Terms and Definitions
advertisement

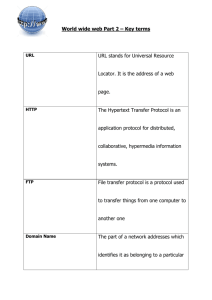
Terms and Definitions Instructions for Terms & Definitions Assignment Using the following list of “Terms and Definitions”, access the web page of your choice and write a description identifying at least 10 of the terms identified in the list. FORMAT: At least ½ page and 2 paragraphs, doublespaced FONT = 12 Times New Roman 1” margins Your name at the top – right justified Class Identification and date – right justified In your narrative, bold and underline the terms you use from the list to describe the web site. Using Print Preview, print out assignment on 1 sheet of paper in Portrait. Internet: a common set of interconnection standards that connect computers worldwide. WWW: World Wide Web or Web (subset of computers on the Internet that makes it easy for people to use who are not computer scientists). URL: Uniform Resource Location (found in the address bar) http: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (set of rules computers use to move files from one computer to another on the Internet. https: Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (the http set of rules but access is limited/secured) FTP: file transfer protocol (set of rules to establish a connection between two computers) IP: Internet Protocol. A unique identification number of each computer Domain Name: The unique name associated with an IP address. Used in the address bar. URL Structure: http://www.bos.org/tangle/perfs/index.html 1 protocol domain name pathname filename ISP: Internet Service Provider (connection with web servers all over the world) Web browser: Software that enables your computer to communicate through an ISP Popular browsers today are: Microsoft Internet Explorer & Mozilla Firefox Network: computers connected to each other LAN: Local Area Network (connected computers that are physically located near each other WAN: Wide Area Network (networked computers not geographically close to each other) HTML: HyperText Markup Language. The language of the Internet Tags: HTML codes that tell the Web browser software how to display the file data. HTML document: a text file that contains HTML tags Hyperlinks or links: instructions that point to other documents or other sections of a document Web page: When a Web browser displays an HTML document Web site: A collection of linked web pages on one computer Home page or Index: The main page of a web site Title Bar: Shows the name of the open Web page and the Browser’s program name Scroll Bar: A bar on the right side of the program that moves the page up and down Status Bar: Found at the bottom of the window, it gives information about the browser’s operations (i.e. page loading, document done, etc.) Menu Bar: Convenient way to execute commands (File, Edit, View, Help, etc.) Navigation Toolbar: Contains buttons that perform basic web browsing functions (i.e. back forward, reload, stop, location, search, etc.) Home button: Takes you back to the home page of the web site Location or Address Bar: place to directly enter a URL or find the URL of a web page Basic Communication on the Internet e-mail: electronic mail (a form of communication in which electronic messages are created and transferred between computers) mail server: a hardware and software system that routes the transmission SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (decides which paths an email takes on the Internet for outgoing messages) POP: Post Office Protocol (handles incoming messages) e-mail address: a unique identification for individuals or organizations (like telephone numbers) user name: a person’s account name host computer or host name: where the person’s mail is stored An e-mail consists of three parts: Message header: Information about the message Message body: the actual message Signature: contains standard information about yourself that the recipient can use to contact you To: here is where you type in the recipient’s full e-mail address cc: Courtesy copy (a copy of your email can go to another party) Bcc: Blind courtesy copy (a copy is sent to someone but the other recipients don’t know it) Group: A single e-mail address that contains several or many individual e-mail addresses From line: includes your (the sender’s) name and e-mail address Subject line: an abbreviated description of the e-mail content Attachment: a way of transmitting files or documents along with the e-mail. Finding information on the Web Web search engine: Web pages that conduct searches of the Web to find the key words you entered. Examples: Google.com, Dogpile.com, Hotbot.com, Altavista.com Bookmark or Favorite: a way to save the URL of a site you would like to revisit Cookie: the file that is written to your computer when you visit a site that contains your info Refresh or Reload button: Reloads the web page from the web server Frame: the current page or part of a web page Copyright: the legal right of the author or owner of an original work to control its reproduction, distribution or sale. Webmaster: the person responsible for maintaining the web page. Temporary Internet Files: When you access a web page, it is stored on your computer’s hard drive so that you don’t have to keep going back to the Web server for it. This increases your speed. Security indicator button: a small picture of a padlock that appears at the right edge of the status bar at the bottom to tell you if the web page is encrypted for safety or not. Encryption: scrambling and encoding data transmission so they are not easy to read if intercepted. Used for credit cards and confidential information to ensure privacy.