File
advertisement

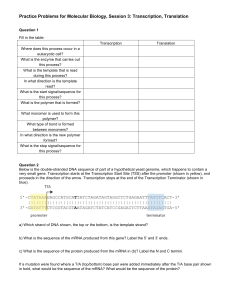
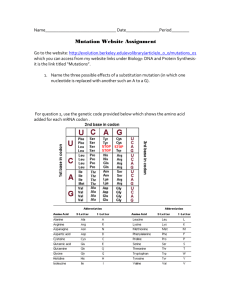
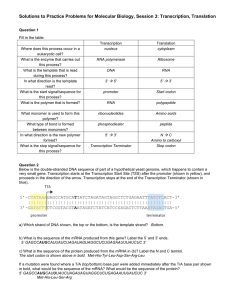
http://bcs.whfreeman.com/hillis1e/#667501__669671__ Animated Tutorial 10.1 Transcription 1. What is the goal of transcription as the initial step in protein creation? 2. What does the RNA polymerase do? What does it bind to in order to start the process? 3. What is occurring during the elongation phase of transcription? 4. In comparison to DNA, what are 3 distinct differences in RNA? 5. What happens to the DNA strand once, RNA is made and the termination site is reached? Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Animated Tutorial 10.2 RNA Splicing 1. Differentiate pre-mRNA and mRNA. 2. What do we call regions of mRNA that are noncoding? 3. What binds to the introns for removal? 4. When these come together what does it form? 5. Following transcription, where is the mature mRNA molecule migrate to from the nucleus? What is it translated into? Quiz 1. 2. 3. Animated Tutorial 10.3 Deciphering the Genetic Code 1. How many nucleotides constitute a codon sequence? 2. Through experimentation, what are the 3 requirements learned that are needed to create a protein? 3. Why is AUG a unique codon? 4. What would be the amino acid sequence for the following mRNA strand: AUG-GAU-UGGUGA? 5. Why are there only 20 amino acids if there are 64 possible combinations of nucleotides? Quiz 1. 2. 3. Animated Tutorial 10.4 Protein Synthesis 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What are the 3 steps of translation? Where is translation occurring in the cell? What occurs in the A site of the large ribosomal subunit? What occurs in the P site of the large ribosomal subunit? What occurs in the E site of the large ribosomal subunit? What does a stop codon bind? Describe the complementary nature of the mRNA strand and the tRNA molecule. Quiz 1. 2. 3. Activity 10.1 Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Summarize the steps involved in protein synthesis utilizing the words in this activity. Activity 10.2 The Genetic Code 1. What is the amino acid for the mRNA codon UGU: 2. What is the amino acid for the anticodon UAU: 3. What is the amino acid for the anticodon CUG (remember this is the 5’ to 3’ direction and the mRNA will be 3’ to 5’ because the strands are antiparallel: 4. What is the amino acid the DNA template strand GAA: 5. What is the amino acid the DNA complementary strand CTC: Interactive Tutorial 10.1 Genetic Mutations 1. What type of mutation did the first problem end up resulting in? How did you come to this conclusion? How would this affect the reaction? 2. What type of mutation did the second problem end up resulting in? How did you come to this conclusion? How would this affect the reaction? 3. What type of mutation did the third problem end up resulting in? How did you come to this conclusion? How would this affect the reaction? 4. How does a silent mutation affect a protein and the rate of a reaction? 5. How does a nonsense mutation affect a protein and the rate of a reaction? 6. How does a missense mutation affect a protein and the rate of a reaction? 7. How does a frameshift mutation affect a protein and the rate of a reaction? Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. Study Chapter 10 Flashcards and Key Terms