Thursday, June 3, 2010
advertisement

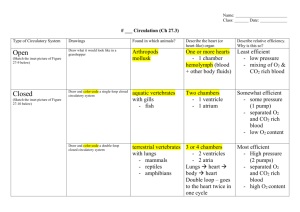
SBI3U Tuesday, June 3, 2008 Read Section 10.1 The Human Circulatory System and the Components of Blood pages 318-322 Describe the 3 essential components of a circulatory system Describe how the Circulatory, Digestive, Respiratory and Urinary systems work together to maintain homeostasis within the body List the components of blood and their relative percentages. Define all words in BOLD Why are Red Blood Cells unique? Describe the structure of a hemoglobin molecule (ensure you describe how many chains are present and what names are given to the chains – see Figure below). How many oxygen molecules (O2) does each hemoglobin molecule carrier within the blood stream? Assuming a person has 25 trillion (from textbook) RBCs in his/her body and each RBC picks up the maximum amount of oxygen each time through the lungs, how many oxygen molecules will be carried to all the tissues in one complete circuit of the person’s blood through the lungs? Handouts: The Components of Blood Answer the following, page 322: Understanding Concepts: 1, 2, 3, 4 Applying Inquiry/ Communication Skills: 5 Read Section 10.2 The Structure and Function of the Human Heart and Blood Vessels pages 323-333 Define all words in BOLD if they are referenced directly in the questions below. Describe the types of tissues found within the heart Describe how many chambers are found in the heart and their names (be specific). What is the function of each chamber (be specific). Name the 3 main circulatory systems within the body. Label the following Figure to the right. Describe the cardiac cycle (see Figure 10.11 and the Figure below) Describe the different types of blood vessels found within the body. Describe their structure (see Table 10.1). What is a capillary bed? Look at the Figure presented to the right. Give a logical explanation to what is happening and what could be regulating this process in the two Figures. This occurs in your body all the time without you knowing it. Describe how the heart’s muscular contractions are controlled? (see Figure 10.15 and the following Figure) What is an ECG? What information does it provide? What is Blood Pressure? How is it measured? What are normal readings for a healthy individual? How does blood pressure change within the circulatory system? (see Figure 10.19). Handouts: Heart Structure Circulatory System Concept Map Structure of the Human Heart The Circulatory System and the Human Heart The Sequence of Blood Flow Anatomy of the Heart Answer the following, page 334: Understanding Concepts: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 a to c, 6 Applying Inquiry/ Communication Skills: 7 a to e, 8 a to c