Processing Assignments, Human Reproduction
advertisement

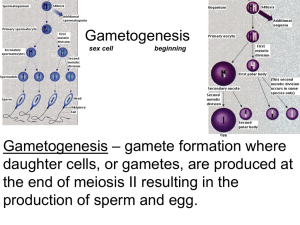
IB Bio Year 2 KEY 46.3 Gametogenesis, pp 1005-1007 1. Both spermatogenesis and oogenesis start with one cell. How many functional gametes are formed in each process? Explain. Spermatogenesis results in 4 sperm cells; oogenesis makes one ovum and 2 (or 3) polar bodies. 2. How is the timing of spermatogenesis different from oogenesis? Explain. Spermatogenesis begins at puberty in men takes roughly 65 days, vs. oogenesis, which starts when a female is a fetus. Oogonia differentiate into 1° oocytes and arrest in prophase of MI before a woman is born, then ONE resumes MI and becomes a 2° oocyte arrested in metaphase of MII several hours before being ovulated. If penetrated by a sperm, the 2° oocyte will finish MII. 3. Distinguish between… spermatid and sperm? Both are haploid, with only one chromatid per chromosome, but a spermatid has not acquired the architecture required of a sperm cell (see #8). polar body and ovum? Both are haploid with two or one chromatid(s) per chromosome (depends on which meiosis phase it is formed by) but the main difference is that polar bodies are throw away cells with very little cytoplasm. Sertoli cell and follicle cell? Sertoli cells nourish cells in spermatogenesis; follicle cells nourish cells in oogenesis. 4. How many chromatids in a human metaphase I primary spermatocyte? 46 chromosomes, each of them with 2 chromatids = 92 chromatids 5. How many chromatids in a human first polar body? The first polar body is the result of MI, so it is a haploid cell (23 chromosomes), but all chromosomes have two chromatids, so 23 x 2 = 46 chromatids 6. How many chromosomes in a human spermatid? A spermatid has completed MI and MII so it has 23 chromosomes, each with one chromatid. See #3 above. 7. Consider two unlinked genes (means, two chromosomes) with alleles R & r, & T & t. In an RrTt man, what fraction of his spermatozoa will contain both r and T? That combination would be present in ¼ of his sperm (recall those Punnett squares for dihybrid crosses!) because at metaphase of MI, there is independent assortment. 8. Draw and label a mature spermatozoan (sperm cell) and a secondary oocyte within its follicle in the ovary, just before it is ovulated. Spermatozoan image credit: http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/spermatozoon Secondary oocyte within follicle image credit: IB Bio Year 2 http://biology.clc.uc.edu/fankhauser/Labs/Anatomy_&_Physiology/A&P203/Reproductive_Tract_Histology/Graafian_ follicle_400x_lbld_P5230526.jpg