RG10.1 Solutions
advertisement

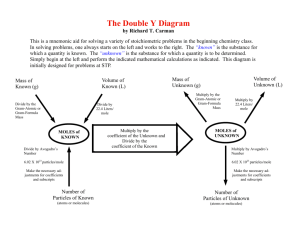
Name ____________________________________________________________ Date __________________ The Mole Before You Read Define the following terms. atomic mass the weighted average mass of the isotopes of an element ______________________________________________________________ atomic mass unit (amu) one-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom ______________________________________________________________ Chapter 2 Write the following in scientific notation 0.00582 5.82 103 ________________________________ 24,367 2.4367 104 ________________________________ 400 4 102 ________________________________ Circle the significant figures in the numbers below. 75,600,000 0.00033 3.140 Chemistry: Matter and Change 125 Science Notebook Name ____________________________________________________________ Date __________________ The Mole Section 1 Measuring Matter Scan Section 1, using the checklist below to preview your text. Read all section titles. Read all boldfaced words. Read all tables and graphs. Look at all pictures and read the captions. Think about what you already know about this subject. Write three questions that come to mind from your reading. Accept all reasonable responses. 1. ____________________________________________________________ 2. ____________________________________________________________ 3. ____________________________________________________________ Use your text to define each term. mole the SI base unit used to measure the amount of a substance _______________________________________________________________ Avogadro's number the number 6.0221367 1023, which is the number of _______________________________________________________________ representative particles in a mole _______________________________________________________________ Counting Particles Use with pages 320–321. List three common counting units and their values. Accept all reasonable responses. Possible answers: one dozen eggs 12 individual eggs 1. ____________________________________________________________ one pair of boots 2 individual boots 2. ____________________________________________________________ one ream of paper 500 sheets 3. ____________________________________________________________ Chemistry: Matter and Change 126 Science Notebook Name ____________________________________________________________ Date __________________ Section 1 Measuring Matter (continued) Use with page 320–321. Describe why chemists needed to invent a new counting unit. The number of atoms or particles in a given substance is so great _______________________________________________________________ that it would be impossible to use conventional counting units. _______________________________________________________________ List three forms of substances that can be measured using moles. Accept all reasonable responses. Possible answers: molecules 1. ____________________________________________________________ atoms 2. ____________________________________________________________ formula units 3. ____________________________________________________________ Converting Between Moles and Particles Use with pages 322–323. Analyze the usefulness of a conversion factor. The conversion factor allows us to express a known quantity in _______________________________________________________________ other units. We can switch unit systems because the units in a _______________________________________________________________ conversion factor are equivalent to each other. _______________________________________________________________ Write the equation for finding the number of representative particles in a number of moles. number of representative particles number of moles 6.02 1023 representative particles 1 mole Explain how you would find the number of moles that are represented by a certain number of representative particles. number of moles 1 mole number of 23 representative particles 6.02 10 representative particles Chemistry: Matter and Change 127 Science Notebook Name ____________________________________________________________ Date __________________ Section 1 Measuring Matter (continued) Particles-toMoles Conversion Use with Example Problem 1, page 324. Summarize Fill in the blanks to help you take notes as you read Example Problem 1. Problem Convert 4.50 1024 atoms of Zn to find the number of mol of Zn. 1. Analyze the Problem Known: 4.50 1024 atoms of Zn number of atoms ______________________ 6.02 10 1 mole Zn ___________ atoms of Zn 23 ? mol Unknown: mole Zn _______ 2. Solve for the Unknown the number of atoms conversion factor number of moles 1mole Zn 4.50 1024 atoms Zn ___________ 6.02 1023 atoms Zn number of moles 7.48 mol Zn __________ 3. Evaluate the Answer moles three significant digits and is less than 10 The answer has _______ _________ REAL-WORLD CONNECTION Suppose you were given each of the following tasks. Analyze which task(s) the mole would be an effective unit for counting. Explain your answer. A. Counting the atoms in a single grain of salt. B. Counting the grains of salt in a very large mine. C. Counting the grains of salt in the world. The mole is an effective counting unit only for vast quantities occupying very small spaces. _________________________________________________________________________________________ Therefore, only Task A can be performed most effectively using the mole as a counting unit. _________________________________________________________________________________________ The The grains of salt in a mine or in the world would result in a mole count too small to be of _________________________________________________________________________________________ any use. _________________________________________________________________________________________ Chemistry: Matter and Change 128 Science Notebook