Practice Homework
advertisement

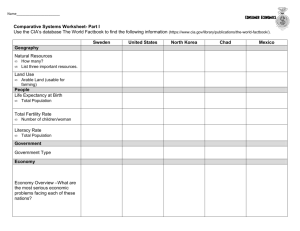
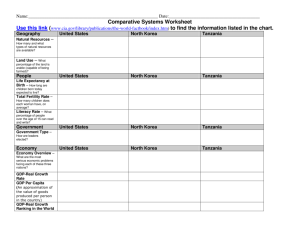
Practice Homework Economics 2000 Market Coordination in Korea 1. Hall and Soskice (2001) identify Germany as a prototypical coordinated market economy (CME) and the USA as a prototypical liberal market economy (LME). We are interested in measuring the degree to which market coordination plays a role in Korea. Use a variety of data sources to ascertain whether the environment in Korea lies closer to a CME or an LME along a number of dimensions. A. Capital Markets To assess the nature of the financial system, use data from World Economic Forum Financial Development Report . From class, we offer some relative measures of Capital Market co-ordination for Germany and USA. Pillar Measure 4.01Deposit money bank assets to GDP%1 6.11Stock Market Turnover to GDP%2 5.05M&A transaction value to GDP%3 Germany 130.36 40.07 2.82 USA 64.63 268.78 5.96 Korea Fill-in the measures from the 2012 report. On which measures is Korea closer to an LME and on which closer to a CME? B. Product Markets Measure the degree to which the coordination of product markets is co-ordinated. i. Get data from the OECD on Product Market Regulation from OECD.StatExtracts. Under Public Sector, Taxation and Market Regulation Market Regulation Economy-wide regulation choose State Control. This measures the degree of government regulation of goods markets on a scale of 0 to 5 with 5 being maximum governmental control with Germany falling from above 3 in 1998 to near 2 in 2008 which is still above the USA level near 1.1. What is the level of product market state control in Korea? Get data from the World Bank Doing Business database on how hard it is to Start a Business. What is the ranking of the USA, Germany and Korea on this measure? Product Market Regulation 4 ii. Measure Product Market Regulation: State Control 0-5 Starting a Business Ranking6 5 Germany 1.96 106 USA 1.10 13 Korea “These are claims on the domestic real nonfinancial sector by deposit money banks as a share of GDP | 2010” 2 “This is the total value of shares traded on stock market exchanges as a percent of GDP | 2010.” 3 “This variable is the rank value of the three-year average of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) transactions in US dollars as a percent of GDP | 2009-2011” 4 “The OECD Indicators of Product Market Regulation (PMR) are a comprehensive and internationally-comparable set of indicators that measure the 1 degree to which policies promote or inhibit competition in areas of the product market where competition is viable. They measure the economy-wide regulatory and market environments” 5 “The OECD Indicators of Product Market Regulation (PMR) are a comprehensive and internationally-comparable set of indicators that measure the degree to which policies promote or inhibit competition in areas of the product market where competition is viable. They measure the economy-wide regulatory and market environments” 6 “Doing Business measures the procedures, time and cost for a small to medium-size limited liability company to start up and operate formally. “ How does Korea compare in terms of coordination of the product market? C. i. a. Labor Markets Measure the degree of Labor Market Regulation. Get general rating. Use data from OECD from OECD.StatExtracts. Under Labour Employment Protection Strictness of employment protection – individual and collective dismissals (regular Report Version 3 for 2011. How is the overall regulation of the Korean labor market relative to Germany and the US? b. Get a specific measure. Use the World Bank Jobs database Link to get data on Weeks of severance pay for redundancy of experienced workers from 2010 to identify restrictions on dismissing workers. ii. How important is long-term employment in Korea? Use data from OECD from OECD.StatExtracts. We know that German workers are more likely to have a long job tenure than American workers. Under Labour Labour Force Statistics Job Tenure Employment by Job Tenure intervals – persons. Get data on for Korea in 2011 under the category of 10 years and over and Total. Calculate the percentage of Korean worker in their current job for more than 10 years. iii. The World Economic Forum Executive Opinion Survey Global Competitiveness Report. provides subjective data on the degree of wage coordination in the economy. Question 7.02 asks: “In your country, how are wages generally set? [1 = by a centralized bargaining process; 7 = by each individual company]” The USA ranks 29th in the World and Germany ranks 141st out of 148 countries. Where does Korea rank? contracts). Measure Strictness of Employment Protection Weeks of severance pay for redundancy of experienced workers Employment by Job Tenure intervals – persons8 .% 7.02 Flexibility of wage determination 7 Germany 2.98 USA 1.17 0 28.8% 29th 43.333 43.9% 141st Korea D. Job Training Measure the degree of vocational training using World Bank EdStats data. Under Series gets 03 Secondary 2 Total Enrolments Technical/vocational enrolment in upper secondary (ISCED 3) as % of total enrolment in upper secondary (ISCED 3) Measure Technical/vocational upper secondary enrolment % Germany 51.49 USA 0 Korea In a recent contribution, political economist Michael Witt reports “Interpreted in the context of the Hall and Soskice (2001) model, Korea falls somewhere between the opposite poles of coordinated and liberal market economies (CMEs and LMEs). Developments over the past fifteen years seem to have pushed the system somewhat closer toward the Anglo-Saxon LME model, though as we have seen actual practice is far from what one would expect of an LME.” Assess this statement in light of the evidence you have collected. “The OECD indicators of employment protection are synthetic indicators of the strictness of regulation on dismissals and the use of temporary contracts. For each year, indicators refer to regulation in force on the 1st of January. “ 8 Job tenure is measured by the length of time workers have been in their current or main job or with their current employer. 7