Accounting 40S
advertisement

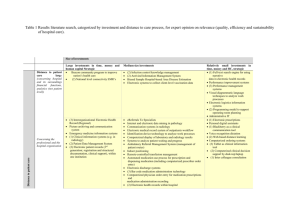
Accounting Principles 40S Course Outline Teacher: Mr. Doyle Room: 236 Textbook: Principles of Accounting 2nd edition (D’Amico) Software: Excel and Simply Accounting The students will also use the Intranet for material. Students will build upon and expand accounting principles and concepts introduced in Accounting Principles 30S with a focus on merchandise and computerized accounting. The creation and maintenance of computer accounting records are an integral part of the curriculum. Problem solving skills using computers, business oriented skills; business ethics, communication and technology are incorporated throughout the course. General Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of the Accounting Principles 40S course, students will: Understand the nature of accounting and the accounting cycle. Demonstrate accounting-related skills, including analysis and interpretation. Use the processes of accounting for problem solving and decision making. Demonstrate knowledge about the integration of accounting and technology. Use technology to enhance accounting procedures. (Excel and Simply) Pursue interests that lead to an enriched lifestyle and life-long learning. Expectations: All students must attend class regularly and be on time. Use of cell phones is prohibited. Use of music players is at the discretion of the teacher. All assignments must be submitted on time. Proper use of computer equipment is mandatory at all times. Any test or quiz that is missed without proper justification will result in a mark of zero. Cheating or plagiarism WILL NOT BE TOLERATED. This will result in a mark of ZERO for all people involved, whether giving or receiving the material. Evaluation: Projects, quizzes and tests are 70% of the final grade. A final exam is held during exam week that is 30% of the final grade. If a student has a mark of 75% or more, he or she will be exempt from the exam. NOTE: There is one exception to this rule—if a student has cheated in any way, he or she will write the exam, regardless of their mark. Tests and quizzes account for about 60% of the mark. Assignments saved in their respective computer folder account for about 40% of the mark. Specific Outcomes for Accounting 40S: Manual accounting procedures are included to provide an understanding of the accounting concepts, principles and processes. These manual accounting procedures are used in a computerized accounting environment within each unit. Accounting Systems 40S will be taught using Excel and Simply Accounting as the primary software applications. Orientation and Review of Accounting 30S We will first review the basic accounting principles that were learned in Accounting 30S. Unit 1: An Introduction to Accounting Systems. Students will demonstrate the skills necessary to: Recognize the different accounting professions. Evaluate technology and communication in the accounting profession. Discuss the ethics of business and accounting. Understand and discuss Electronic Commerce. o Explain the concept of Internet banking. o Differentiate between bank credit cards and non-bank credit cards. o Determine credit card/debit card discount expense. o Explain credit card drafts. o Distinguish between debit cards and smart cards. Understand the need for computerized accounting systems. Compare and contrast the manual and the computerized accounting system. Understand Monetary Policy Unit 2: Receivables – Merchandise Sales & Receipts. Students will demonstrate the skills necessary to: Enter transactions into a computerized accounting software that involves sales and customer accounts through the sales journal. Enter transactions into a computerized accounting software that involve sales and customer accounts being paid through the receipts journal. Record transactions involving sales returns, allowances, and discounts as well as cheques that are returned by the bank, unable to be processed due to non-sufficient funds. Analyze reports that will help to develop skills for management positions. Unit 3: Payables – Merchandise Purchases & Payments. Students will demonstrate the skills necessary to: Enter transactions into a computerized accounting software that involve purchases and paying suppliers through the purchases journal. Enter transactions into a computerized accounting software that involve purchases and paying suppliers through the payments journal. Record transactions involving purchases returns, allowances, and discounts. Payments include full payment of account, partial payments, and prepayments or deposits. Payments may include discounts. Analyze reports that will help to develop skills for management positions. Unit 4: Merchandise Inventory in a Manual and a Computerized Accounting System. Students will demonstrate the skills necessary to: Distinguish between perpetual and periodic inventory systems. Analyze and compare journal entries for perpetual and periodic inventory systems. Discuss the implications and benefits of a computerized inventory system. Recognize the impact of inventory control on the value of the merchandise inventory. Prepare a cost of goods sold report. Apply the appropriate principles and concepts. Unit 5: Advanced Adjusting Entries. Students will demonstrate the skills necessary to: Distinguish between accrued expenses and accrued revenue. Calculate the accrued expenses. Analyze and record the entries for accrued expenses. Calculate the accrued revenue. Analyze and record the entries for accrued revenue. Distinguish between accrued and unearned revenue. Calculate the unearned revenue. Analyze and record the entries for unearned revenue. Apply the appropriate accounting principle. Unit 6: Special Transactions and Analysis. Students will demonstrate the skills necessary to: Differentiate between condensed and comparative income statements. Analyze and interpret comparative and condensed income statements. Interpret financial data using trend analysis and accounting ratios. Identify the equity section of a corporate balance sheet. Differentiate between owner’s equity and shareholders’ equity. Distinguish between common and preferred shares. Define retained earnings. Interpret the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet Compare and contrast liquidity, borrowing capacity, and profitability ratios Unit 7: Setting Up a Business – Accounts, Customers & Suppliers. (Simply) Students will demonstrate the skills necessary to: Convert manual accounting records to a computerized system for an existing business. Establish a computerized accounting system for a new business. Unit 8: Completing the Accounting Process in a Computerized Accounting System. Students will demonstrate the skills necessary to: Review the year end procedures in a manual accounting system. Apply the year end procedures to a computerized accounting system.