7 Earth's Fresh Water
advertisement

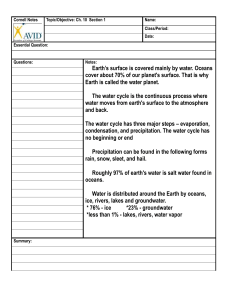
UNIT 8 EARTHS FRESH WATER How much water do we use? 140 billion gallons daily in the United States alone Expected to grow Water takes up 70% of our Earth! 97.2 % Salt Water 2.2 % Glaciers/Icecaps 0.6 % Surface/Underground 0.01 % Rivers/Lakes/Streams 0.0001 % Atmosphere Red Book Pg. 361 Of the Fresh Water 76% Ice 12% Shallow Groundwater 11% Deep Groundwater .34% Lakes and Rivers .037% Water Vapor Red Book Pg. 361 This leaves 15% of our fresh water available for use. .42% of all water on Earth Why don’t we run out of water? The Water Cycle The continuous process by which water moves throughout the environment The Water Cycle From oceans and freshwater supplies to the air, land and back to the oceans The Water Cycle 3 Steps to the Water Cycle Evaporation Condensation Precipitation The Water Cycle Evaporation/Transpiration When water changes to vapor or gas The Water Cycle Condensation When vapor turns to liquid The Water Cycle Precipitation Water returns to the Earth Rain, snow, sleet or hail How do people use water? Agriculture Irrigation for farming Industry Uses water to produce objects Uses (cont.) Transportation People and goods Recreation Swimming, boating, etc. Fresh Water Usage Handout! Water Usage Lab Fill out chart on back of lab sheet List 10 other ways to conserve water (#3) In your lab report explain how much water you could save and how you are planning to do it. Hint: Use data from chart. Water Cycle Quiz Water Cycle Quiz 5&6. Describe 2 of the 4 steps in the water cycle. 7. In your own words, describe the water cycle. 8. Explain why there are water shortages if the earth's total water volume is constant. Water Cycle Bonus 2 Types of fresh water on the surface Running water Standing water Running Water Surface runoff - Water that enters a river after a heavy downfall Watershed - Area where runoff drains into the river system Watersheds Standing Water Lakes and ponds - depends on size Reservoirs Artificial lake built by damming a stream or river Quabbin Reservoir Construction 1936-1946 412 billion gallons flooded the Swift River valley Largest man-made reservoir in the world Quabbin Reservoir (cont.) Floods left Prescott, Enfield, and Greenwich under water. Blue Hills Reservoir Constructed in the early 1950s Provided storage until 1981 Removed due to water quality. MA Watersheds The Water Cycle What is Groundwater? Water that remains in the ground Water beneath the Surface Ground- water seeps between pores in the soil Permeable vs. Impermeable Permeability -The ability of material to let water pass through it Permeable or Impermeable? Impermeable Permeable Underground Zones Zone of saturation Zone of aeration Water table Aquifer Artesian well Zone of Saturation Underground area where all pores are filled with water Zone of Aeration (Unsaturated Zone) Dry region where the pores are filled mostly with air Water table Area including the zone of saturation and zone of aeration soaked with water How do we bring groundwater to the surface? Wells - Drill a hole below the water table and pump water to the surface Aquifers Layer of permeable rocks that allows the water to flow sideways between impermeable layers Sandstone, gravel, sand Aquifers Aquifers Artesian well Artesian well Well water that flows on its own without pumping QUIZ QUIZ Ecology Book Water as a universal solvent • • • • • • Acid Base pH Solute Solvent Polar molecule Solute • The substance that dissolves in a solution Solvent • The liquid in which the solute dissolves Polar Molecule • A molecule that has a negative charge at one end and a positive charge at the other Acid • Solution with more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions Base • Solution with more hydroxide than hydrogen ions pH • Units by which acids and bases are measured • pH less than 7 = Acid pH greater than 7 = Base • Importance of Water • • • • Resists changes in temperature Universal solvent Polar molecule Neutral pH How do we make water drinkable? Public and private water supplies often need treatment to improve water quality Measurement of substances in water besides molecules Read from Red Book pg. 395-398 Water Quality Appearance and taste Acidity (pH) Hardness Hard water does not mix well with soap Disease Health Standards Water Quality 1. First Filtration - Screens 2. Coagulation - Alum added 3. Second Filtration 4. Chlorination - Cl added 5. Aeration - Releases gasses 6. Additional treatment - Fluoride Treating Wastewater 1. Primary treatment Water slows down particles fall out 2. Secondary treatment Filtered through gravel & bacteria 3. Additional treatment Chlorine added