CLASS Presentation - Alabama State University
advertisement

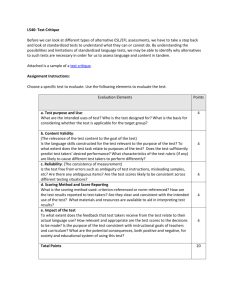
ALABAMA STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF FOUNDATIONS AND PSYCHOLOGY _________________________________________________________________ SYLLABUS FOR MEASUREMENT AND EVALUATION IN EDUCATION __________________________________________________________________ COURSE NUMBER: EDU 301 DESCRIPTION: An introductory course for early childhood, elementary and secondary teachers and prospective teachers, which is designed to improve the methods of evaluating student achievement, performance and progress. A major focus of the course is devoted to applications of the evaluation and measurement processes. A second focus of the course is the fundamental principles of tests and measurement with an emphasis on practical applications in the classroom. CREDIT HOURS: 3 Semester Hours (Fall/Spring) PREREQUISITE: PSY 251: General Psychology INSTRUCTOR: Dyann Bayan, Ed.D. OFFICE LOCATION: McGehee Hall: Room 205 OFFICE TELEPHONE: (334) 229-6925 E-MAIL: dbayan@alasu.edu OFFICE HOURS: As Posted or By Appointment Prepared by _____________________________________________________ Dyann Bayan, Ed.D. Date Approved by _________________________________________________________ Department Chairperson Date ________________________________________________________ Dean, College of Education Date COMMITMENT TO DIVERSITY: In our commitment to furthering knowledge and fulfilling our educational mission, Alabama State University seeks a campus climate that welcomes, celebrates, and promotes respect for the entire variety of human experience. In our commitment to diversity, we welcome people from all backgrounds and we seek to include knowledge and values from many cultures in the curricula and in the extracurricular life of the campus. Dimensions of diversity shall include, but not limited to the following: race, ethnicity, gender, age, religious beliefs, disability, socioeconomic status, sexual orientation and cultural orientation. AMERICAN WITH DISABILITIES ACT: Any student requiring alternative formats for testing and/or handouts for this course, or other types of accommodations due to a handicapping condition should advise the instructor within the first week of class. CLASS ATTENDANCE POLICY: Each student is expected to attend all lectures, seminars, laboratories and fieldwork for each registered class, including the first class session. Attendance is required to verify official enrollment and continuance in each course. When students are absent from class for authorized reasons such as death in the family, illness, hindrance by true emergency situations or University activities, they will be allowed to make up assignments/examinations that they missed. Instructors, of course, are not obligated to provide makeup opportunities for students who are absent unless the absences have been officially approved. (See complete “Policy for Class Attendance” via ASU Course Book). WITHDRAWAL FROM A COURSE POLICY: A student may withdraw without penalty from a course prior to midterm. No grade is given when the student withdraws officially during this period. The deadline date for withdrawing from a course is stipulated in the academic calendar. When a student as a result of emergency circumstances is forced to withdraw from a course after the established withdrawal date for the term, the student may petition, in writing, the dean of the school in which the course is offered for approval to withdraw from a course. A student may not withdraw from a course after the deadline if he/she is failing. (See complete “Policy for Student Withdrawal From A Course” via ASU Course Book). “I” GRADE POLICY: An “I” (incomplete) grade is assigned in instances in which a student is likely to pass the course upon completion of requirements to change the “I” grade. To yield credit for a course for which a grade of “I” has been assigned, course requirements must be completed by the end of the next semester of enrollment, not to exceed two calendar years. When reporting the “I” grade, faculty will include the alternate grade that the student has earned, factoring in all course requirements, e.g., I (B), I (C). (See complete “Policy for I Grade” via ASU Course Book). 2 A. PURPOSE OF THE COURSE The purpose of this course is to provide the student with a seminal learning experience with assessment, testing and measurement in teaching and numerous opportunities to comprehend, synthesize and integrate the knowledge acquired through in-depth reading, assignments and practical experience. This course addresses the basic concepts of educational measurement and the application of traditional methods of testing and measurement. In addition, this course introduces the contemporary educational term, assessment, as an integral component of the teachinglearning process. Consistent with the conceptual framework of the College of Education, the theme “Educator As Decision Maker”, states… “decision-making is basic to high quality teaching and student achievement”, this course underscores decision making as the essential component in the assessment of student learning and performance and therefore provides a sound foundation for using effective assessment and measurement in teaching. “Educator As Decision Maker” as a conceptual framework for this course will contribute to helping students to develop an understanding of course content through experiential learning, synthesis of their learning, examination of student performance through subjective lenses after objective observation and through practicing some aspects of assessment and measurement in teaching. As a result, students will have the ability to create their own schematics and make informed educational decisions that will translate into effective assessment and measurement strategies in their own classrooms. B. METHODS OF INSTRUCTION The primary method of instruction for this course is interactive lectures. This method provides students with the opportunities to interactive in class lectures during which the blend of diverse grade levels and disciplines will provide an excellent base for discussion of course content from different points of views. A secondary method of instruction is a learning teams approach. This method provides students with the opportunities to work collectively and productively to engage in selfdirected learning experiences that will act as a catalyst for course content discussions. Important to this class is an extensive pedagogical framework for the facilitation of learning that includes required readings, vignette reactions, ponder applications, assignments, assigned conversations, team teaching, class presentations, practicum observations and interim examinations. 3 C. COURSE OBJECTIVES: After reading, and class lectures, students will be able to: Objective 1. Comprehend the fundamental psychometric properties of validity in the context of educational assessment. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (iii) Learning Outcomes: A. B. C. D. E. F. Define the concept of validity. Describe the nature of validity. Describe the major types of validity evidence. Explain how validity coefficients are interpreted. Explain the standard error of estimate. Identify the appropriate type of validity evidence given in illustrations of practical applications. Objective 2. Comprehend the fundamental psychometric properties of reliability in the context of educational assessment. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (iii) Learning Outcomes: A. B. C. D. E. F. Define the concept of reliability. Describe the nature of reliability. Describe the three major methods of estimating reliability. Define the standard error of measurement. Explain the relationship between reliability and validity. Identify the appropriate method of estimating reliability given in illustrations of practical applications. Objective 3. Comprehend various aspects of standardized tests and various methods used to interpret the results of standardized tests. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (iii), CF (CA: 2.4) Learning Outcomes: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Describe the major characteristics of standardized tests. Explain the terms norms and norm groups. Explain norm-referenced and criterion-referenced interpretations. Discuss the nature of assessment bias. Define percentile rank and explain its interpretation. Define stanine score and explain its interpretation. Define grade equivalent score and explain its interpretations. Interpret the results of various scoring methods. Objective 4. Critique reviews of standardized achievement or aptitude tests. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (iii) Learning Outcomes: A. B. C. D. E. F. Locate sources for reviews of standardized tests. Use a test review evaluation form to prepare a summary of information. Identify the reviewer of a standardized test. Discuss the composition of the norm group. Discuss the types of scores and interpretations. Discuss the validity and reliability 4 Objective 5. Comprehend characteristics of different types of assessment strategies. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (i), NCATE (4) Learning Outcomes: A. B. C. D. Define assessment, test and measurement. Describe the main purpose of assessment. Differentiate between placement and diagnostic assessment. Differentiate between formative and summative assessment. Objective 6. Comprehend the role of instructional objectives in the instructional process and the assessment process. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (vi), INTASC (8) Learning Outcomes: A. B. C. D. E. Define the terms instructional objectives and learning outcomes. Describe the characteristics of instructional objectives. Describe the three types of domains addressed by instructional objectives. Use Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives. Identify instructional objectives and learning outcomes given in practical application illustrations. F. Identify the appropriate type of domain given in practical application illustrations. Objective 7. Construct a teacher-made classroom test. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (v), INTASC (8), NCATE (4), CF (RP: 1.4) Learning Outcomes: A. Develop a teacher-made test designed to measure learning outcomes for a specific content area and grade level. B. Develop an instructional objective and learning outcomes for the teacher-made test. C. Develop various types of selected-response test items for the test. D. Develop various types of constructed-response test items for the test. Objective 8. Comprehend the roles of observational techniques for assessing learning and development. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (i), INTASC (8), NCATE (4) Learning Outcomes: A. Define formal and informal observations. B. Discuss the advantages and limitations of formal and informal observations. C. Distinguish between various observational techniques for assessing students with diverse needs. Objective 9. Develop strategies for improving test performance. Learning Outcomes: A. Prepare strategies for reducing students’ test anxiety. B. Prepare strategies for enhancing students’ study skills and test taking skills. INTASC: PRAXIS: SDE: CF: Interstate New Teachers Assessment and Support Consortium Professional Assessments for Beginning Teachers Alabama State Department of Education Standards Conceptual Framework (College of Education - Alabama State University) RP: Reflective Practitioners, CA: Change Agents, LL: Lifelong Learners 5 Objective 10. Comprehend performance-based assessments and scoring systems. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (vii), (2) (c) 5. (viii), (2) (c) 5. (ix), INTASC (8), CF (CA: 2.5) Learning Outcomes: A. B. C. D. Define performance assessments. Discuss developing performance objectives in the cognitive and affective domains. Discuss selecting appropriate evaluative criteria. Discuss scoring rubrics, checklists and rating scales. Objective 11. Comprehend various methods of grading and reporting student progress. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (vii), NCATE (4) Learning Outcomes: A. B. C. D. Define the term grade. Distinguish between absolute and relative grading. Explain various criteria for assigning grades. Discuss reporting and informing parents and others of students’ grades. Objective 12. Analyze state mandated assessments and tests results. NCATE (4), ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (iv), (2) (c) 5. (vi), (2) (c) 5. (xii), Learning Outcomes: A. Summarize demographics and tests results from state mandated assessments used in Alabama public schools. B. Explain school accountability status and the criteria for determining accountability status. C. Explain adequate yearly progress for school accountability. D. Identify the components of adequate yearly progress. Objective 13. Conduct required classroom observation hours in an educational setting. CF (RP: 1.7) Learning Outcomes: A. Prepare a practicum observation paper, which specifically discusses key assessment and measurement information obtained from a classroom teacher during the observation experience. B. Present lessons learned presentation based on the observation experience. Objective 14. Develop a student performance plan. ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (ii), (2) (c) 5. (v), (2) (c) 5. (xi), NCATE (4), INTASC (8), CF (RP: 1.6), CF (RP: 1.7), CF (CA: 2.3) Learning Outcomes: A. Discuss monitoring student performance and measuring student progress. B. Discuss providing student feedback and using assessments and tests results. Objective 15. Comprehend descriptive statistical measures used in education evaluation. ALSDE: (5) (c) 4. (i), CF (CA: 2.1) Learning Outcomes: A. Describe the measures of central tendency and their appropriate use. B. Describe the measures of variability and their appropriate use. C. Use appropriate statistical procedures to compute and interpret measures of central tendency and measures of variability for given distribution of scores. 6 ALIGNMENT OF COURSE OBJECTIVES WITH ALSDE STANDARDS, NCATE, INTASC, AND ASU CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK OUTCOMES Course Objectives NCATE and INTASC Standards Conceptual Framework State Department of Education Standards Assessment 1. Comprehend the fundamental psychometric properties of validity in the context of educational assessment ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (iii) Class Discussions Standardized Test Review Assignment Mid Term Examination 2. Comprehend the fundamental psychometric properties of reliability in the context of educational assessment ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (iii) Class Discussions Standardized Test Review Assignment Mid Term Examination 3. Comprehend various aspects of standardized tests and various methods used to interpret the results of standardized tests ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (iii) CF (CA: 2.4) Class Discussions Mid Term Examination 4. Critique reviews of standardized achievement or aptitude tests ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (iii) Class Discussions Standardized Test Review Assignment 5. Comprehend characteristics of different types of educational assessments ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (i) Class Discussions Practical Application Class Activity ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (vi) Class Discussions Practical Application Class Activity ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (v) Class Discussions Test Construction Project Assignment 6. Comprehend the role of instructional objectives in the instructional process and the assessment process INTASC (8) 7. Construct a teacher-made classroom test NCATE (4) INTASC (8) CF (RP: 1. 4) D. ASSESSMENT AND EVALUATION Objectives 1 - 3 will be assessed on the Mid-Term Examination. 70 points out of 100 points. Objective 4 will be evaluated on the completion of a critique of a standardized test review as described in the assignment for Standardized Test Review Evaluation. 25 points out of 35 points. Objectives 5 - 7 will be evaluated on the completion of a teacher-made test as described in the assignment for Test Construction Project. 80 points out 100 points. 7 Course Objectives 8. Comprehend the roles of observational techniques for assessing learning and development NCATE and INTASC Standards Conceptual Framework NCATE (4) INTASC (8) State Department of Education Standards ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (i) 9. Develop strategies for improving test performance INTASC (8) 11. Comprehend various methods of grading and reporting student progress 12. Analyze state mandated assessments and tests results ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (vii) ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (viii) ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (ix) Team Teaching Assignment NCATE (4) ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (vii) Team Teaching Assignment NCATE (4) ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (iv) ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (vi) ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (xii) SAT 10, ARMT and ADAW Tests Results Report Assignment CF (CA: 2.5) CF (RP: 1.7) 13. Conduct required classroom observation hours in an educational setting 15. Comprehend descriptive statistical measures used in education evaluation Team Teaching Assignment Team Teaching Assignment 10. Comprehend performancebased assessments and scoring 14. Develop a student performance plan Assessment NCATE (4) INTASC (8) Field Experience CF (RP: 1.6) CF (RP: 1.7) CF (CA: 2. 3) ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (ii) ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (v) ALSDE: (2) (c) 5. (xi) Student Performance Plan Assignment CF (CA: 2.1) ALSDE: (5) (c) 4. (i) Final Examination Objectives 8 - 11 will be evaluated on team teaching an assigned topic relevant to assessment and measurement in teaching as described in the assignment for Team Teaching. 35 points out of 45 points. Objective 12 will be evaluated on the completion of state mandated test scores reports and a class presentation as described in the assignment for State Mandated Test Scores Reports. 45 points out of 60 points. Objective 13 will be evaluated on the completion of the required observation hours, a written paper and lessons learned presentation as described in the assignment for Practicum Observation Paper. 45 points out of 60 points. Objective 14 will be evaluated on the completion of a proposed plan for assessing student performance as described in the assignment for Assessment of Student Performance Plan. 80 points out of 100 points. Objective 15 will be evaluated on the Final Examination. 70 points out of 100 points. Objective 15 will be evaluated on the Final Examination. 8 STANDARDIZED TEST REVIEW EVALUATION SCORING RUBRIC EVALUATIVE CRITERIA POINTS POSSIBLE TEST BACKGROUND 5 TEST REVIEWER 5 STANDARDIZED/NORMS 5 TEST SCORES 5 RELIABILITY ESTIMATES 5 VALIDITY EVIDENCE REVIEWERS’ COMMENTS VALUE = PASSING = 5 5 35 POINTS 25 POINTS TEAM TEACHING SCORING RUBRIC EVALUATIVE CRITERIA POINTS POSSIBLE CONTENT Demonstrated general knowledge about the topic 20 DELIVERY Discussed the topic without reading the information word for word 15 HANDOUT Distributed information that is germane to the topic 10 VALUE = PASSING = 45 POINTS 35 POINTS 9 STATE MANDATED TEST SCORES REPORTS AND CLASS PRESENTATION SCORING RUBRIC EVALUATIVE CRITERIA POINTS POSSIBLE ALABAMA DIRECT ASSESSMENT OF WRITING (2 QUESTIONS) 15 ALABAMA READING AND MATHEMATICS TEST (5 QUESTIONS) 25 STANFORD ACHIEVEMENT TEST 10 (2 QUESTIONS) 10 CLASS PRESENTATION (Brief Overview of Assessments) 10 VALUE = PASSING = 60 POINTS 45 POINTS PRACTICUM OBSERVATION PAPER AND LESSONS LEARNED PRRESENTATION SCORING RUBRIC EVALUATIVE CRITERIA POINTS POSSIBLE Content (Coverage of Assessment and Measurement Information) 35 Writing Mechanics (Sentence Structure, Grammar, Punctuation, and Spelling) 10 Class Presentation (“Lessons Learned”) 15 VALUE = PASSING = 60 POINTS 45 POINTS 10 ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT PERFORMANCE PLAN SCORING RUBRIC EVALUATIVE Criteria ACCEPTABLE Response EXCELLENT Response Monitor Student Performance 20 pts. 25 pts. Measure Student Progress 20 pts. 25 pts. Provide Student Feedback 20 pts. 25 pts. Use Assessment Results 20 pts. 25 pts. VALUE = PASSING = 100 POINTS 80 POINTS E. GRADING SYSTEM Grades for this course will be based on the following requirements: Midterm Examination Assignments Final Examination The final course grade will be the total points earned converted to a letter grade equivalent as indicated in the following grading scale: 100 points 400 points 100 points GRADING SCALE A B C D F = = = = = 11 550 – 600 500 – 549 450 – 499 400 – 449 000 – 399 F. CLASS POLICIES LATE ASSIGNMENTS Late Assignments will not be accepted beyond two class sessions beginning with the due date. The due date counts as the first class session. The next class session counts as two class sessions. Late Assignments will receive 5 points deduced from the total points earned for any assignment. This policy applies to the policy above. Late Assignments will be accepted with no penalty deducted from students who have obtained an official excuse from the Office of Student Affairs for the date the assignment was due. MAKE-UP ASSIGNMENTS Make-Up Assignments are granted to students who have obtained an official excuse from the Office of Student Affairs. Make-Up Assignments may be granted to students without an official excuse from the Office of Students Affairs only at the instructor’s discrepancy. MAKE-UP EXAMINATIONS Make-Up Examinations will be given only after the Office of Student Affairs has granted an official excuse for the date of an exam. Make-Up Examinations may be given to a student without an official excuse from the Office of Student Affairs only at the instructor’s discrepancy. 12 G. REQUIRED COURSE TEXTBOOK Linn, R. L., & Miller, M. D. (2005). Measurement and assessment in teaching (9th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall. SUPPLEMENTARY REFERENCES American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, & National Council on Measurement in Education (1999). Standards for educational and psychological testing. Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association. American Federation of Teachers, National Council on Measurement in Education, & National Education Association (1990). Standards for teacher competence in educational assessment of students. Washington, DC: American Federation of Teachers. Joint Committee on Standards for Educational Evaluation (2003). The student evaluation standards. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press. National Council on Measurement in Education (1995). Code of professional responsibilities in educational measurement. Washington, DC: Author. Plake, B. S., Impara, J. C., & Spies, R. A. (Eds.). (2004). The sixteenth mental measurements yearbook. Lincoln, NE: Buros Institute of Mental Measurements. 13 FURTHER READING Amrein, A. L., & Berliner, D.C. (2003). The effects of high-stakes testing on student motivation and learning. Educational Leadership, 60(5), 32-38. Anderson, L. W., & Bourke, S. F. (2000). Assessing affective characteristics in the schools (2nd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum. Andrade, H. G. (2000). Using rubrics to promote thinking and learning. Educational Leadership, 57(5) February: 13-18. Bhola, D. S., Impara, J. C., & Buckendahl, C. W. (2003). Aligning tests with states’ content standards: Methods and issues. Educational Measurement Issues and Practices, 22(3), 21-27. Bloom, B., Englehart, M., Furst, E., Hill, W., & Krathwohl, D. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals. Handbook I: Cognitive domain. White Plains, NY: Longman. Brookhart, S. M. (2004). Grading. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Merrill Prentice Hall. Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika, 16, 297-334. Doherty, K. M. (2002). Education issues: Assessment. Education Week on the web. Retrieved May 14, 2003, from www.edweek.org. Farr, R. C., & Tone, B. (1994). Portfolio and performance assessment: Helping students evaluate their progress as readers and writers. New York: Harcourt Brace. Goldberg, M. F. (2004). The test mess. Phi Delta Kappan, 85(5), 361-366. 14 Gronlund, N. E. (2002). How to write and use instructional objectives (6th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill/Prentice Hall. Guskey, T. R., & Bailey, J. M. (2001). Developing grading and reporting systems for student learning. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press. Harrow, A. J. (1972). A taxonomy of the psychomotor domain. New York: David McKay. Kober, N. (2002). Teaching to the test: The good, the bad, and who’s responsible. Test Talk for leaders (Issue 1). Washington, DC: Center on Educational Policy. Retrieved May 13, 2003, from www.cep-dc.org. Krathwohl, D., Bloom, B., & Masia, B., (1964). Taxonomy of educational objectives: Book 2: Affective domain. White Plains, NY: Longman. Kubiszyn, T., & Borich, G. (2007). Educational testing and measurement: Classroom application and practice (8th ed.). New York: Wiley. Kuder, G. F., & Richardson, M. W. (1937). The theory of the estimation of reliability. Psychometrika, 2, 151-160. Lyman, H. B. (1998). Test scores and what they mean. Boston: Allyn & Bacon. Manzo, K. K. (2003). Essay scoring goes digital. Education Week, 22, 39-40, 42. McMillan, J. H. (2004). Classroom assessment: Principles and practice of effective instruction (3rd ed.) Boston: Allyn & Bacon. Millman, J. (1997). Grading teachers, grading schools. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press. 15 Moskal, B. M. (2000). Scoring rubrics: What, when, and how? Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 7(3). Munk, D. D., & Bursuck, W.D. (2003). Grading students with disabilities. Educational Leadership, 61(2), 38-43. Nissman, B. (2000). Teacher-tested classroom management strategies. Upper Saddle River, NJ, Merrill. Nitko, A. J. (2004). Educational assessment of students (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall/Merrill Education. Popham, W. J. (2000). Modern educational measurement: Practical guidelines for educational leaders (3rd ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon. Popham, W. J. (2003). Test better, Teach better: The instructional role of assessment. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development. Price, K. M., & Nelson, K. L. (2003). Daily planning for today’s classroom: A guide to writing lesson and activity plans (2nd ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Publishing. Stiggens, R. J. (2001). Student-involved classroom assessment (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill Prentice Hall. Tombari, M., & Borich, G. (1999). Authentic assessment in the classroom. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall. 16