Chapter 7 - Cloudfront.net
advertisement
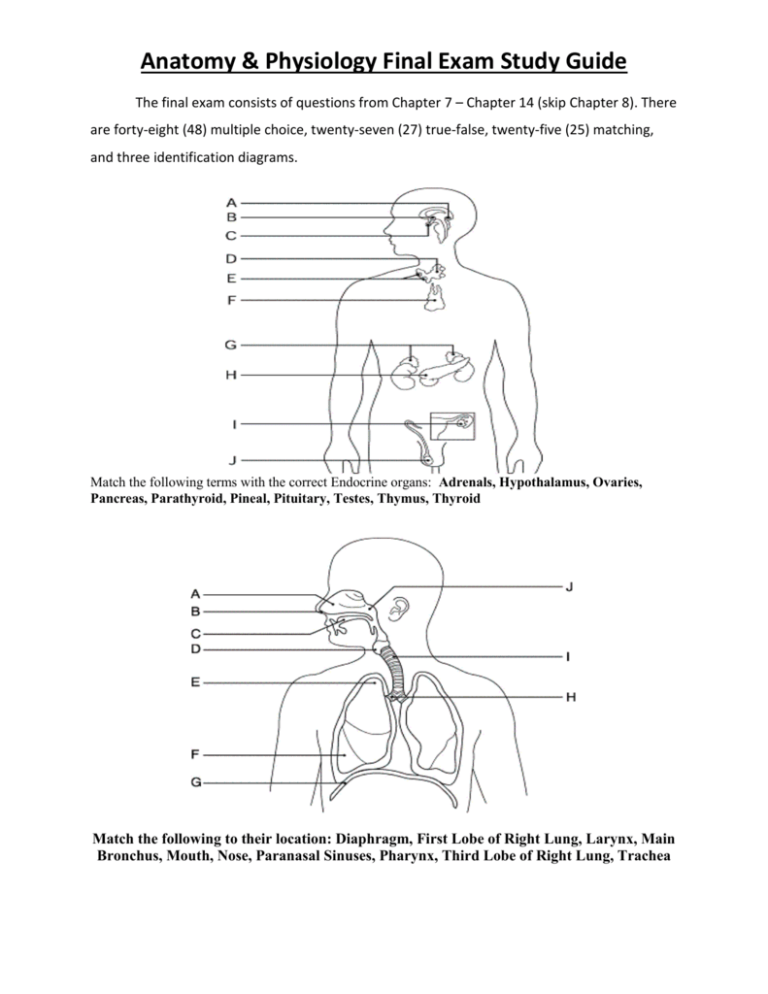
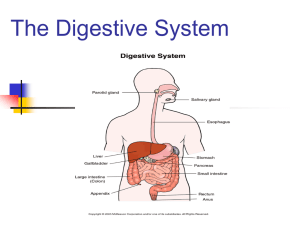
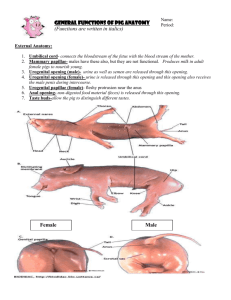
Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide The final exam consists of questions from Chapter 7 – Chapter 14 (skip Chapter 8). There are forty-eight (48) multiple choice, twenty-seven (27) true-false, twenty-five (25) matching, and three identification diagrams. Match the following terms with the correct Endocrine organs: Adrenals, Hypothalamus, Ovaries, Pancreas, Parathyroid, Pineal, Pituitary, Testes, Thymus, Thyroid Match the following to their location: Diaphragm, First Lobe of Right Lung, Larynx, Main Bronchus, Mouth, Nose, Paranasal Sinuses, Pharynx, Third Lobe of Right Lung, Trachea Match the following terms: Anus, Appendix, Esophagus, Gallbladder, Large Intestine, Liver, Mouth, Pancreas, Pharynx, Rectum, Salivary Glands, Small Intestine, Spleen, Stomach, and Tongue Chapter 7 Define the following divisions of the nervous system. Central Nervous System (CNS) – Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Autonomic Nervous System – Collections of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS are called _______________________. The gap between two communicating neurons is termed the _______________________. The ____________________ reflex involves skeletal muscles. What are the three regions of the brain stem? What does the medulla oblongata control? The _________________ plexus serves the shoulder and arm. Match the following brain regions to their main actions: Broca’s Area Auditory (hearing) area Occipital Lobe Primary somatic sensory area Parietal Lobe Motor speech Posterior Association Area Recognizing patterns/faces Temporal Lobe Visual (seeing) area Chapter 9 A ___________________ occurs when the thyroid gland enlarges due to a low iodine diet. The____________________________ produces antidiuretic hormone. __________________ production peaks during the night to help regulate sleep/awake cycles. The hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary are actually made in the ________________. The main target of insulin is ____________________ levels of the blood. What is Addison’s disease? What is Grave’s disease? What is Cushing’s syndrome? Insulin is produced by cells of the pancreatic islets called ________________________. The _____________________ gland is located in the neck surrounding the trachea. Match the hormone with the action it performs: Calcitonin Stimulates contractions; bonding hormone Growth Hormone Lowers blood calcium levels Insulin Involved in daily sleep awake cycles Melatonin Regulates growth rates in the body Oxytocin Lowers blood glucose levels Chapter 10/Chapter 11 Your ____________________ is the percentage of erythrocytes in your blood. Living at high altitudes for a long period of time could result in _______________________. Blood normally takes _________________ minutes to clot. How are red blood cells and white blood cells different? The volume of blood pumped out with each ventricular contraction is known as _______________________. ________________________ carry oxygenated blood back to the heart from the lungs. The ________________ valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle. ___________________ makes up the majority of blood content. An abnormal increase in red blood cells is called _______________________. Match the following parts of the heart with their primary actions: Aorta Receives blood from superior/inferior vena cava Left Atrium Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs Left Ventricle Receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary vein Right Atrium Pumps blood out of the heart to rest of body Right Ventricle Largest blood vessel in the body What are the differences between veins, arteries, and capillaries? Chapter 12 The _______________ are lymphoid tissues that trap and remove bacteria entering the throat. Lymph tissues found within the walls of the small intestine are called _____________________. The first line of defense against an attack from a potential invader is _____________________. B cells develop immunocompetence in the _________________________. What specific type of acquired immunity is provided by vaccines? ___________________ are tissue grafts taken from an unrelated person, while ___________________ are tissue grafts taken from an identical twin. Chapter 13 What are the four main events of respiration? The process of breathing is called ____________________________. Oxygen enters the trachea and then passes into the ____________________ before the lungs. Removal of the _____________________ would result in the inability to speak. Extremely slow breathing is termed ____________________________. The emergency surgical opening of the trachea is called a ______________________. What is SIDS? Chapter 14 The majority of nutrient absorption takes place in the ________________________________. The process of mixing food back and forth in the small intestine is called _______________________. ________________________ converts milk protein into sour milk in infants. The purpose of mastication is to ___________________________________. Chyme spends approximately _______________ hours in the small intestine. ____________________ is the process by which larger molecules are built from smaller ones, while __________________ is the process of breaking down larger molecules into smaller ones. What are the four main functions of the alimentary canal? Proteins are broken down into smaller molecules called _________________________. Match each organ with it main role in digestion: Esophagus Vast majority of nutrient absorption Large Intestine Moves food from mouth to stomach Liver Breaks down food with hydrochloric acid Small Intestine Produces bile to store in gallbladder Stomach Absorbs water/vitamin K before defecation Chapter 15 The term _______________________ describes the location of the kidneys in the body. The triangular regions of the kidneys separated by columns are called renal ________________. What is glomerular filtration? What is tubular reabsorption? What substances are typically reabsorbed in this process? Kidney inflammation is called ___________________________. The process of emptying the bladder is called voiding or ______________________. The average adult produces _____________mL of urine in a day. The pigment that gives urine its yellow color is called _______________________. What is the urethra? What are the differences between the male and female urethra? What are the two sphincters found around the urethra? Which is controlled by smooth muscle? Which is controlled by skeletal muscle?