What is Internet
advertisement

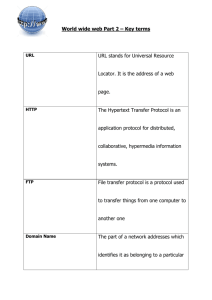
Internet What is Internet Internet is a computer network made up of millions of networks worldwide. No one knows exactly how many computers are connected to the Internet. It is certain, however, that these number in the millions and are increasing at a rapid rate. No one is in charge of the Internet. What is Internet There are organizations which develop technical aspects of this network and set standards for creating applications on it, but no governing body is in control. The Internet backbone, through which Internet traffic flows, is owned by private companies. What is Internet All computers on the Internet communicate with one another using the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol suite, abbreviated to TCP/IP. Computers on the Internet use a client/server architecture. The remote server machine provides files and services to the user's local client machine. Software can be installed on a client computer to take advantage of the latest access technology. Services accessible through Internet Electronic mail File transfer Vast information resources Interest group membership Interactive collaboration Multimedia displays Real-time broadcasting Shopping opportunities Breaking news, and much more. COMPONENTS OF THE INTERNET World Wide Web E-mail Telnet FTP E-mail Discussion Groups USENET News Chat etc. World Wide Web The World Wide Web is a system of Internet servers that supports hypertext to access several Internet protocols on a single interface. The World Wide Web is often abbreviated as the Web or WWW. The World Wide Web was developed in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee of the European Particle Physics Lab (CERN) in Switzerland World Wide Web Almost every protocol type available on the Internet is accessible on the Web. They are • E-mail (Simple Mail Transport Protocol or SMTP) Distributes electronic messages and files to one or more electronic mailboxes Telnet (Telnet Protocol) Facilitates login to a computer host to execute commands FTP (File Transfer Protocol) Transfers text or binary files between an FTP server and client World Wide Web Usenet (Network News Transfer Protocol or NNTP) - Distributes Usenet news articles derived from topical discussions on newsgroups HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) Transmits hypertext over networks. This is the protocol of the WWW. The World Wide Web provides a single interface for accessing all these protocols. World Wide Web How can we access World Wide Web (Web) Using one of the Web Browsers What's in a Web browser? A Web browser contains the basic software you need in order to Find Retrieve View and Send information over the Internet. What's in a Web browser? This includes software that lets you: Send and receive electronic-mail (or email) messages worldwide nearly instantaneously. Read messages from newsgroups (or forums) about thousands of topics in which users share information and opinions. Browse the World Wide Web (or Web) where you can find a rich variety of text, graphics, and interactive information. What is a URL? URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator The URL specifies the Internet address of a file stored on a host computer connected to the Internet. Every file on the Internet, no matter what its access protocol, has a unique URL. Web software programs use the URL to retrieve the file from the host computer and the directory in which it resides. This file is then displayed on the monitor connected to the user's local machine. What is a URL? URLs are translated into numeric addresses using the Internet Domain Name System (DNS). The numeric address is actually the "real" URL. Since numeric strings are difficult for humans to use, alphneumeric addresses are employed by end users. Once the translation is made, the Web server can send the requested page to the user's Web browser. Anatomy of a URL Usually it consists of four parts: Protocol Server (or domain) Path and Filename. Sometimes there's no path or filename. Anatomy of a URL Here's an example: http://www.microsoft.com/windows/default.asp http is the protocol www.microsoft.com is the server windows/ is the path default.asp is the filename CGI (Common Gateway Interface) It refers to a specification by which programs can communicate with a Web server. A CGI program, or script, is any program designed to accept and return data that conforms to the CGI specification. The program can be written in any programming language, including C, Perl, and Visual Basic Script. Search engines: Finding the needle in the haystack A search engine is a service that indexes, organizes, and often rates and reviews Web sites. Different search engines work in different ways: • • • Some rely on people to maintain a catalog of Web sites or pages. Some use software to identify key information on sites across the Internet. Some combine both types of service. Search engines Some Common Search Engines: MSN Yahoo Lycos AltaVista WebCrawler InfoSeek Snap Excite All About E-mail To send and receive electronicmail messages, or e-mail, over the Internet and to organize your messages, you need An e-mail account through an Internet service provider (ISP) or online service provider. An e-mail client—e-mail software for your computer E-mail Clients Microsoft Outlook Microsoft Outlook Express Netscape Messenger Eudora Or Some Web based Email Client E-mail terminology There are many acronyms associated with e-mail: SMTP—simple mail transfer protocol; the standard rules that many e-mail clients use to handle outgoing e-mail messages. POP3—postoffice protocol version 3; the standard rules that many e-mail clients use to handle incoming e-mail messages. MIME—multipurpose Internet mail extensions; a format for turning an e-mail attachment, such as a Microsoft Word file, into ASCII text so it can be sent from one e-mail account to another. Internet Threats & Security Since Internet is accessible to many it is also prone to attacks from hackers. The threats to the Inter are as follows: • Disclosure • Masquerade (Spoofing) • Unauthorised Access • Loss of Integrity • Denial of Service Internet Threats & Security Theft of Service & Resources: Internet is used as a channel for delivery of service. Hence, unauthorised access to the services is a theft. The impacts due to threats are: • Loss of trade secrets • Information is lost (Critical data, proprietary info, Contracts) • Increased cost of security systems Internet Threats & Security • • • • • Loss of reputation and goodwill It is very costly to correct and recover information Contractual commitments are not met properly Loss of Income Legal and regulatory non compliance Internet Threats & Security Internet Security Controls: Data Security & Controls Firewall Security Corporate Internet Policy & procedures Data Encryption