Astronomy
advertisement

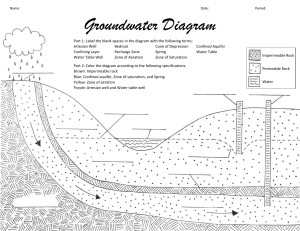
Earth Science Name_____________________________ Chapter 14 Period_____________________________ Worksheet Date______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Wells, Springs, and Karst Topography True or False (0.25 points each) Read each statement below. If the statement is true, write T in the space provided. If the statement is false, write F in the space provided. _____ 1. Because hot water tends to have fewer minerals dissolved in it than cold water, hot springs often contain very small concentrations of minerals. _____ 2. The layer of cap rock in an artesian formation is impermeable. _____ 3. Hot springs generally have temperatures at of very near the boiling point of water. _____ 4. Geysers tend to build deposits of the silicate mineral geyserite. _____ 5. Ordinary springs are commonly located where the water table intersects the ground surface. Multiple Choice (0.25 points each) Choose the one best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided. _____ 6. Which of the following is often the source of water in a desert oasis? A. an ordinary well C. a hot spring B. an artesian spring D. a geyser _____ 7. A sloping layer of permeable rock sandwiched between two layers of impermeable rock and exposed at the surface is a(n) _____. A. mud pot C. hot spring B. ordinary well D. artesian formation _____ 8. Which of the following features is represented by this diagram? A. travertine terrace C. geyser B. cap rock D. artesian well _____ 9. Groundwater is sometimes heated beneath the Earth’s surface as it passes through areas where there has been recent _____. A. severe drought C. aquifer contamination B. mineral deposition D. volcanic activity _____ 10. Pumping water from a well creates a lowered area of the water table called a _____. A. cone of depression C. fissure spring B. perched water table D. paint pot Multiple Choice (0.25 points each) Choose the one best response. Write the letter of choice in the space provided. _____ 1. The formations suspended from the roofs of caverns formed from the deposition of dissolved material are called _____. A. fissures C. natural bridges B. stalactites D. disappearing streams _____ 2. The mineral that forms cone-shaped cavern formations is _____. A. calcite C. geyserite B. magnesium D. iron _____ 3. One of the major disadvantages of hard water is that it A. cannot be used for drinking. B. contaminates groundwater aquifers. C. inhibits the flow of water up through artesian wells. D. damages appliances due to the buildup of mineral deposits. _____ 4. What formation is represented in the diagram? A. size C. weight B. shape D. composition Fill in the Blank (0.25 points each) Complete each statement by writing the correct term or phrase in the space provided _______________ 5. A surface depression that forms as a result of the collapse of a cave roof is called a _____. _______________ 6. Most caverns are formed by the solution of rock be weak acids by the process of _____. _______________ 7. Water that contains few dissolved minerals is called _____. _______________ 8. Regions where the effects of chemical weathering due to groundwater are clearly visible at the surface are said to have _____. _______________ 9. Large tunnels or caves in areas with extensive limestone deposits that often contain smaller connecting chambers are called _____. _______________ 10. The uncollapsed rock between a pair of sinkholes forms an arch of rock called a _____.