File
advertisement

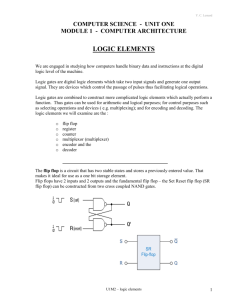
B.S Anangpuria Institute of Technology & Management Branch: CSE/IT (4th SEM) Session-2009 Computer Architecture and Organization CSE – 210-E Unit -1 Basic Principles Lecture – 3: • Sequential logic Blocks Latches Flip flops Registers Counters Submitted by: Prerna Mittal 1 • Sequential logic Blocks : logic blocks whose output logic value depends on the input values and the state of the blocks – In this we have the concept of memory which was not applicable for combinational circuits. The various sequential blocks or circuits are: Latches: • A latch is a kind of bistable multivibrator, an electronic circuit which has two stable states and thereby can store one bit of information. Today the word is mainly used for simple transparent storage elements, while slightly more advanced non-transparent (or clocked) devices are described as flip-flops. Informally, as this distinction is quite new, the two words are sometimes used interchangeably. S-R latch: To overcome the restricted combination, one can add gates to the inputs that would convert (S,R) = (1,1) to one of non-restricted combinations. That can be: Q = 1 (1,0) — referred to as an S-latch Q = 0 (0,1) — referred to as an R-latch Keep state (0,0) — referred to as an E-latch D-LATCH Forbidden input values are forced not to occur by using an inverter between the inputs. 2 D Q Q E (enable) E Q’ D(data) D 0 1 Q(t+1) 0 1 D E Q’ Q Q’ Flip Flops: D – flip flop: 3 If you compare the D-flip flop and D – latch the only difference you find in the circuit is that latches do not have clocks and flip – flops have it. So you can note down the difference between latches and flip – flops as: • Latch is an edge triggered device whereas Flip flop is a level triggered. • The output of a latch changes independent of a clock signal whereas the Output of a Flip - Flop changes at specific times determined by a clocking signal. • In Latch We do not require clock pulses and flip flops are clocked devices. Characteristics - State transition occurs at the rising edge or falling edge of the clock pulse Latches respond to the input only during these periods Edge-triggered Flip Flops (positive) respond to the input only at this time 4 Counters: A counter is a device which stores (and sometimes displays) the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock signal. 4 – bit binary counter: A0 A1 A2 A3 Q Q Q Q J K J K J K J K Clock Counter Enable Output Carry RING COUNTER: In Ring Counter the output of 1st flip flop is moved to the input of 2nd flip flop. 5 JOHNSON COUNTER : In Johnson counter the output of last flip flop is inverted and given to the first flip flop. Registers: It refers to a group of flip-flops operating as a coherent unit to hold data. This is different from a counter, which is a group of flip-flops operating to generate new data by tabulating it. 6 Shift register: A register that is capable of shifting data one bit at a time is called a shift register. The logical configuration of a serial shift register consists of a chain of flip-flops connected in cascade, with the output of one flip-flop being connected to the input of its neighbor. The operation of the shift register is synchronous; thus each flip-flop is connected to a common clock. Using D flip-flops forms the simplest type of shiftregisters. Bi- directional shift register with parallel load A0 A1 A2 A3 Q Q Q Q D C D C D C D C 4x1 MUX Clock S0S1 SeriaI I0 Input 4x1 MUX 4x1 MUX I1 4x1 MUX I2 Serial I3 Input Summary: 7 Sequential circuits: output logic value depends on the input values and the state of the blocks. These circuits have memory. Various combinational circuits are: o Latches: An electronic circuit which has two stable states and thereby can store one bit of information o Flip flops: It also has 2 stable states but with memory. o Counter: A device which stores number of times a particular event or process has occurred. o Registers: A group of flip-flops operating as a coherent unit to hold data. Important Questions derived from this: Q1. What is the difference in latch and flip flop? Q2. Explain Johnson counter? Q3. Draw shift register with parallel load. 8