Plate Tectonics Study Guide: Earth's Interior & Continental Drift
advertisement

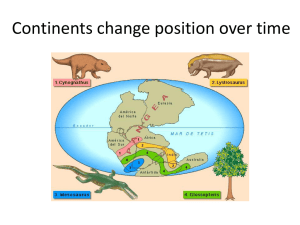
Chapter 1 Study Guide – Plate Tectonics Section 1 – Earth’s Interior 1. What are the two main types of evidence to learn about the Earth’s interior? a. direct from rock samples b. indirect from seismic waves What are the three main layers of the Earth and what are they made up of? a. crust – a layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and ocean floor b. mantle – very hot rock that is solid c. core – made mostly of iron and nickel. It has a liquid outer core and a solid inner core Continental Drift What was Wegener’s hypothesis? -All of the continents had once been joined together in a single landmass and have since drifted apart Why did scientists reject Wegener’s hypothesis? -He could not provide a satisfactory explanation for the force that pushes or pulls the continents Bonus Question: What 3 types of evidence supported Wegener’s hypothesis? a. land features b. fossils c. climate changes What was the name of the single landmass? -Pangaea Sea Floor Spreading What is sea floor spreading? -the process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor. Bonus Question: What were the 3 types of evidence that supported Hess’s theory of sea floor spreading? a. eruptions of molten material b. magnetic stripes in the rock of the ocean floor c. the ages of the rocks What is subduction? -the process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deep ocean trench and back in to the mantle. The theory of plate tectonics What is a plate? -a section of the lithosphere that slowly moves over the asthenosphere, carrying pieces of continental and oceanic crust. What is the theory of plate tectonics? -it explains the formation, movement, and subduction of Earth’s plates