Bacteria & Virus Booklet
advertisement

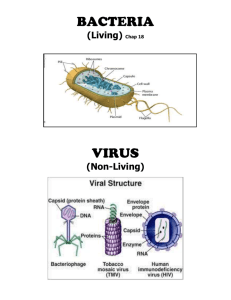
Name:______________ Period_______ Draw a Venn diagram using these 17 terms: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Cell wall Smaller of two Larger of two Causes disease Living organism Not living Affected by antibiotics Has protein coat Lytic cycle Lysogenic cycle Cannot reproduce alone Can reproduce Contains genetic material AIDS Tetanus Strep throat Influenza BACTERIA (Living) Chap 18 VIRUS (Non-Living) Name:______________ Period_______ 1. Bacteria a single celled organism lacking a nucleus. 2. Nucleoid organism that must take in organic molecules for both energy and carbon. 3. Capsule organism that is photosynthetic but needs organic compounds as a carbon source. 4. Pilus organism that makes organic carbon molecules from carbon dioxide using energy from chemical reactions. 5. Binary fission organism that uses energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into carbon compounds. 6. Heterotrophs organism that requires a constant supply of oxygen in order to live. 7. Photoautotrophs organism that cannot live in the presence of oxygen. 8. Chemoautotrophs organism, such as a bacterium, that can live in the absence as well as in the presence of atmospheric oxygen. 9.Endospore 10. Bacteriaphage (device) 11. Capsid 12. Vector Category Sexually Transmitted diseases Respiratory diseases Skin diseases Digestive tract diseases Nervous system diseases Other diseases Bacterial Disease (pg. 524) Category Sexually Transmitted diseases Childhood Diseases Respiratory Diseases Skin Disease Digestive tract Diseases Nervous system Disease Other Diseases Viral Disease (pg. 525) Name:______________ Period_______ DISEASES CAUSED BY BACTERIA & VIRUSES ABOUT BACTERIA 13. What makes bacteria prokaryotic? (pg.516) 31. What is a pathogen? (pg. 1076) ARCHAEBACTERIA 14. 32. What two ways do bacteria cause a disease? (pg.524) EUBACTERIA Size (pg.516) Cell wall (pg. 517) 33. List 3 ways to bacteria (prokaryotes) metabolize. (520-521) a) Where they live (pg. 517) 15. Bacteria Shape (pg. 519) b) c) 34. What is a prion and what is its shape? (pg531) Bacilli Cocci 16. Bacteria arrangement: Know these! 35. How are bacterial infection treated? (pg.1082) 36. How are viral infections treated? (pg. 1089) 17. How do bacteria (prokaryotes) move? (pg. 519) 18. What is the pili used for? (pg. 518) Spirilli Name:______________ Period_______ DRAW, COLOR AND LABEL THE BACTERIUM ON PAGE 518 Virus Concept Map Viruses are cause are transferred by 1. 2. as are may sometimes lead to prions cancer viroids 7. 4. Pg.519 19. How can now prokaryotes be identified _________________ By comparing ____, evolutionally ________ can be determined. Historically, scientists identified prokaryotes by which three types of criteria a) b) c) SARS such as 8. insects 5. Word Bank 6. Animals Chickenpox Flu Humans Lifeless particles Measles Vectors Viral diseases 9. such as Name:______________ Period_______ 28. Describe the LYSOGENIC CYCLE. (Viral reproduction)(pg. 528) 20. Define Obligate anaerobes, Facultative anaerobes and Obligate aerobes (pg, 520) 21. Reproduction (pg. 520) DESCRIBE DIAGRAM Binary Fission Conjugation 29. What is a retroviruses and what does it cause? (pg. 530) 22. Importance of Bacteria (pg. 522-523) Decomposers – Nitrogen Fixers – 30. Are viruses alive? Why or why not? (pg.525) a) What are root nodules used for? Human Uses (Normal flora, Foods and Medicines) – Name:______________ Period_______ ABOUT VIRUSES 23. Draw and Label the 4 viruses on page 526-527 24. What is a virus? (pg. 525) 25. What is a virus composed of? (pg. 526 look at the different types) 26. How does a virus attach to a cell? (pg. 527) Do all viruses have the same attachment mechanism? Why or Why not. 27.