoracic cavity. Helps breathing process Thoracic cavity - Chest cavity including the heart, lungs, trachea, area between the neck region and the diaphragm. Epiglottis - The thin elastic cartilaginous structure located at the root of the tongue that folds over the e glottis to prevent food and liquid from entering the trachea during the act of swallowing. Excretory - Removes metabolic wastes and foreign substances from body Kidney - Extracts waste and foreign substances from the bloodstream Ureter - Transports urine from kidneys to bladder Urinary Bladder - Stores urine Urethra - Allows urine to exit the body (from bladder to outside body) Reproductive Male Testes - Male reproductive gland which produces sperm Epididymis - Sperm duct that carries sperm away from testes to vas deferens Penis - The male organ of copulation and of urinary excretion Vas Deferens - A duct that carries sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct Female Ovaries - Female reproductive organ that stores eggs and produces estrogen and progesterone Fallopian Tubes - Duct that carries eggs from Ovary to uterus Uterus - Hollow muscular organ located in the pelvic cavity of female mammals in which the fertilized egg implants and develops Vagina - Genital canal leading from the opening of the vulva to the cervix Nervous Cerebrum - The large, rounded structure of the brain occupying most of the cranial cavity, divided into two cerebral hemispheres that are joined at the bottom by the corpus callosum. It controls and integrates motor, sensory, and higher mental functions, such as thought, reason, emotion, and memory. cerebellum -region of the brain involved with coordination of skeletal muscle activity; located posteriorly and caudally to the cerebrum brainstem -collective term used to describe the area of the brain containing the pons and the medulla spinal cord -column of nerve tissue running from the brain down the vertebral column; contains sensory, motor and association tracts Hypothalamus- controls emotions; brain Medulla- lower part of brainstem, controls blood pressure, breathing, automatic functions External: umbilical cord-term referring to the cord supplying nourishment to and waste removal from the fetus umbilical arteries -pair of arteries that return blood from the fetus to the placenta; located within the umbilical cord umbilical vein -carries oxygenated blood from the placenta into the fetus; located within the umbilical cord urogenital opening-common area in the female into which both the vagina and urethra open kidney -excretory organ responsible for the filtration of waste products from the blood nephrons structural and functional units of the kidney; filtering components Dorsal- back Ventral- front Other “blue baby”- An infant born with cyanosis as a result of a congenital cardiac or pulmonary defect that causes inadequate oxygenation of the blood. Diagrams: