Cost Classification: Accounting Study Material
advertisement
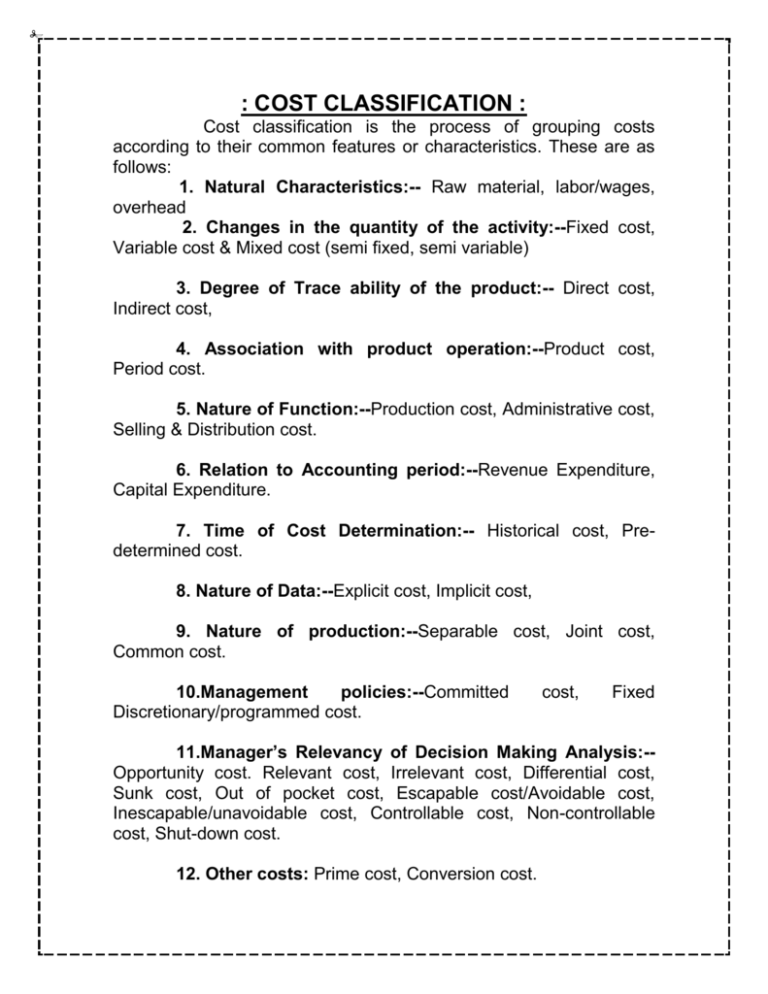
: COST CLASSIFICATION : Cost classification is the process of grouping costs according to their common features or characteristics. These are as follows: 1. Natural Characteristics:-- Raw material, labor/wages, overhead 2. Changes in the quantity of the activity:--Fixed cost, Variable cost & Mixed cost (semi fixed, semi variable) 3. Degree of Trace ability of the product:-- Direct cost, Indirect cost, 4. Association with product operation:--Product cost, Period cost. 5. Nature of Function:--Production cost, Administrative cost, Selling & Distribution cost. 6. Relation to Accounting period:--Revenue Expenditure, Capital Expenditure. 7. Time of Cost Determination:-- Historical cost, Predetermined cost. 8. Nature of Data:--Explicit cost, Implicit cost, 9. Nature of production:--Separable cost, Joint cost, Common cost. 10.Management policies:--Committed Discretionary/programmed cost. cost, Fixed 11.Manager’s Relevancy of Decision Making Analysis:-Opportunity cost. Relevant cost, Irrelevant cost, Differential cost, Sunk cost, Out of pocket cost, Escapable cost/Avoidable cost, Inescapable/unavoidable cost, Controllable cost, Non-controllable cost, Shut-down cost. 12. Other costs: Prime cost, Conversion cost. 1) Fixed cost:---The costs which are not changed with the increase /decrease in the production. Such as Depreciation on machinery, maintenance of production, manager’s salary, factory rent, factory electricity. The fixed costs are totally fixed, but the per unit fixed cost is decreased with the increase of the production. Such as-Production Dep. on Per unit Machine Quantity machinery Depreciation 1,000 10,000 10 2,000 10,000 5 5,000 10,000 2 10,000 10,000 1 2).Variable costs:---The costs which are changed with the increase/decrease in of production, are called variable cost. It always varies according to the level of the production. The variable cost always varies, but the per unit variable cost is fixed. Such as, wages of the workers. Production (Pant) 1 5 10 100 Used cloth (Meter) 1.50 7.50 15.00 150.00 Per unit cloth (Meter) 200 200 200 200 Total cloth cost 300 1500 3000 30,000 per unit pant 300 300 300 300 (*) Mixed cost (semi variable and semi mixed): -3. Semi fixed cost is also called step cost or ladder cost. Fixed cost remains fixed up to certain level of production. Fixed cost totally fixed, but per unit cost is variable. So it is called Semi fixed cost. SL No. of workers Supervision cost 1 10 5000 2 20 10,000 3 30 15,000 4 40 20,000 5 50 25,000 4. Semi variable cost is basically changing. Such as—maintenance of Machinery and repairing cost is semi-variable cost. Suppose, maintenance of machinery per month is TK. 10,000 and per hour repairing charge tk 200. So, it is called semi-variable cost. Product purchase unit Total cost (Tk). Per unit cost (Tk). 500 1000 2.00 1000 1500 1.50 1500 2100 1.40 2000 2600 1.30 2500 3000 1.20 5. Raw material cost:-Raw materials are used in production process of a product or services. The cost of this raw material is called Raw material cost. Again, the cost, which is related with purchasing or acquiring raw material, called material cost. It is also two types--i. Direct raw material. ii. Indirect raw material Product/Item 1. Garments (shirts). 2.Clothes 3. Jute item 4. Furniture Direct r/m Indirect raw material Clothes Cotton, button Thread, cotton, raw Color, starch cotton Jute Batching oil Wood Varnish, screw, 6. Labor cost/wages cost:-- The workers wages & salary which is related with production , is called labor cost., i.e. the cost of remuneration . Such as wages, salaries, commissions, bonuses etc. of employees of an undertakings. It is also two types: --- i. Direct labour. ii. Indirect labour. Direct labour Employees salary Employees wages, remuneration Indirect labour Cleaner, caretaker wages Night guard, manager salary 7. Overhead cost:--All the costs except material and labour related with the product, is called overhead cost. All indirect costs are called overhead cost. Indirect overhead cost Factory rent, office cost Depreciation on machinery etc. 8. Production costs:--All costs of manufacturing which are incurred in producing a product are called production costs. 9. Administrative cost:-All costs associated with the general management of the company as a whole (such as executive compensation, executive travel cost, secretarial salaries and depreciation of office Buildings and equipment). 10.Selling and Distribution cost:-All costs necessary to secure customer orders and get the finished product or service into the hands of the customer(Such as sales commission, advertising and depreciation of delivery equipment and finished goods warehouses. 11.Direct cost:-Which costs are directly related with the production is called direct cost. Direct costs are three types—Such as –Direct raw material, direct labour and direct expenses. i. Direct raw materials are those materials that became an integral part of the finished product and that can be physically and conveniently traced it. Such as Wood is the direct raw material for the producing table and chair ii.Direct labour are those labour that can be easily (physically and conveniently) traced to the individual units of product. Direct material + direct labour=Prime cost. iii.Direct expenses or costs are those that can be easily and conveniently trace to the particular cost objects. All the costs of manufacturing a product other than direct materials and direct labour(such as-indirect materials, indirect labour, factory utilities and depreciation of factory buildings and equipment.) Direct labour + manufacturing cost=Conversion Cost. 12. Indirect cost:-Which costs are not directly related with the production, are called indirect cost. Indirect cost are three types—such as indirect raw material, indirect labour and overhead. i. Indirect raw material are those which are not the main element of production, but they help in production. ii. Indirect labor cost are those cost which can not be conveniently traced directly to particular products. 13. Revenue expenditure:--Which benefit can be enjoyed for 1 year or less than one year or is enjoyed in the current year, is called a revenue expenditure. These exp. are recurring or repetitive in nature. These are shown in the income statement. Such as – salaries, rent, etc. 14. Capital expenditure:--Which benefit will be enjoyed in future and hasn’t yet used, is called capital expenditure . These expenditures are non-recurring or non-repetitive in nature. These are shown in the balance sheet as assets. Such as –purchase of machinery, furniture, etc. 15. Product cost:-Product costs include all the costs that are involved in acquiring or making product. In the case of manufactured goods, these costs consist of direct materials, direct labour and manufacturing overhead. Product cost are viewed as “attaching” to units of product as the goods are purchased or manufactured and they remain attached as the goods go into inventory awaiting sale. So, product cost is assigned to an inventory account on the balance sheet. When the goods are sold, the costs are released from inventory as expenses (typically called cost of goods sold) and matched against sales revenue. Since product costs are initially assigned to inventories, they are also known as inventorial costs. 16. Period costs: All the costs that are not included in product costs. These costs are expenses shown in the income statement in the period in which they are incurred, using the usual rules of accrual accounting you have already learned in financial accounting. Period costs are not included as part of the cost of either purchased or manufactured goods. Sales, commissions and office rent are good examples of the kind of costs we are taking about. Neither commissions nor office rent are included as part of the cost of purchased or manufactured goods. Rather both the items treated as expenses on the income statement in the period in which they are incurred. Thus, they are said to be period costs. At last, all selling and administrative expenses are considered to be period costs . 17. Opportunity cost:-The potential benefit that is given up when one alternative is selected over another .i.e. the maximum value of the sacrificed projects, is called opportunity cost. For example:-if a person has a chance of investing and if he has a lots of options, then he has to select only one project and he has to sacrifice the others, and the value of the best sacrificed project is called opportunity cost. 18. Historical costs:--Which costs have incurred already in the past, are called historical costs. It is very important for financial accounting. It has some qualities, such as— real objective, reliable and not biased. 19. Pre-determined costs:-It is also called standard cost. To plan and control in the future, there is a need of some standards. Controlling is impossible without standard. So, what will be the next production cost in future, it is to be determined at first. This predetermined cost is called standard costs. Sometimes, the standard cost depends on the basis of historical cost and the situation of the future plan. 20. Explicit costs:--The costs which have clear evidence or documents, is called explicit costs. All historical costs are called explicit costs. The assets’ value are shown in the account on the basis of explicit costs. Such as—Salaries, rent, utility, gas, bill, telephone bill, which have clear bill. 21. Implicit costs:--The costs which have no clear evidence or documents, is called implicit cost. Such as- in case of valuing goodwill, the exact value can be determined approximately. 22. Joint costs:--If in any production process, if more than one product is produced, the cost of all products produced is called joint cost. Such as—soap and glycerin are produced in the same production process. 23. Common costs:--If any asset is used in producing different products, then those costs are commonly called common cost. Such as:--Computer, are used commonly in producing different products. 24. Committed cost:--The cost which will have to be incurred obviously for producing purpose, it is called committed cost. Such as –Purchasing machine, which will have to purchase, insurance costs, etc. 25. Shut-down cost:-The cost which is related or consistent with the shut down of the production of any product, is called shutdown cost. i.e. the cost which is incurred though the production is stopped, such as loss of goodwill, factory rent. Etc. 26. Sunk cost:-The cost which has already been incurred and which cachanged by any new decision made now or in the future. 27. Escapable cost:/Avoidable cost:-The cost which can be avoided is called escapable cost. 28.Inescapable cost/Unavoidable cost:-The cost which can not be avoided , is called inescapable cost/unavoidable cost. 29.Controllable cost:-The cost which can be controlled, is called controllable cost .i.e. wastage. 30.Uncontrollable cost:-The cost which can not be controlled, is called uncontrollable cost. i.e. accident, fire, natural disaster, cyclone. 31.Shut-down cost:-The cost which is related or consistent with the shut down of the production of any product, is called shutdown cost. i.e. the cost which is incurred though the production is stopped, such as loss of goodwill, factory rent. Etc. 32. Prime cost—Direct materials and direct labor costs are totally called prime cost. 33. Conversion cost—Direct labour and manufacturing overhead are totally called conversion cost. Direct labour and overhead cost are incurred in the conversion of materials into finished goods. That’s why it is called conversion cost. 34. Relevant cost:-A cost that differs between alternatives in a particular decision making. That means which are relevant in decision-making. All costs are not relevant, but only future costs, which are different in different alternatives, are called relevant cost. 35. Irrelevant cost:-Which cost are not relevant in decision making , are called irrelevant cost. All sunk costs are irrelevant cost.








