Tools for Processing
advertisement

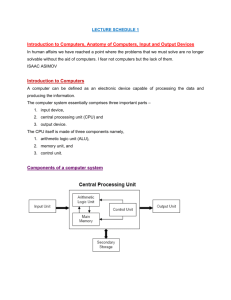
11 IPT Processing Tools for Processing What is processing? Processing is the of data - changing, editing, or updating the data. For example, correcting spelling, altering a photo, editing sound effects in a video or changing the price of a product are all processing, as they result in a change to the data. Processing is central to the operation of all information systems, as all information processes depend on processing to achieve their purpose. Relationship between processing and other information processes Other information processes use data but do not alter it. That is, Organising … Analysing … makes sense of the Storing and retrieving … maintains the data, but not its actual contents. . , but leaving the data unchanged. . It changes the physical representation of the In all of the above, the central processing unit (CPU) or some other processor, is executing instructions to manage, and control the operation of the information process – it does not change the actual data first collected. Processing occurs in information processes, as data is changed as a result of every instruction executed- however, the data in this case is the data that controls, manages and directs the operations being done, not the data collected for the information systems use. Types of processing An information system should reflect the methods used to process the information. If people are working individually and rarely share work they use a non-networked information system. If they are working as a team and need to share resources and data, then a networked information system is appropriate. There are three types of processing used with networks to increase a computer’s performance. Centralised processing – controlled by a or a CPU. It uses a central computer (a powerful mini or mainframe computer) to perform processing for multiple users. In the past, terminals (a monitor, keyboard and connection to the central computer) unable to perform any processing were used. Later, more intelligent terminals (which contained a ) were used which could independently perform simple organising, collecting and displaying processes. This allows the central computer to concentrate on the main task of data processing, although it must allocate time to each user to the limited number of processing instructions executed at a time (time-sharing). Advantages – cheap and relatively simple to set up. Disadvantages – if this system malfunctions, the entire system ‘goes down’ as the system totally depends on the central computer; also, each system is from other systems. Distributed processing – consists of to shared data and resources. Processing tasks and resources such as printers and storage devices can be between computer systems using a network (or the internet). Advantages – processing can still continue even when some of the workstations are not functioning; shared workload and resources; not necessary for all systems to be in the same location. Disadvantages – complex networking and to set up. Parallel processing – is the processing of instructions using multiple processors or CPU’s in a single computer system. Each CPU performs a different processing task, or the same task but on different parts of the data. Advantages – enormous and processing Tools for Information Processes Boughton07 11 IPT Processing power (super computers); reduces the involved in managing large number of user file requests on large networks. Disadvantages – hardware needed is and complex. Processing Hardware Image, audio and video data types need fast processors and a lot of storage space. The enormous quantities of data mean that compression is used frequently to reduce the storage and transmission problems. It also means that a lot of extra processing will be required to work with this type of data, particularly to compress and decompress this data. Parts of the CPU The main components are: ALU – Arithmetic Logic Unit Control unit - Registers Clock Buses Activity: Label the diagram of the CPU below with the missing components and the data buses: System Clock Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Cache The Fetch-Execute cycle Software and hardware work together to process the input of the computer system. This process is carried out by the fetch-execute cycle of the CPU. Each instruction in a program is stored in a separate memory location, called an address. The CPU goes through the fetch-execute cycle for each instruction in the program. Activity: Using your text (page 170) and the handout to complete the following: 1. Describe each of the steps in the fetch-execute cycle Tools for Information Processes Boughton07 11 IPT Processing 2. Label the diagram of the fetch-execute cycle below: The Fetch Execute Cycle 3. What is a cache? Why are they used in modern computer systems? 4. What is pipelining? Processing Speed The processing speed of a computer system is determined by a range of factors related to the CPU and memory. In particular the following two features can have a great impact on the speed of data processing: Activity: Describe how these two features of a CPU that can effect its data processing speed: Clock Speed Data Bus width Processing Software The software tools used to process data are often the same tools used to collect and organise data. 1. Copy the table 7.1 showing the software tools for processing each of the data types, from page 172 – include its heading. Tools for Information Processes Boughton07 11 IPT Processing 2. Briefly (1-2 lines) describe the role each of these software tools in the data processing. 3. Read pages 172 – 174 of the text and answer the following questions from the Activities on page 174: Question 4, 5. Non-computer processing tools System users require that allows them to understand the process involved to obtain the results they want. It should be easy to , explain all the and avoid the use of . User documentation should be provided in more than one documentation, and . , where possible. Eg. hypertext Activity: 1. Explain the importance of user documentation. 2. Distinguish between the documentation for users and documentation for system participants. 3. List and outline the types of documentation that system participants require. Social and Ethical issues 1. In a paragraph of writing, describe the issues that relate to the processing of data: Security Ownership Bias 2. Read the InfoBox on page 178 of the text. List some of the arguments to support the statement, then answer the question at the bottom of the article. Tools for Information Processes Boughton07