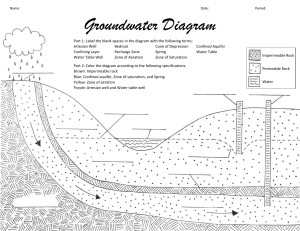
Name
advertisement

Name: _______________________________ Date: _________________ Period: ______ Study Guide: Chapter 14 – Groundwater Circle or Underline the Correct Choice The water table is at the top of which layer? - zone of aeration or zone of saturation Which dissolved mineral is most common in hard water? – calcium, potassium, or sodium Which type of rock will make the best aquifer? – basalt, sandstone or slate Where will one find the deepest water table? – desert, grassland, or swamp What is formed when a stalagmite and stalactite meet? – pillar, riser or stand What is the permeability of rocks with few to no pores? – permeable or impermeable What characteristic determines the amount of water that ground can store? – subsidence, porosity, or permeability Which of the following locations will not have a zone of aeration? – desert, grassland, or swamp What is the upper layer of rock in an artesian formation? – aquifer, cap rock, or keystone What is created as steam rises through silt or acidic water mixes with clay? – fumarole, hot spring, or mudpot Which of the following is an income of the water budget? – rain, evaporation, or run off Which is an example of water budget spending? – evaporation, rain, or snow What fills the pore spaces in the zone of saturation? – air, oil or water What moist area of soil lies immediately above the water table? – bedrock, capillary fringe, or topsoil What is it called when the level of ground drops as water is removed from the soil? – recession, salinization, or subsidence Hard water can stain your drains and faucets. What does the residue of hard water look like? – greasy tar, gummy sludge or chalky powder Water from an artesian formation that is far from the water source will be ___________. cold & shallow cold & deep hot & shallow hot & deep Which formation hangs from the ceiling? – stalactite or stalagmite What are regions of calcite bedrock that are characterized by sinkholes and lost rivers? artesian fronts karst topography sedimentary escarpments Organic material called humus is found in this layer. - capillary fringe, mid-layer, or surface soil What size grains are found in impermeable rocks? – fine, medium, or large How are the permeable and impermeable rock layers arranged in an artesian formation? Top Layer ____________________ Middle Layer ____________________ Bottom Layer ____________________ Match the Term with its Definition ______ aquifer A. hot, highly acidic groundwater ______ artesian formation B. permeable rock that transports ground water ______ fumarole C. column of water shot from a hot spring ______ geyser D. water flowing down a hillside ______ mudpot E. steam released from ground fissures ______ spring F. permeable rock between impermeable layers Circle or Underline if the statement is True or False True or False If porosity is high, permeability likely will be low. True or False The zone of aeration is above the zone of saturation. True or False Rounded rocks will have less pore space than round rocks. True or False Artesian water is typically harder than groundwater. True or False The water table is closer to the surface in valleys than in hills. True or False Warm water dissolves more minerals than cold water. True or False Poorly sorted soils have less pore space than well sorted soils. Be prepared to explain the following concepts. 1. The formation of a desert oasis from an artesian formation 2. How pumice has large pores yet remains impermeable 3. Compare and contrast porosity and permeability 4. The depth of an ordinary well Define each month of the water budget as a period of recharge (R), surplus (S), usage (U), or deficit (D). Assume that the soil can hold a maximum of 100 mm of water and that the soil is completely saturated at the end of April. APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV Supply 90 60 60 55 80 120 85 80 Need 60 75 105 125 85 70 55 40 Supply minus need 30 Water in Soil 100 Water Budget Section S