General Functions of Pig Anatomy
advertisement

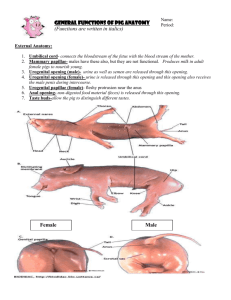
General Functions of Pig Anatomy (Functions are written in italics) Name: Period: External Anatomy: 1. Umbilical cord- connects the bloodstream of the fetus with the blood stream of the mother. 2. Mammary papillae- males have these also, but they are not functional. Produces milk in adult female pigs to nourish young. 3. Urogenital opening (male)- urine as well as semen are released through this opening. 4. Urogenital opening (female)- urine is released through this opening and this opening also receives the male penis during intercourse. 5. Anal opening- non-digested food material (feces) is released through this opening. 6. Glottis- the opening between the vocal cords at the upper part of the palate. Covers the trachea when you swallow so food goes down the esophagus. 7. Hard Palate- the relatively hard, bony anterior portion of the palate 8. Soft Palate- the movable fold that is suspended from the rear of the hard palate and closes off the nasal cavity from the oral cavity during swallowing or sucking. 9. Taste buds-allow the pig to distinguish different tastes. Endocrine System: 1. Thymus Gland: located on the pericardium on the upper part of the heart and also has arms that extend into the neck. White blood cells produced in the bone marrow travel here to mature. 2. Thyroid Gland: small reddish gland located at the base of the neck. Produces several hormones which regulate both the metabolic rate (how much energy you produce by burning up glucose) and the amount of calcium in your blood. Respiratory System: 1. Diaphragm- a muscular wall that divides the chest (pleural) cavity from the abdominal (peritoneal) cavity. Contracts and relaxes helping to force air into and out of the lungs. 2. Larynx- Voice box of the pig. Allows the pig to “oink” 3. Lungs- Allows oxygen to diffuse into the bloodstream as carbon dioxide is being released from the bloodstream. 4. Trachea- Carries air between the lungs and the throat. Lymphatic System: 1. Spleen: flattened organ attached to the stomach by the greater omentum. Stores extra red blood cells in case of blood loss. Stores white blood cells used in fighting off foreign substances. Digestive System 1. Stomach- sack which stores food so you don’t have to eat every two hours. Stores and partially digests food. 2. Liver- The largest internal organ of the body. Makes bile, which aids in the digestion of fat. Detoxifies poisons like alcohol. Stores extra glucose in the form of starch. 3. Gall Bladder- Sack on the bottom of one of the liver lobes. Stores bile until it is ready to move into the duodenum. 4. Esophagus- tube leading from the throat to the stomach. Muscular contractions push food from mouth the stomach. 5. Pyloric Sphincter- ring of muscle that closes off the opening between the stomach and the small intestine. Ensures that food stays in the stomach long enough to complete digestion. 6. Duodenum- The first part of the small intestine which has ducts (tubes) leading into it from the liver/gall bladder and pancreas. Bile and pancreatic enzymes are mixed with food here. 7. Jejuno-ileum- All the small intestine except for the duodenum. Digestion of food is completed here and nutrients are absorbed through its walls into the blood stream. 8. Caecum-a pouch off the digestive tract between the small intestine and the colon. Produces enzymes that digest cellulose. 9. Spiral colon-spiraled part of the large intestine. Absorbs water, vitamins, and minerals from the food and moves them into the bloodstream. 10. Descending colon- The part of the large intestine leading from the spiral colon down to the rectum. Same function as the spiral colon. 11. Pancreas- Makes digestive enzymes that are used in the small intestine. Makes the hormone, insulin, which regulates the amount of sugar in the blood 12. Bile duct-.brings bile from the gall bladder and liver to the duodenum. Excretory System: 1. Kidneys: Removes excess water and wastes such as urea and salts from the blood. This fluid is know as urine. 2. Ureters: Carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. 3. Urinary Bladder: sack located on the lower ventral body wall between the two umbilical arteries. Stores urine until it is eliminated from the body. Reproductive System: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Ovaries: Produces the eggs in the female and also produces the hormones estrogen and progesterone which in turn regulate the menstrual cycle. Fallopian tubes: Move the egg toward the uterus. Fertilization takes place here. Uterus: The embryo connects to the mother’s bloodstream here with the development of the placenta. Fetus develops here. Vas deferens: Moves sperm up and into the penis during ejaculation. Testes: Produces sperm as well as the hormone testosterone. Scrotum: Holds the testes outside the body cavity, keeping the sperm at the right temperature in order to remain alive. Circulatory System: 1. Umbilical Vein: Carries blood rich in Oxygen and food from the placenta of the mother to the fetus. 2. Umbilical Artery: Carries blood through the umbilical cord low in oxygen and food from the fetus to the placenta of the mother. 3. Right Atrium- Collects blood low in oxygen and filled with food from the body and pumps it into the right ventricle. 4. Right Ventricle- Collects blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs. 5. Left Atrium- Collects blood from the lungs rich in oxygen and food and pumps it to the left ventricle. 6. Left Ventricle- Collects blood from the left atrium and pumps it throughout the body. 7. Pericardium- a membrane (mesentery) surrounding the heart. Secretes a watery fluid to prevent the heart from rubbing against surrounding organs when it beats. 8. Coronary Vein- blue blood vessel located on the front (ventral) surface of the heart. (May not be injected in all pigs.) Drains the heart muscle tissue of blood and moves it back into the right atrium. 9. Coronary Artery- red blood vessel located on the front (ventral) surface of the heart. (May not be injected in all pigs) Brings blood from the aorta and supplies the heart muscle tissue with food and oxygen. 10. Pulmonary Trunk- takes blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. 11. Aortic Arch- behind the pulmonary trunk and forming an arch leading toward the lower part of the body. Carries blood rich in food and oxygen from the left ventricle to all parts of the body. 12. Dorsal Aorta- continuation of the aorta along the dorsal body wall behind the lungs, liver, and small intestine. Carries blood rich in food and oxygen to the lower body organs and to the legs. 13. Posterior Vena Cava- Brings blood through the umbilical cord low in oxygen and rich in carbon dioxide from the lower body to the right atrium. 14. Superior Vena Cava-Brings blood low in oxygen and rich in CO2 from the upper body to the heart. 15. Pulmonary Artery- an artery that carries low O2 blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs. 16. Pulmonay Vein- a vein that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart (left atrium) Membranes/Cavities: 1. Parietal pleura and parietal peritoneum- membranes which line the chest and abdominal cavity. Secrete watery fluids to lubricate the movement of internal organs. 2. Visceral pleura and visceral peritoneum- membranes which directly cover organs in the chest and abdominal cavity. Secrete watery fluids to lubricate the movement of internal organs. 3. Greater Omentum- a membrane (mesentery). Holds the spleen in place by attaching it to the stomach. 4. Intestinal mesentery- any of several folds of the peritoneum that connect the intestines to the dorsal abdominal wall, especially found around the jejunum and ileum.