Name Class Date Section: Seed Plants Complete each statement by
advertisement

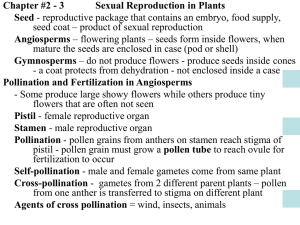
Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Section: Seed Plants Complete each statement by writing the correct term in the space provided. 1. Seed plants are classified into two groups—the ______________________ and the ______________________. 2. Seeds were an important adaptation that enhanced the survival and ______________________ of seed plants. In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term. b ____ 3. angeion d ____ 4. angiosperm a ____ 5. gymnos e ____ 6. gymnosperm a. means “naked” b. means “case” c. means “seed” d. a flowering plant e. a seed plant that does not form fruit c ____ 7. sperma Complete each statement by writing the correct term or phrase in the space provided. 8. A male gametophyte of a seed plant develops into a(n) ______________________ pollin grain______________________. 9. A female gametophyte develops inside a(n) _________ovule_____________, which is a multicellular structure that is part of the sporophyte. 10. The transfer of pollen grains from a male reproductive structure of a plant to a female reproductive structure of a plant is called _pollination_________________. 11. When a pollen grain reaches a compatible female reproductive structure, a(n) ________________pollen tube______ ______________________ emerges from the pollen grain and grows from the pollen grain to an ovule. Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 6 Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Directed Reading continued 12. The fusion of an egg and a sperm during sexual reproduction is called _____fertilization _____________. Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 13. What reproductive advantage for survival on land do seed plants have over seedless plants? • Unlike seedless plants, seed plants do not require water to reproduce sexually. • Reproduction in seed plants is also characterized by a greatly reduced gametophyte and a dominant sporophyte. 14. Besides being a method of dispersal, what advantages do seeds provide the embryos of seed plants? Tough caot of the seed protect the embryo from mechanical injury and harsh environment also the seed contains nutrients that help the embryo to grow in the early stages . 15. List and describe two ways that seeds are dispersed. Dispersed by wind details on Pg 555 _________________________________ Dispersed By animals Pg 555 _______________________________________ In the space provided, write which of the following gymnosperms—conifers, cycads, ginkgo, or gnetophytes—is being described. ginkgo _______________ 16. only one living species; has fan-shaped leaves cycads _______________ 17. have short stems and palmlike leaves; produce male and female cones on separate plants conifers, ______________ 18. trees and shrubs with needlelike or tiny leaves gnetophytes ___________ 19. diverse group of trees, shrubs, and vines Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 7 Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Directed Reading continued Study the following steps in the life cycle of a pine tree. Determine the order in which the steps take place, beginning with the zygote. Write the number of each step in the space provided. 1 ____ 20. The zygote and ovule develop into a seed, which grows into a new sporophyte. 6 ____ 21. A mature pine produces male and female cones. 4 ____ 22. Sperm enter the ovule through a pollen tube, and fertilization occurs. 2 ____ 23. Male and female spores form on the scales of the cones. 5 ____ 24. Pollination occurs when a pollen grain lands near an ovule. 3 ____ 25. Spores develop into male and female gametophytes. Complete each statement by underlining the correct term in the brackets. 26. The [gametophyte / sporophyte] generation is dominant in conifers. 27. The seeds of pines travel away from their parent plant in a manner that is similar to that of a [helicopter / hot-air balloon]. 28. The modified leaves of a cone are called [petals / scales]. 29. [Female / Male] cones develop into seed cones. 30. Male and female cones are produced on different plants in [all / some] gymnosperms. Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 8 Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Section: Seed Plants In the space provided, write which of the following plant groups— angiosperms or gymnosperms—is being described. gym _________________ 1. have a name that literally means “naked seed” ang __________________ 2. seeds; vascular tissue; fruits; flowers; pollen ang __________________ 3. have a name that comes from the Greek word for “case” gym _________________ 4. vascular tissue; dominant sporophyte; cones; pollen; include pines In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. _____ 5. A pollen grain contains a. endosperm. b. an embryo. c. sperm. d. Both (b) and (c) _____ 6. In gymnosperms, male and female gametophytes develop within a. cones. c. seeds. b. flowers. d. fruits. _____ 7. In pine trees, pollen is formed in a. male cones. b. female cones. c. tiny, inconspicuous flowers. d. Both (a) and (b) _____ 8. Which of the following plants is best suited for a cold, dry climate? a. cycad c. ginkgo b. conifer d. gnetophyte _____ 9. Compared to their sporophytes, the gametophytes of seed plants are a. much larger. b. the same size. c. much smaller. d. variable in size throughout the life cycle. _____ 10. In seed plants, the sperm are delivered to eggs by a. wind. c. tiny wings. b. water. d. pollen tubes. Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 9 Plant Diversity and Life Cycles