ACF 103 – Fundamentals of Finance
advertisement

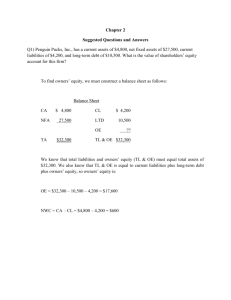
ACF 103 – Fundamentals of Finance Tutorial 1 - Solutions Chapter 1 1. When a firm is meeting the present needs of the firm without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs it is commonly referred to as ________. * A. sustainability B. personal social responsibility C. the investment decision D. None of the above answers are correct. 2. The ________ decision is concerned about the make-up of the right-hand side of the balance sheet with the dividend policy of the firm being integral as well as the mechanics of physically requiring the necessary funds. A. investment * B. financing C. asset management D. wealth management 3. The ________ decision is concerned about charging the manager with an appropriate level of operating responsibility over existing assets to supervise the assets efficiently. A. investment B. financing * C. asset management D. wealth management 4. The price of a share of common stock in a publicly-traded firm represents ________. A. earnings after tax divided by the number of shares outstanding B. the book value of the firm's assets less the book value of its liabilities C. the board of directors' assessment of the intrinsic value of the firm * D. the market's evaluation of a firm's present and future performance 5. The long-run objective of financial management should be to ________. A. maximize the firm's earnings after taxes B. maximize the firm's earnings per share * C. maximize the value of the firm's common stock D. maximize the firm's percentage of product market share Chapter 2 1. A 30-year corporate bond issued in 2005 would now trade in the ________. A. primary money market B. secondary money market C. primary capital market * D. secondary capital market 2. A. B. The expected return on a security typically increases as ________. default risk decreases marketability increases ACF 103 HAUT 2014 Tutorial 1 Solns 1 * C. maturity increases D. taxability decreases 3. The term structure of interest rates refers to the relationship between yield and ________. * A. maturity, for the same security class B. risk, for securities with the same maturity C. rating, for securities with the same maturity D. marketability, for securities with the same tax status 4. Text book Ch 2 problem # 2 (p.37) Answer: Cost Depreciation in year: Equipment $28,000.00 Machine $53,000.00 1 9,332.40 2 12,446.00 3 4,146.80 4 2,074.80 5 6 $28,000.00 10,600.00 16,960.00 10,176.00 6,105.60 6,105.60 3,052.80 $53,000.00 5. Text book Ch 2 question # 13 (p.36) Answer: Financial markets allow for efficient allocation in the flow of savings in an economy to ultimate users. In a macro sense, savings originate from savingssurplus economic units whose savings exceed their investment in real assets. The ultimate users of these savings are savings-deficit economic units whose investments in real assets exceed their savings. Efficiency is introduced into the process through the use of financial markets. Since the savings-surplus and savings-deficit units are usually different entities, markets serve to channel these funds at the least cost and inconvenience to both. As specialization develops, efficiency increases. Loan brokers, secondary markets, and investment bankers all serve to expedite this flow from savers to users. 6. In general, what would be the likely effect of the following occurrences on the money and capital markets? a. The savings rate of individuals in the country declines. b. The government taxes capital gains at the ordinary income tax rate. c. Unanticipated inflation of substantial magnitude occurs, and price levels rise rapidly. d. Savings institutions and lenders increase transaction charges for savings and for making loans. Answer: ACF 103 HAUT 2014 Tutorial 1 Solns 2 a. b. c. d. All other things being the same, the cost of funds (interest rates) would rise. If there are no disparities in savings pattern, the effect would fall on all financial markets. It would lower the demand for common stock, bonds selling at a discount, real estate, and other investments where capital gains are an attraction for investment. Prices would fall for these assets relative to fixed income securities until eventually the expected returns after taxes for all financial instruments were in equilibrium. Great uncertainty would develop in the money and capital markets and the effect would likely be quite disruptive. Interest rates would rise dramatically and it would be difficult for borrowers to find lenders willing to lend at a fixed interest rate. Disequilibrium would likely to continue to occur until the rate of inflation reduced to a reasonable level. Financial markets would be less efficient in channelling funds from savers to investors in real estate. Chapters 6 & 7 1. Here are Fang Jiang's balance sheets for 2011 and 2012. Current Assets Cash and Equivalents Short-Term Investments Accounts Receivable Inventories Other Current Assets Total Current Assets Current Liabilities Accounts Payable Short-Term Debt Other Current Liabilities Total Current Liabilities a. b. c. 2012 $3,122 $2,104 $7,232 $3,632 $ 1,414 $17,504 2011 $3,600 $6,020 $6,258 $3,086 $ 1,202 $20,166 Change -$ 478 -$3,916 $ 974 $ 546 $ 212 -$2,662 $10,346 $ 576 $2,802 $13,724 $10,222 $ 554 $2,196 $12,972 $ 248 $ 22 $ 606 $ 752 What is the Net Working Capital for (i) 2012? (ii) 2011? What is the Change in Net Working Capital (NWC)? Assuming the Operating Cash Flows (OCF) are $14,130 and the Net Capital Spending (NCS) is $4,744, what is the Cash Flow from Assets? Answer: a. Net Working Capital for 2012 is $17,504 - $13,724 = $3,780 b. Net Working Capital for 2011 is $20,166 - $12,972 = $7,194 Decrease in Net Working Capital (NWC) = $3,780 - $7,194 = -$3,414 c. Assuming that Operating Cash Flows (OCF) are $14,310, Net Capital Spending (NCS) is $4,744, and Decrease in Net Working Capital is -$3,414, we get: Cash Flow from Assets = OCF - NCS – Decrease in NWC = $14,310 - $4,744 - (-$3,414) = $12,980. ACF 103 HAUT 2014 Tutorial 1 Solns 3 2. From the following balance sheet accounts of Hubei Corporation: a. construct balance sheets for 2013 and 2014 b. list all the working capital accounts c. find the net working capital for the years ending 2013 and 2014 d. calculate the change in net working capital for the year 2014 Account Balance 2013/12/31 Accumulated Depreciation $8,468 Accounts Payable $5,800 Accounts Receivable $6,320 Cash $2,420 Common Stock $9,556 Inventory $8,694 Long-Term Debt $7,200 Plant, Property & Equipment $17,350 Retained Earnings $3,760 Balance 2014/12/31 $9,732 $6,420 $7,288 $2,980 $14,556 $10,332 $4,860 $19,680 $4,712 Answer: a. The Balance Sheets for the two years are: Assets: 2013 Current Assets Cash $2,420 Accounts Receivable $6,320 Inventory $8,694 Total Current Assets $17,434 Long-Term Assets Plant, Prop. & Equip $17,350 Minus Acc. Depreciation ($8,468) Net P P & E $8,882 TOTAL Assets $26,316 Liabilities Current Liabilities Accounts Payable $5,800 Long-Term Liabilities Long-term Debt $7,200 Total Liabilities $13,000 Owner’s Equity Common Stock $9,556 Retained Earnings $3,760 Total Owner’s Equity $13,316 TOTAL Liab. & O.E. $26,316 2014 $2,980 $7,288 $10,332 $20,600 $19,680 ($9,732) $9,948 $30,548 $6,420 $4,860 $11,280 $14,556 $4,712 $19,268 $30,548 b. The Working Capital Accounts are: Cash, Accounts Receivable, Inventory, and Accounts Payable c. The Net Working Capital for 2013 and 2014: Net Working Capital = Cash + Accounts Rec. + Inventory – Accounts Pay. ACF 103 HAUT 2014 Tutorial 1 Solns 4 2013 Net Working Capital = $2,420 + $6,320 + $8,694 - $5,800 = $11,634 2014 Net Working Capital = $ $2,980+ $7,288 + $10,332 - $6,420 = $14,180 d. The Change in Net Working Capital for 2014 is, $14,180 - $11,634 = $2,546 or an increase in Net Working Capital of $2,546. or an increase in Net Working Capital of $2,546. 3. From the following income statement accounts of Xi’an Ltd a. produce the income statement for the year b. produce the operating cash flow for the year Income Statement Accounts for the Year Ending 2014 Cost of Goods Sold $14,190 Interest Expense $ 2,880 Taxes $ 3,180 Revenue $29,840 SG&A Expenses $ 4,540 Depreciation $ 2,580 Answer: a. b. Income Statement Revenue Cost of Goods Sold SG&A Expenses Depreciation EBIT Interest Expense Taxable Income Taxes Net Income $29,840 $14,190 $ 4,540 $ 2,580 $ 8,530 $ 2,880 $ 5,650 $ 3,180 $ 2,470 Operating Cash Flow OCF = EBIT – Taxes + Depreciation OCF = $8,530 - $3,180 + $2,580 = $7,930 ACF 103 HAUT 2014 Tutorial 1 Solns 5