Golgi Body or Golgi Apparatus - Mr. Lesiuk
advertisement

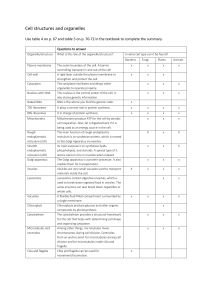
CELL STRUCTURE : PART TWO Golgi Body or Golgi Apparatus - Stack, of a half dozen or more flattened sacs. - On one side, protein-filled vesicles are received from the E.R. - Responsible for sorting/modifying proteins and packaging them into vesicles over at the other side. - From here the vesicles move to different locations in the cell. Vacuoles - Storage areas for water, sugars, and salts. Vessicles - Very small vacuoles - Act as storage sites for various kinds of molecules, but most often used for transporting materials. - Can be formed either by the Golgi Apparatus/ER or from an in-folding of the cell membrane. VESICLE FORMATION ILLUSTRATED BELOW: Lysosomes - Special vacuoles formed by the Golgi body. - Contains powerful hydrolytic enzymes used to digest substances entering the cell. These enzymes may also be used to digest organelles that are of no further use. (Autodigestion). Ribosomes - Bean-shaped structures. - Each contains two - rRNA and protein subunits. - Function as the site for protein synthesis (translation). - Found on E.R. (proteins for export), or by themselves out in the cytoplasm. (Proteins for use within the cell). - Several ribosomes together in a line, all producing the same protein, form what is called a polyribosome (polysome) - Produced in the nucleolus of the nucleus when rRNA and Proteins combine, then move out of nucleus. Ribosomes on E.R. = Rough ER Mitochondria - React glucose with oxygen to release energy, this energy is stored in ATP molecules and then used by the cells to carry out specialized functions eg. Movement, cell transport. - During cellular respiration oxygen is used up and carbon dioxide is given off. - C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy - Considered the powerhouse of the cell. - Structurally it consists of two membranes. - The inner membrane loops back and fourth through the inner fluid (matrix) of the mitochondria. This increases its surface area and allows it to form shelf-like structures (folds) called cristae. - This inner membrane is the site of cellular respiration. Cytoskeleton - Provides internal structure to maintain the cell’s shape, also anchors the organelles and allows them to move when such movement is required. - Composed of microfilaments and microtubules. Microfilaments – (Actin) - Extremely thin protein fibers usually found in bundles. - Similar in composition to the protein in muscle (allows for contraction). - Associated with cell movement such as : “Cyclosis”, cytoplasmic streaming, amoeboid movement and the “pinching off” process that occurs during cell division. Microtubules - Thin cylinders which are several times larger than microfilaments. - Each cylinder contains 13 rows of a globular protein (tubulin) which is arranged in a spiral fashion. - Found in both cytoplasm and in certain organelles. - Used to construct materials essential for the formation of cilia, flagella and centrioles. Microtubule Centrioles - Very short cylinders with a 9 + 0 arrangement of microtubules. - Give rise to basal bodies which in turn direct the formation of cilia and flagella. - Also used to help direct movement of material through the cell. Cilia - Short, numerous, hair-like projections that are used for locomotion by many unicellular organisms. - Membrane–bound collections of microtubules (9 pairs arranged around a central pair, giving rise to a (9 + 2 pattern). - Each pair of outer microtubules (doublet) also has pairs of arms projecting toward a neighboring doublet and spokes extending toward the central pair of microtubules. Flagella - Like cilia but can be very much longer. - Also used for the locomotion of organisms and gametes (sperm). See diagrams below